电化学(中英文) ›› 2022, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (2): 2108501. doi: 10.13208/j.electrochem.210850
所属专题: “电催化和燃料电池”专题文章
• 电化学前沿专辑(蔡文斌教授、廖洪钢教授、彭章泉研究员主编) • 上一篇 下一篇
王雪1,2, 张丽1, 刘长鹏1,2, 葛君杰1,2, 祝建兵1,2,*( ), 邢巍1,2,*(
), 邢巍1,2,*( )
)
收稿日期:2021-11-01
修回日期:2021-12-02
出版日期:2022-02-28
发布日期:2021-12-18
Xue Wang1,2, Li Zhang1, Chang-Peng Liu1,2, Jun-Jie Ge1,2, Jian-Bing Zhu1,2,*( ), Wei Xing1,2,*(
), Wei Xing1,2,*( )
)
Received:2021-11-01
Revised:2021-12-02
Published:2022-02-28
Online:2021-12-18
Contact:
*Tel: (86-431)85262147, E-mail:
摘要:
碱性介质中的氧还原反应是金属-空气电池和阴离子交换膜燃料电池的重要电化学过程。但是,其动力学缓慢,因而引起了对高效电催化剂的广泛研究。其中,非贵金属催化剂可有效地规避铂基催化剂成本和储量的问题,而备受关注。但其挑战在于将性能提高到可与Pt基催化材料媲美。鉴于非贵金属催化剂的组成和结构对催化性能有着至关重要的影响,精准地调控催化剂的结构有望消除非贵金属催化剂和商业铂基催化剂的活性差距。在该评述中,我们致力于总结通过结构调控来提升性能的研究进展。我们首先介绍了四种极具代表性的非贵金属催化剂,包括非金属碳基材料、金属化合物、石墨化碳层包覆金属颗粒、原子分散的金属-氮-碳材料,突出了催化活性位点和催化机理。随后,针对于这些催化剂,我们归纳了从微纳尺度到原子层面的结构调控策略,如分级多孔结构的设计、界面工程、缺陷工程以及原子对活性位点的构建。我们着重讨论了结构和性能之间的依赖关系。从加速传质、增加可及的活性位点数量、可调控的电子状态和多组分之间的协同效应,讨论了这些结构变化引起的活性改进的起源。最后,我们对该领域存在的挑战以及未来的前景进行了展望。
王雪, 张丽, 刘长鹏, 葛君杰, 祝建兵, 邢巍. 碱性介质中非贵金属氧还原催化剂的结构调控进展[J]. 电化学(中英文), 2022, 28(2): 2108501.
Xue Wang, Li Zhang, Chang-Peng Liu, Jun-Jie Ge, Jian-Bing Zhu, Wei Xing. Recent Advances in Structural Regulation on Non-Precious Metal Catalysts for Oxygen Reduction Reaction in Alkaline Electrolytes[J]. Journal of Electrochemistry, 2022, 28(2): 2108501.
Table 1
Reaction equations of ORR in alkaline conditions.
| Mechanism | Overall reaction | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Four-electron process | Dissociation pathway | O2 + 2* → 2O* 2O* + 2e- + 2H2O → 2OH* + 2OH- 2OH* + 2e- → 2OH- + 2* | O2 + 2H2O + 4e- → 4OH- |
| Associative pathway | O2 + * → O2* O2* + H2O + e- → OOH* + OH- OOH* + e- → O* + OH- O* + H2O + e- → OH* + OH- OH* + e- → OH- + * | ||
| Two-electron process | O2 + * → O2* O2* + H2O + e- → OOH* + OH- OOH* + e- → HO2- +* | O2 + H2O + 2e- → HO2- + OH- | |
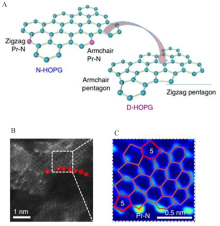
Figure 1
(A) Illustration of the edge defect reconstruction; (B) The HAADF-STEM image of N-G. The nitrogen atoms are marked with the red circles; (C) Expanded image of the dotted box in (B) (‘5’ indicates the pentagons). Reproduced with permission of Ref. 24, copyright 2019 Springer Nature. (color on line)
Figure 2
(A) Schematic illustration showing the synthesis of N, S co-doped carbon catalysts; (B, C) Free-energy diagrams of the ORR mechanism at different electrode potentials (U) on (B) N doped carbon and (C) N, S co-doped carbon. The * denotes the free C site on doped carbon structure. Insets: the optimized structure of N doped and N, S co-doped carbon structure. The gray, blue and yellow balls denote C, N and S, respectively. Reproduced with permission of Ref. 34, copyright 2016 Royal Society of Chemistry. (color on line)
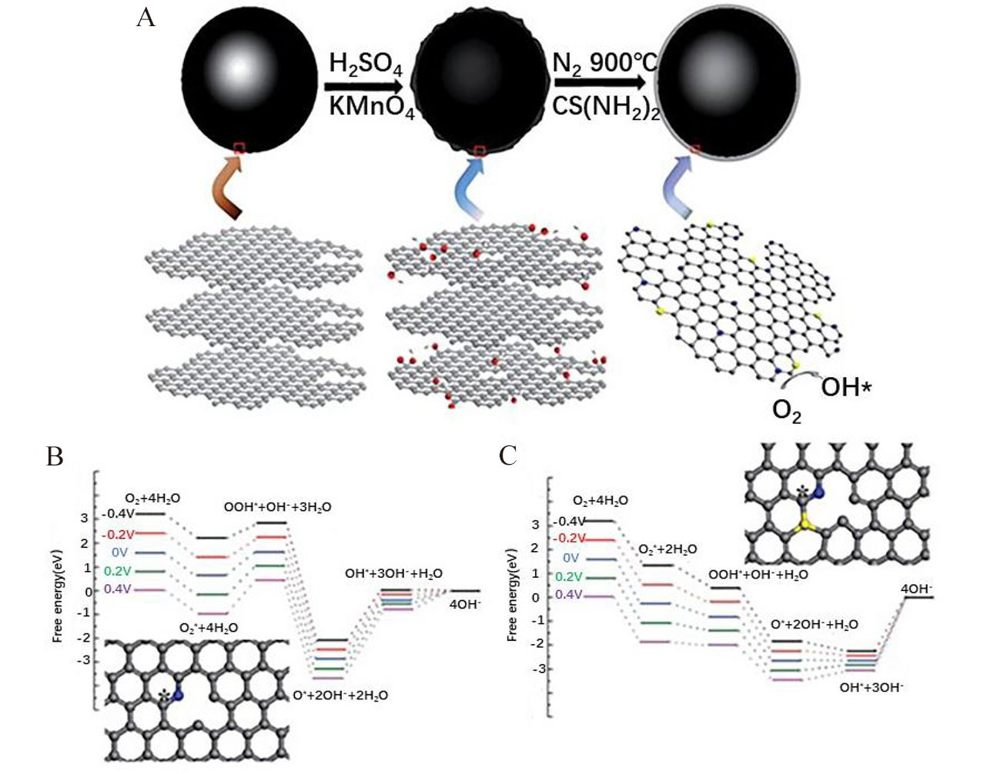
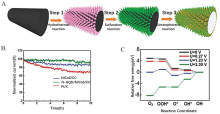
Figure 3
(A) Flow diagram for the synthesis processes of 3D N-GQDs/NiCo2S4/CC composite; (B) Durability testing curves in 0.1 mol·L-1 KOH; (C) Relative Gibbs free energy diagram of NiCo2S4 for the ORR at different potentials. Reproduced with permission of Ref. 54, copyright 2019 Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim. (color on line)
Figure 4
(A, B) Transmission electron microscopic images of Fe3C encapsulated in N-doped carbon nanotubes/carbon black composite; (C) Results of the DFT calculations. PDOS of the p orbitals of C atoms bonded to Fe in Fe3C@SWNT compared with that in pure SWNT; (D) ORR polarization plots after 20000 cycles in O2-saturated 0.1 mol·L-1 KOH. Reproduced with permission of Ref. 63, copyright 2015 Royal Society of Chemistry. (color on line)
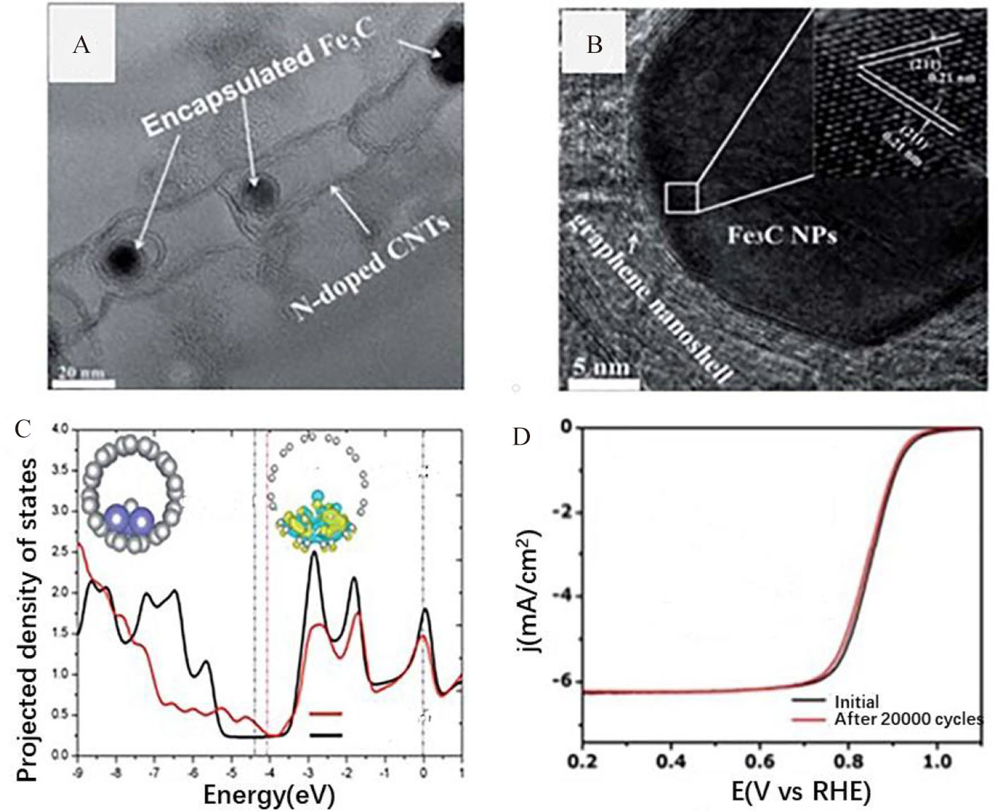
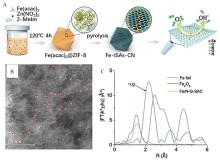
Figure 5
(A) Schematic illustration for the formation of Fe-N-C catalysts using ZIF-8 as an active site host; (B) Aberration-corrected HAADF-STEM image of the isolated Fe atoms involved Fe/N-G-SAC catalyst; (C) Fourier transforms of k3-weighted Fe K-edge EXAFS data. Reproduced with permission of Ref. 81, copyright 2020 Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim. (color on line)
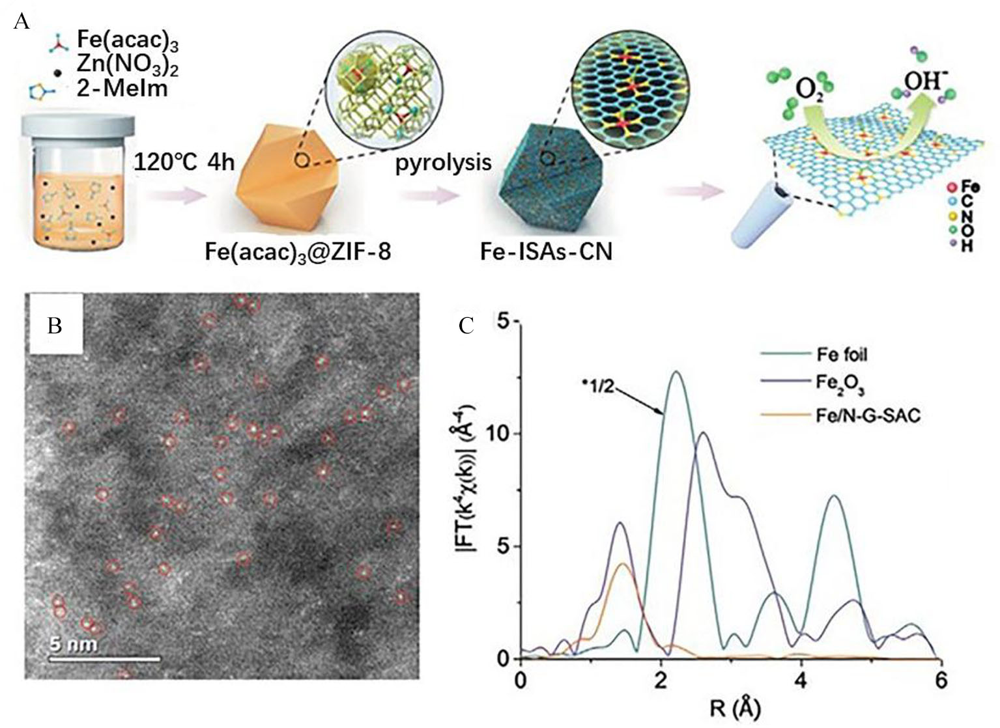
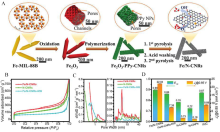
Figure 6
(A) Graphical illustration for the synthesis process of Fe/N-CNRs; (B) N2 adsorption-desorption results and (C) Pore diameter distribution results for Fe/N-CNRs, N-CNRs, and Fe/N-CNRs-NW; (D) E1/2 and kinetic current density (Jk)@0.85V results of these catalysts. Reproduced with permission of Ref. 79, copyright 2021 Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim. (color on line)
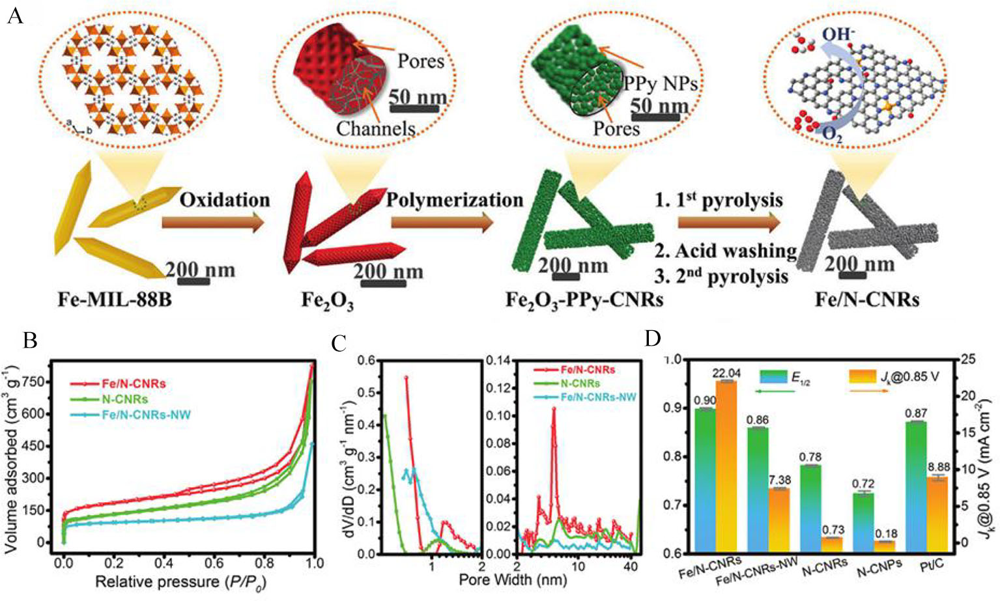
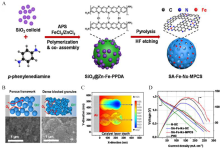
Figure 7
(A) Synthetic scheme for the preparation of SA-Fe-Nx-MPCS catalyst; (B) Schematic illustration of the air electrodes and their SEM images; (C) COMSOL multiphysics modeling of O2 diffusion into the air electrode; (D) Polarization and power density curves of flow batteries with the prepared catalysts and Pt/C. Reproduced with permission of Ref. 80, copyright 2021 Elsevier. (color on line)
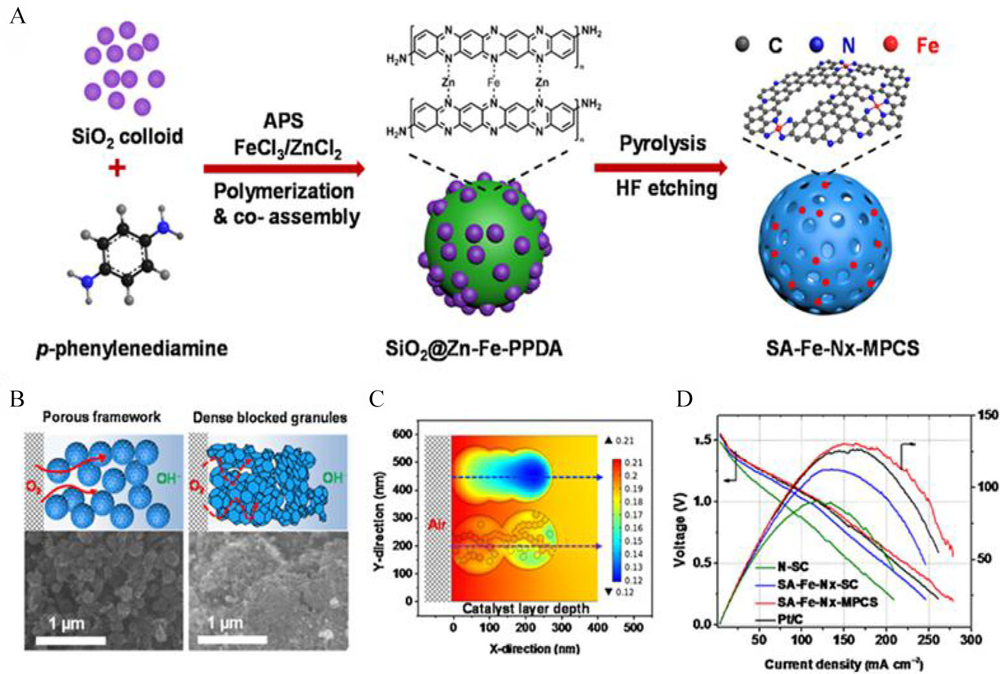
Figure 8
(A) Schematic illustration revealing the synthetic strategy of the TMs@NCx composite; (B) ORR polarization curves for TMs@NCx samples in O2-saturated 0.1 mol·L-1 KOH at scan rate of 5 mV·s-1 and rotation speed of 1600 r·min-1; (C) Jk of ORR at different potentials on different catalysts. Reproduced with permission of Ref. 70, copyright 2016 American Chemical Society. (color on line)
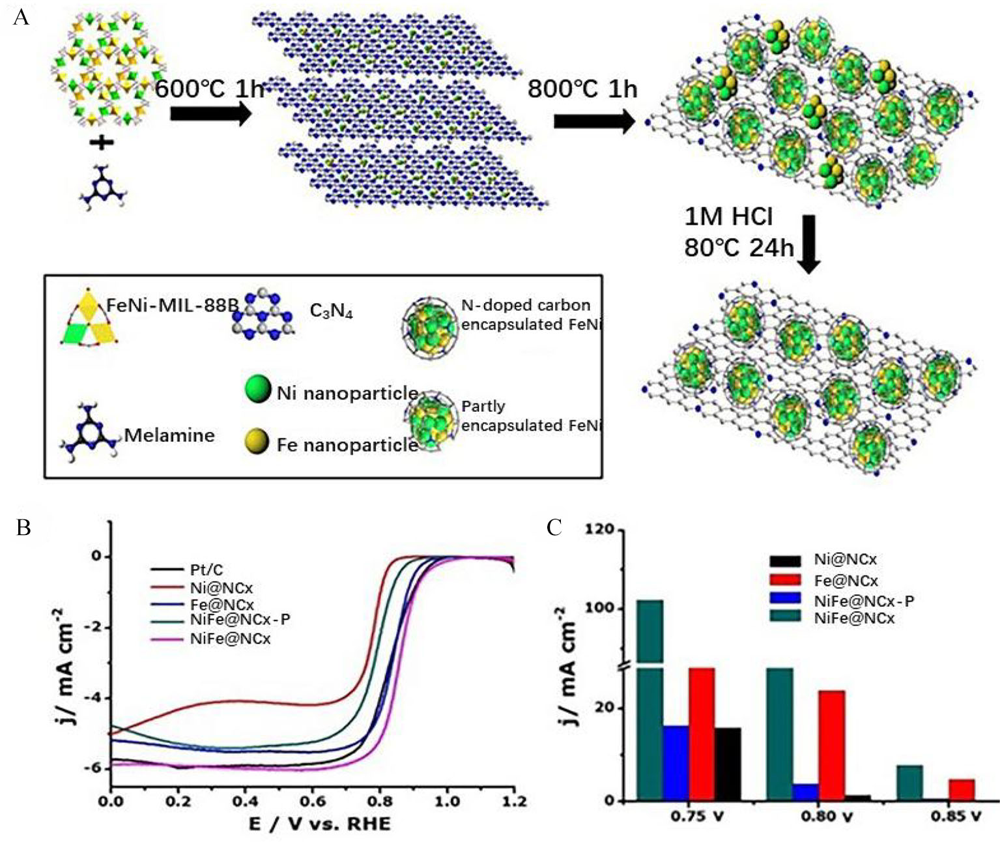
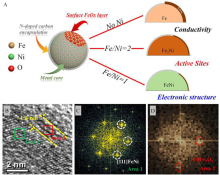
Figure 9
(A) Schematic illustration for the Ni doping strategy to regulate the interface structure of the as-derived catalysts; (B) RTEM image, and (C, D) FFT patterns derived from the regions of the areas 1 and 2 in (B). Reproduced with permission of Ref. 97, copyright 2020 Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim. (color on line)
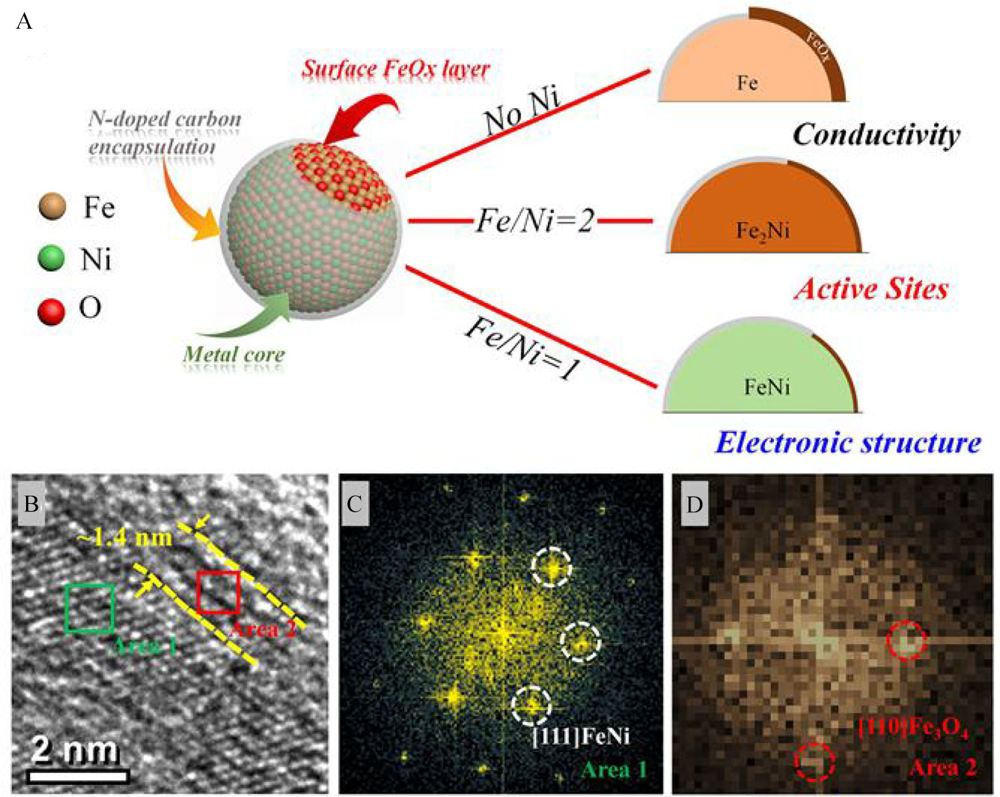
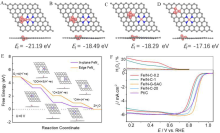
Figure 10
(A-D) Various Fe cluster/Fe-N4 site configurations and the corresponding formation energy (Ef); (E) ORR Gibbs free energy diagrams on the edge and in-plane sites; (F) ORR polarization curves of the Fe/N-G-SAC, other Fe-based counterparts and the commercial Pt/C. Reproduced with permission of Ref. 81, copyright 2020 Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim. (color on line)
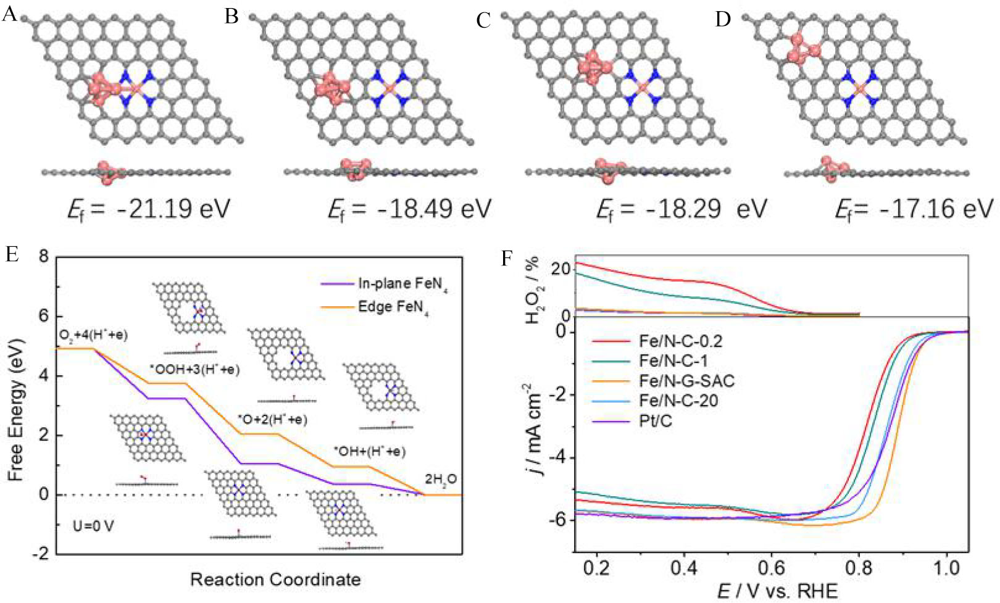
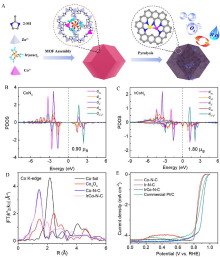
Figure 11
(A) Schematic illustration for the synthetic procedure of diatomic IrCo-N-C catalyst; (B, C) Partial density of states for Co-3d orbitals in (B) CoN4, (C) IrCoN5; (D) Fourier transformed extended X-ray adsorption fine structure (FT-EXAFS) spectra at Co K-edge; (E) The ORR polarization curves of IrCo-N-C, single-atom Co-N-C and Ir-N-C, and commercial Pt/C in 0.1 mol·L-1 KOH solution. Reproduced with permission of Ref. 103, copyright 2021 American Chemical Society. (color on line)
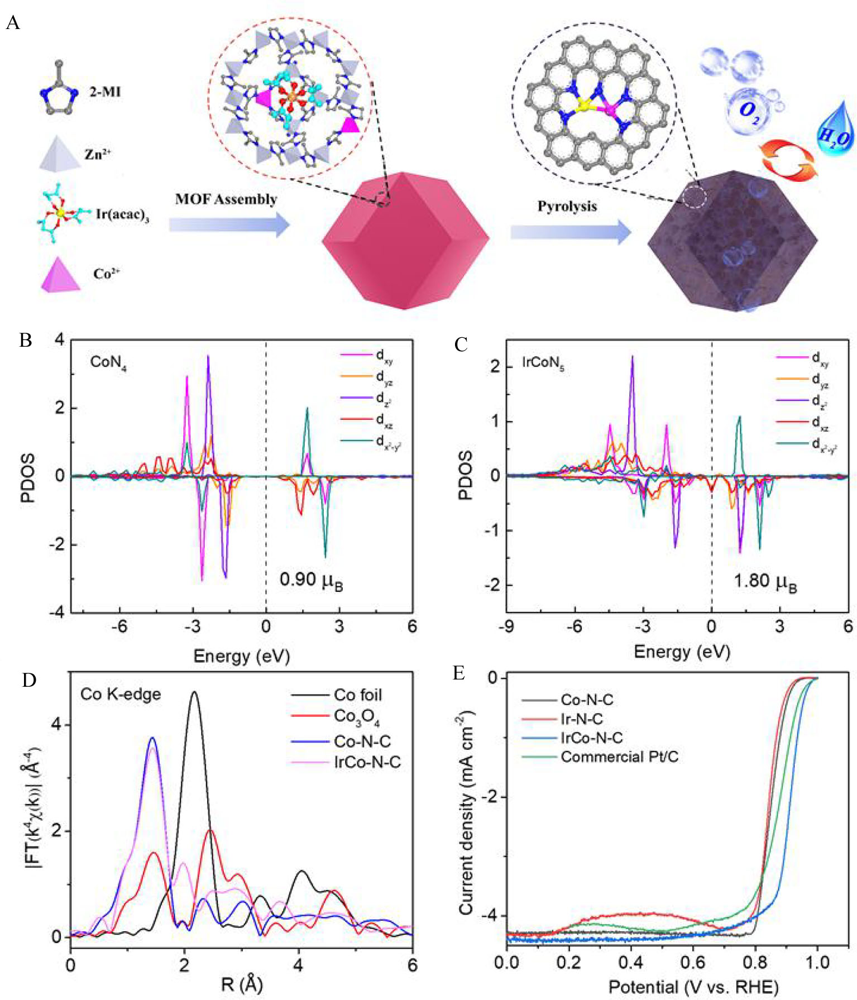
Table 2
The ORR performance and synthesis method of the representative NPMCs reported in literature.
| Sample | E1/2 (V vs. RHE) | Synthesis method |
|---|---|---|
| N-doping carbon[ | 0.853 | Template method |
| N, S co-doping carbon[ | 0.83 | Hummers’ method |
| N, S, O tri-doped carbon nanosheet[ | 0.86 | Template method |
| VACNTs-MnO2[ | / | Nebulized ethanol assisted infiltration and pyrolysis method |
| Mn@LaCoO3[ | 0.72 | Polyol-assisted solvothermal method |
| FeNiCo-P[ | 0.84 | Pyrolysis method |
| Co2P -Co, N, and P multi-doped carbon material[ | 0.843 | Phosphidation |
| C@CoCx[ | 0.8 | Solid-solid separation method |
| Fe3C@rGO[ | 0.8 | Pyrolysis method |
| FexN@N-doped carbon[ | 0.84 | NH3- histidine assisted method |
| NiCo-P[ | 0.82 | Electrospinning route |
| NiCo2S4@g-C3N4-CNT[ | 0.76 | Two-step hydrothermal |
| N-GQDs@NiCo2S4[ | 0.86 | Hydrothermal, sulfuration and electrophoretic deposition |
| Fe3C/N-doped carbon[ | 0.86 | Pyrolysis method |
| CoFe/N, P co-doped carbon nanovesicles[ | 086 | Impregnation and pyrolysis method |
| Co/N, S co-doped carbon[ | 0.85 | Two-step calcination methods |
| Pt1/FeOx[ | / | Pyrolysis method |
| Fe/N-CNRs[ | 0.9 | Pyrolysis method |
| SA-Fe-Nx-MPCS[ | 0.88 | Template method |
| Fe/N-G-SAC[ | 0.89 | Template method |
| Co-Nx-C[ | / | Template method |
| CoO@Mn3O4[ | / | Adsorption and reduction method |
| carbon-CoP[ | 0.81 | Phosphorization method |
| FexN[ | 0.89 | Pyrolysis method |
| CoO/CoxP[ | 0.86 | Phosphorization method |
| FexN@N-doped GO[ | / | Pyrolysis method |
| TiCoNx-rGO[ | 0.902 | Pyrolysis method |
| Co2N5[ | 0.79 | Pyrolysis method |
| FeCoN5[ | 0.86 | Pyrolysis method |
| IrCoN5[ | 0.911 | ZIFs-assisted host-guest method |
| FeNi-SAs@NC[ | 0.907 | Pyrolysis method |
| [1] |
Lewis N S, Nocera D G. Powering the planet: Chemical challenges in solar energy utilization[J]. PNAS, 2006, 103(43):15729-15735.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.0603395103 URL |
| [2] | Arges C G, Ramani V, Pintauro P N. Anion exchange me-mbrane fuel cells[J]. Electrochem. Soc. Interface, 2010, 19(2):31-35. |
| [3] |
Cheng F Y, Chen J. Metal-air batteries: from oxygen reduction electrochemistry to cathode catalysts[J]. Chem. Soc. Rev., 2012, 41(6):2172-2192.
doi: 10.1039/c1cs15228a URL |
| [4] |
Nörskov J K, Rossmeisl J, Logadottir A. Origin of the overpotential for oxygen reduction at a fuel-cell cathode[J]. J. Phys. Chem. B, 2004, 108(46):17886-17892.
doi: 10.1021/jp047349j URL |
| [5] |
Niu W J, He J Z, Gu B N, Liu M C, Chueh Y L. Opportunities and challenges in precise synjournal of transition metal single‐atom supported by 2D materials as catalysts toward oxygen reduction reaction[J]. Adv. Funct. Mater., 2021, 31(35):2103558.
doi: 10.1002/adfm.v31.35 URL |
| [6] | Liu M M, Wang L L, Zhao K N, Shi S S, Shao Q S, Zhang L, Sun X L, Zhao Y F, Zhang J J. Atomically dispersed metal catalysts for the oxygen reduction reaction: synjournal, characterization, reaction mechanisms and electrochemical energy applications[J]. Energy & Environ Sci., 2019, 12(10):2890-2923. |
| [7] |
Wu G, Zelenay P. Nanostructured nonprecious metal catalysts for oxygen reduction reaction[J]. Acc. Chem. Res., 2013, 46(8):1878-1889.
doi: 10.1021/ar400011z URL |
| [8] |
Feng Y, Alonso-Vante N. Nonprecious metal catalysts for the molecular oxygen-reduction reaction[J]. Phys. Status Solidi, 2010, 245(9):1792-1806.
doi: 10.1002/pssb.v245:9 URL |
| [9] |
Zhu C Z, He L, Fu S F, Dan D, Lin Y H. Highly efficient nonprecious metal catalysts towards oxygen reduction reaction based on three-dimensional porous carbon nanostructures[J]. Chem. Soc. Rev., 2016, 45(3):517-531.
doi: 10.1039/C5CS00670H URL |
| [10] |
Gong K P, Du F, Xia Z H, Durstock M, Dai L M. Nitrogen-doped carbon nanotube arrays with high electrocatalytic activity for oxygen reduction[J]. Science, 2009, 323(5915):760-764.
doi: 10.1126/science.1168049 URL |
| [11] |
Zhang L P, Lin C Y, Zhang D T, Gong L L, Zhu Y H, Zhao Z H, Xu Q, Li H J, Xia Z H. Guiding principles for designing highly efficient metal-free carbon catalysts[J]. Adv. Mater., 2019, 31(13):1805252.
doi: 10.1002/adma.v31.13 URL |
| [12] |
Daems N, Sheng X, Vankelecom I F J, Pescarmona P P. Metal-free doped carbon materials as electrocatalysts for the oxygen reduction reaction[J]. J. Mater. Chem. A, 2014, 2(12):4085-4110.
doi: 10.1039/C3TA14043A URL |
| [13] |
Quílez-Bermejo J, Morallón E, Cazorla-Amorós D. Metal-free heteroatom-doped carbon-based catalysts for ORR: A critical assessment about the role of heteroatoms[J]. Carbon, 2020, 165:434-454.
doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2020.04.068 URL |
| [14] |
Liang Y Y, Li Y G, Wang H L, Zhou J G, Wang J, Regier T, Dai H J. Co3O4 nanocrystals on graphene as a synergistic catalyst for oxygen reduction reaction[J]. Nat. Mater., 2011, 10(10):780-786.
doi: 10.1038/nmat3087 URL |
| [15] |
Odedairo T, Yan X C, Ma J, Jiao Y L, Yao X D, Du A J, Zhu Z H. Nanosheets Co3O4 interleaved with graphene for highly efficient oxygen reduction[J]. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2015, 7(38):21373-21380.
doi: 10.1021/acsami.5b06063 URL |
| [16] |
Deng D H, Yu L, Chen X Q, Wang G X, Jin L, Pan X L, Deng J, Sun G Q, Bao X H. Iron encapsulated within pod-like carbon nanotubes for oxygen reduction reaction[J]. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2013, 52(1):371-375.
doi: 10.1002/anie.201204958 URL |
| [17] |
He Y H, Liu S W, Priest C, Shi Q R, Wu G. Atomically dispersed metal-nitrogen-carbon catalysts for fuel cells: advances in catalyst design, electrode performance, and durability improvement[J]. Chem. Soc. Rev., 2020, 49(11):3484-3524.
doi: 10.1039/C9CS00903E URL |
| [18] |
Chen M J, He Y H, Spendelow J S, Wu G. Atomically dispersed metal catalysts for oxygen reduction[J]. ACS Energy Lett., 2019, 4(7):1619-1633.
doi: 10.1021/acsenergylett.9b00804 URL |
| [19] |
Zhu Y Z, Sokolowski J, Song X C, He Y H, Mei Y, Wu G. Engineering local coordination environments of atomically dispersed and heteroatom-coordinated single metal site electrocatalysts for clean energy-conversion[J]. Adv. Energy. Mater., 2020, 10(11):1902844.
doi: 10.1002/aenm.v10.11 URL |
| [20] |
Pan Y, Zhang C, Liu Z, Chen C, Li Y D. Structural regulation with atomic-level precision: from single-atomic site to diatomic and atomic interface catalysis[J]. Matter, 2020, 2(1):78-110.
doi: 10.1016/j.matt.2019.11.014 URL |
| [21] |
Liu D B, He Q, Ding S Q, Song L. Structural regulation and support coupling effect of single-atom catalysts for heterogeneous catalysis[J]. Adv. Energy. Mater., 2020, 10(32):2001482.
doi: 10.1002/aenm.v10.32 URL |
| [22] |
Ling T, Jaroniec M, Qiao S Z. Recent progress in engineering the atomic and electronic structure of electrocatalysts via cation exchange reactions[J]. Adv. Mater., 2020, 32(46):2001866.
doi: 10.1002/adma.v32.46 URL |
| [23] |
Zhang L P, Xu Q, Niu J B, Xia Z H. Role of lattice defects in catalytic activities of graphene clusters for fuel cells[J]. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2015, 17(26):16733-16743.
doi: 10.1039/C5CP02014J URL |
| [24] |
Jia Y, Zhang L Z, Zhuang L Z, Liu H L, Yan X C, Wang X, Liu J D, Wang J C, Zheng Y R, Xiao Z H, Taran E, Chen J, Yang D J, Zhu Z H, Wang S Y, Dai L M, Yao X D. Identification of active sites for acidic oxygen reduction on carbon catalysts with and without nitrogen doping[J]. Nat. Catal., 2019, 2(8):688-695.
doi: 10.1038/s41929-019-0297-4 |
| [25] |
Hu C G, Paul R, Dai Q B, Dai L M. Carbon-based metal-free electrocatalysts: from oxygen reduction to multifunctional electrocatalysis[J]. Chem. Soc. Rev., 2021, 50(21):11785-11843.
doi: 10.1039/D1CS00219H URL |
| [26] |
Gao F, Zhao G L, Yang S, Spivey J J. Nitrogen-doped fullerene as a potential catalyst for hydrogen fuel cells[J]. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2013, 135(9):3315-3318.
doi: 10.1021/ja309042m URL |
| [27] |
Sidik R A, Anderson A B, Subramanian N P, Kumaraguru S P, Popov B N. O2 reduction on graphite and nitrogen-doped graphite: experiment and theory[J]. J. Phys. Chem. B, 2006, 110(4):1787-1793.
doi: 10.1021/jp055150g URL |
| [28] |
Xing T, Zheng Y, Li L H, Cowie B C C, Gunzelmann D, Qiao S Z, Huang S M, Chen Y. Observation of active sites for oxygen reduction reaction on nitrogen-doped multilayer graphene[J]. ACS Nano, 2014, 8(7):6856-6862.
pmid: 24882522 |
| [29] |
Guo D H, Shibuya R, Akiba C, Saji S, Kondo T, Nakamura J. Active sites of nitrogen-doped carbon materials for oxygen reduction reaction clarified using model catalysts[J]. Science, 2016, 351(6271):361-365.
doi: 10.1126/science.aad0832 URL |
| [30] |
Ding W, Wei Z D, Chen S G, Qi X Q, Yang T, Hu J S, Wang D, Wan L-J, Alvi S F, Li L. Space-confinement-induced synjournal of pyridinic- and pyrrolic-nitrogen-doped graphene for the catalysis of oxygen reduction[J]. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2013, 52(45):11755-11759.
doi: 10.1002/anie.v52.45 URL |
| [31] |
Luo E G, Xiao M L, Ge J J, Liu C P, Xing W. Selectively doping pyridinic and pyrrolic nitrogen into a 3D porous carbon matrix through template-induced edge engineering: enhanced catalytic activity towards the oxygen reduction reaction[J]. J. Mater. Chem. A, 2017, 5(41):21709-21714.
doi: 10.1039/C7TA07608H URL |
| [32] |
Silva R, Al-Sharab J, Asefa T. Edge-plane-rich nitrogen-doped carbon nanoneedles and efficient metal-free electrocatalysts[J]. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2012, 51(29):7171-7175.
doi: 10.1002/anie.201201742 URL |
| [33] |
Zhao Y, Yang L J, Chen S, Wang X Z, Ma Y W, Wu Q, Jiang Y F, Qian W J, Hu Z. Can boron and nitrogen co-doping improve oxygen reduction reaction activity of carbon nanotubes?[J]. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2013, 135(4):1201-1204.
doi: 10.1021/ja310566z pmid: 23317479 |
| [34] |
Zhu J B, Li K, Xiao M L, Liu C P, Wu Z J, Ge J J, Xing W. Significantly enhanced oxygen reduction reaction performance of N-doped carbon by heterogeneous sulfur incorporation: synergistic effect between the two dopants in metal-free catalysts[J]. J. Mater. Chem. A, 2016, 4(19):7422-7429.
doi: 10.1039/C6TA02419J URL |
| [35] |
Chen W, Chen X, Qiao R, Jiang Z, Jiang Z J, Papovi? S, Raleva K, Zhou D. Understanding the role of nitrogen and sulfur doping in promoting kinetics of oxygen reduction reaction and sodium ion battery performance of hollow spherical graphene[J]. Carbon, 2022, 187:230-240.
doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2021.11.020 URL |
| [36] |
Razmjooei F, Singh K P, Song M Y, Yu J S. Enhanced electrocatalytic activity due to additional phosphorous doping in nitrogen and sulfur-doped graphene: A comprehensive study[J]. Carbon, 2014, 78:257-267.
doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2014.07.002 URL |
| [37] |
Xing Z H, Xiao M L, Guo Z L, Yang W S. Colloidal silica assisted fabrication of N,O,S-tridoped porous carbon nanosheets with excellent oxygen reduction performance[J]. Chem. Commun., 2018, 54(32):4017-4020.
doi: 10.1039/C8CC00846A URL |
| [38] |
Yang Z, Zhou X M, Jin Z P, Liu Z, Nie H G, Chen X A, Huang S M. A facile and general approach for the direct fabrication of 3D, vertically aligned carbon nanotube array/transition metal oxide composites as non-Pt catalysts for oxygen reduction reactions[J]. Adv. Mater., 2014, 26(19):3156-3161.
doi: 10.1002/adma.201305513 URL |
| [39] |
Sun J, Du L, Sun B Y, Han G K, Ma Y L, Wang J J, Huo H, Du C Y, Yin G P. Bifunctional LaMn0.3Co0.7O3 perovskite oxide catalyst for oxygen reduction and evolution reactions: The optimized e(g) electronic structures by ma-nganese dopant[J]. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2020, 12(45):24717-24725.
doi: 10.1021/acsami.0c03983 URL |
| [40] |
Ren D Z, Ying J, Xiao M L, Deng Y P, Ou J H, Zhu J B, Liu G H, Pei Y, Li S, Jauhar A M, Jin H L, Wang S, Su D, Yu A P, Chen Z W. Hierarchically porous multimetal-based carbon nanorod hybrid as an efficient oxygen catalyst for rechargeable zinc-air batteries[J]. Adv. Funct. Mater., 2020, 30(7):1908167.
doi: 10.1002/adfm.v30.7 URL |
| [41] | Liu H T, Guan J Y, Yang S X, Yu Y H, Shao R, Zhang Z P, Dou M L, Wang F, Xu Q. Metal-organic framework-derived Co2P nanoparticle/multi-doped porous carbon as a trifunctional electrocatalyst[J]. Adv. Mater., 2020, 32(36):2003649. |
| [42] |
Parra-Puerto A, Ng K L, Fahy K, Goode A E, Ryan M P, Kucernak A. Supported transition metal phosphides: activity survey for HER, ORR, OER, and corrosion resistance in acid and alkaline electrolytes[J]. ACS Catal., 2019, 9(12):11515-11529.
doi: 10.1021/acscatal.9b03359 |
| [43] |
Liu W W, Ren B H, Zhang W Y, Zhang M W, Li G R, Xiao M L, Zhu J B, Yu A P, Ricardez-Sandoval L, Chen Z W. Defect-enriched nitrogen doped-graphene quantum dots engineered NiCo2S4 nanoarray as high-efficiency bifunctional catalyst for flexible Zn-air battery[J]. Small, 2019, 15(44):1903610.
doi: 10.1002/smll.v15.44 URL |
| [44] |
Yu Y D, Zhou J, Sun Z M. Novel 2D Transition-Metal Carbides: Ultrahigh performance electrocatalysts for overall water splitting and oxygen reduction[J]. Adv. Func. Mater., 2020, 30(47):2000570.
doi: 10.1002/adfm.v30.47 URL |
| [45] |
Rasaki S A, Shen H, Thomas T, Yang M. Solid-solid separation approach for preparation of carbon-supported cobalt carbide nanoparticle catalysts for oxygen reduction[J]. ACS Appl. Nano. Mater., 2019, 2(6):3662-3670.
doi: 10.1021/acsanm.9b00601 URL |
| [46] |
Huang H T, Chang Y, Jia J C, Jia M L, Wen Z H. Understand the Fe3C nanocrystalline grown on rGO and its performance for oxygen reduction reaction[J]. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy, 2020, 45(53):28764-28773.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2020.07.226 URL |
| [47] | Wang M, Yang Y S, Liu X, Pu Z H, Kou Z K, Zhu P P, Mu S C. The role of iron nitrides in the Fe-N-C catalysis system towards the oxygen reduction reaction[J]. Nano-scale, 2017, 9(22):7641-7649. |
| [48] |
Tian X L, Wang L, Chi B, Xu Y, Zaman S, Qi K, Liu H, Liao S, Xia B Y. Formation of a tubular assembly by ultrathin Ti0.8Co0.2N nanosheets as efficient oxygen reduction electrocatalysts for hydrogen-/metal-air fuel cells[J]. ACS Catal., 2018, 8(10):8970-8975.
doi: 10.1021/acscatal.8b02710 URL |
| [49] |
Kreider M E, Gallo A, Back S, Liu Y, Siahrostami S, No-rdlund D, Sinclair R, Norskov J K, King L A, Jaramillo T F. Precious metal-free nickel nitride catalyst for the oxygen reduction raction[J]. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2019, 11(30):26863-26871.
doi: 10.1021/acsami.9b07116 URL |
| [50] | Tian Y H, Xu L, Qiu J X, Liu X H, Zhang S Q. Rational design of sustainable transition metal-based bifunctional electrocatalysts for oxygen reduction and evolution reactions[J]. Sustain.Mater.Techno., 2020, 25:e00204. |
| [51] |
Wang M Y, Han B H, Deng J J, Jiang Y, Zhou M Y, Lucero M, Wang Y, Chen Y B, Yang Z Z, N'diaye A T, Wang Q, Xu Z C J, Feng Z X. Influence of Fe substitution into LaCoO3 electrocatalysts on oxygen-reduction activity[J]. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2019, 11(6):5682-5686.
doi: 10.1021/acsami.8b20780 URL |
| [52] |
Surendran S, Shanmugapriya S, Sivanantham A, Shanmugam S, Kalai Selvan R. Electrospun carbon nanofibers encapsulated with NiCoP: A multifunctional electrode for supercapattery and oxygen reduction, oxygen evolution, and hydrogen evolution reactions[J]. Adv. Energy Mater., 2018, 8(20):1800555.
doi: 10.1002/aenm.v8.20 URL |
| [53] |
Han X P, Zhang W, Ma X Y, Zhong C, Zhao N Q, Hu W B, Deng Y D. Identifying the activation of bimetallic sites in NiCo2S4@g-C3N4-CNT hybrid electrocatalysts for synergistic oxygen reduction and evolution[J]. Adv. Mater., 2019, 31(18):1808281.
doi: 10.1002/adma.v31.18 URL |
| [54] |
Liu W W, Ren B H, Zhang W Y, Zhang M W, Li G R, Xiao M L, Zhu J B, Yu A P, Ricardez-Sandoval L, Chen Z W. Defect-enriched nitrogen doped-graphene quantum dots engineered NiCo2S4 nanoarray as high-efficiency bifunctional catalyst for flexible Zn-air battery[J]. Small, 2019, 15(44):1903610.
doi: 10.1002/smll.v15.44 URL |
| [55] |
Strickland K, Elise M W, Jia Q Y, Tylus U, Ramaswamy N, Liang W T, Sougrati M T, Jaouen F, Mukerjee S. Highly active oxygen reduction non-platinum group metal electrocatalyst without direct metal-nitrogen coordination[J]. Nat. Commun., 2015, 6:7343.
doi: 10.1038/ncomms8343 pmid: 26059552 |
| [56] |
Varnell J A, Tse E C M, Schulz C E, Fister T T, Haasch R T, Timoshenko J, Frenkel A I, Gewirth A A. Identification of carbon-encapsulated iron nanoparticles as active species in non-precious metal oxygen reduction catalysts[J]. Nat. Commun., 2016, 7:12582.
doi: 10.1038/ncomms12582 pmid: 27538720 |
| [57] |
Chen M X, Zhu M Z, Zuo M, Chu S Q, Zhang J, Wu Y, Liang H W, Feng X L. Identification of catalytic sites for oxygen reduction in metal/nitrogen-doped carbons with encapsulated metal nanoparticles[J]. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2020, 59(4):1627-1633.
doi: 10.1002/anie.v59.4 URL |
| [58] |
Chen X Q, Xiao J P, Wang J, Deng D H, Hu Y F, Zhou J G, Yu L, Heine T, Pan X L, Bao X H. Visualizing electronic interactions between iron and carbon by X-ray chemical imaging and spectroscopy[J]. Chem. Sci., 2015, 6(5):3262-3267.
doi: 10.1039/C5SC00353A URL |
| [59] |
Hu Y, Jensen J O, Zhang W, Huang Y J, Cleemann LN, Xing W, Bjerrum, N J, Li Q F. Direct synjournal of Fe3C-functionalized graphene by high temperature autoclave pyrolysis for oxygen reduction[J]. ChemSusChem, 2014, 7(8):2099-2113.
doi: 10.1002/cssc.201402183 URL |
| [60] |
Aijaz A, Masa J, Rsler C, Antoni H, Fischer R A, Schuhmann W, Muhler M. MOF-templated assembly approach for Fe3C nanoparticles encapsulated in bamboo-like N-doped CNTs: highly efficient oxygen reduction under acidic and basic conditions[J]. Chem. Eur. J., 2017, 23(50):12125-12130.
doi: 10.1002/chem.201701389 URL |
| [61] |
Kong A, Zhang Y, Chen Z, Chen A, Li C, Wang H, Shan Y. One-pot synthesized covalent porphyrin polymer-derived core-shell Fe3C@carbon for efficient oxygen electroreduction[J]. Carbon, 2017, 116:606-614.
doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2017.02.046 URL |
| [62] |
Hu Y, Jensen J O, Zhang W, Cleemann L N, Xing W, Bjerrum N J, Li Q F. Hollow spheres of iron carbide nanoparticles encased in graphitic layers as oxygen reduction catalysts[J]. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2014, 53(14):3675-3679.
doi: 10.1002/anie.v53.14 URL |
| [63] |
Zhu J B, Xiao M L, Liu C P, Ge J J, St-Pierre J, Xing W. Growth mechanism and active site probing of Fe3C@N-doped carbon nanotubes/C catalysts: guidance for building highly efficient oxygen reduction electrocatalysts[J]. J. Mater. Chem. A, 2015, 3(43):21451-21459.
doi: 10.1039/C5TA06181D URL |
| [64] |
Xiao M L, Zhu J B, Feng L G, Liu C P, Xing W. Meso/Macroporous nitrogen-doped carbon architectures with iron carbide encapsulated in graphitic layers as an efficient and robust catalyst for the oxygen reduction reaction in both acidic and alkaline solutions[J]. Adv. Mater., 2015, 27(15):2521-2527.
doi: 10.1002/adma.201500262 URL |
| [65] |
Nandan R, Pandey P, Gautam A. Atomic Arrangement Modulation in CoFe nanoparticles encapsulated in N-doped carbon nanostructures for efficient oxygen reduction reaction[J]. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2021, 13(3):3771-3781.
doi: 10.1021/acsami.0c16937 URL |
| [66] |
Lv C C, Liang B L, Li K X, Zhao Y, Sun H W. Boosted activity of graphene encapsulated CoFe alloys by blending with activated carbon for oxygen reduction reaction[J]. Biosens. Bioelectron., 2018, 117:802-809.
doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2018.07.020 URL |
| [67] | Liu Y, Wu X, Guo X, Lee K, Sun Q, Li X, Zhang C, Wang Z, Hu J, Zhu Y, Leung M K H, Zhu Z. Modulated FeCo nanoparticle in situ growth on the carbon matrix for high-performance oxygen catalysts[J]. Mater. Today Energy, 2021, 19:100610. |
| [68] |
Hou Y, Cui S M, Wen Z H, Guo X R, Feng X L, Chen J H. Electrocatalysis: Strongly coupled 3D hybrids of N-doped porous carbon nanosheet/CoNi alloy-encapsulated carbon nanotubes for enhanced electrocatalysis[J]. Small, 2015, 11(44):5939.
doi: 10.1002/smll.201570267 URL |
| [69] |
Niu L J, Liu G H, Li Y F, An J W, Zhao B Y, Yang J S, Qu D, Wang X Y, An L, Sun Z C. CoNi alloy nanoparticles encapsulated in N-doped graphite carbon nanotubes as an efficient electrocatalyst for oxygen reduction reaction in an alkaline medium[J]. ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng., 2021, 9(24):8207-8213.
doi: 10.1021/acssuschemeng.1c02098 URL |
| [70] |
Zhu J B, Xiao M L, Zhang Y L, Jin Z, Peng Z Q, Liu C P, Chen S L, Ge J J, Xing W. Metal-organic framework-induced synjournal of ultrasmall encased NiFe nanoparticles coupling with graphene as an efficient oxygen electrode for a rechargeable Zn-air battery[J]. ACS Catal., 2016, 6(10):6335-6342.
doi: 10.1021/acscatal.6b01503 URL |
| [71] |
Wang Z, Ang J M, Liu J, Ma X, Kong G H, Zhang Y F, Yan T, Lu X H. FeNi alloys encapsulated in N-doped CNTs-tangled porous carbon fibers as highly efficient and durable bifunctional oxygen electrocatalyst for rechargeable zinc-air battery[J]. Appl. Catal. B: Environ., 2019, 263:118344.
doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2019.118344 URL |
| [72] |
Niu H J, Chen S S, Feng J J, Zhang L, Wang A J. Assembled hollow spheres with CoFe alloyed nanocrystals encapsulated in N, P-doped carbon nanovesicles: An ultra-stable bifunctional oxygen catalyst for rechargeable Zn-air battery[J]. J. Power Sources, 2020, 475:228594.
doi: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2020.228594 URL |
| [73] |
Dong Z, Li M X, Zhang W L, Liu Y J, Wang Y, Qin C L, Yu L T, Yang J, Zhang X, Dai X P. Cobalt nanoparticles embedded in N, S Co-doped carbon towards oxygen reduction reaction derived by in-situ reducing cobalt sulfide[J]. ChemCatChem, 2019, 11(24):6039-6050.
doi: 10.1002/cctc.v11.24 URL |
| [74] |
Qiao B, Wang A, Yang X, Allard L F, Jiang Z, Cui Y, Liu J, Li J, Zhang T. Single-atom catalysis of CO oxidation using Pt1/FeOx[J]. Nat. Chem., 2011, 3(8):634-641.
doi: 10.1038/nchem.1095 URL |
| [75] |
Lefevre M, Proietti E, Jaouen F, Dodelet J P. Iron-based catalysts with improved oxygen reduction activity in poly-mer electrolyte fuel cells[J]. Science, 2009, 324(5923):71-74.
doi: 10.1126/science.1170051 URL |
| [76] |
Chen Y J, Ji S F, Wang Y G, Dong J C, Chen W X, Li Z, Shen R A, Zheng L R, Zhuang Z B, Wang D S, Li Y D. Isolated single iron atoms anchored on N-doped porous carbon as an efficient electrocatalyst for the oxygen reduction reaction[J]. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2017, 56(24):6937-6941.
doi: 10.1002/anie.201702473 URL |
| [77] |
Zhao X L, Shao L, Wang Z M, Chen H B, Yang H P, Zeng L. In situ atomically dispersed Fe doped metal-organic framework on reduced graphene oxide as bifunctional electrocatalyst for Zn-air batteries[J]. J. Mater. Chem. C, 2021, 9(34):11252-11260.
doi: 10.1039/D1TC02729H URL |
| [78] |
Zhao X, Shao L, Wang Z, Chen H, Yang H, Zeng L. In situ atomically dispersed Fe doped metal-organic framework on reduced graphene oxide as bifunctional electrocatalyst for Zn-air batteries[J]. J. Mater. Chem. C, 2021, 9(34):11252-11260.
doi: 10.1039/D1TC02729H URL |
| [79] |
Gong X F, Zhu J B, Li J Z, Gao R, Zhou Q Y, Zhang Z, Dou H Z, Zhao L, Sui X L, Cai J J, Zhang Y L, Liu B, Hu Y F, Yu A P, Sun S H, Wang Z B, Chen Z W. Self-templated hierarchically porous carbon nanorods embedded with atomic Fe-N4 active sites as efficient oxygen reduction electrocatalysts in Zn-air batteries[J]. Adv. Funct. Mater., 2021, 31(8):2008085.
doi: 10.1002/adfm.v31.8 URL |
| [80] |
Fu X G, Jiang G P, Wen G B, Gao R, Li S, Li M, Zhu J B, Zheng Y, Li Z Q, Hu Y F, Yang L, Bai Z Y, Yu A P, Chen Z W. Densely accessible Fe-Nx active sites decorated mesoporous-carbon-spheres for oxygen reduction towards high performance aluminum-air flow batteries[J]. Appl. Cata. B: Environ., 2021, 293:120176.
doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2021.120176 URL |
| [81] |
Xiao M L, Xing Z H, Jin Z, Liu C P, Ge J J, Zhu J B, Wang Y, Zhao X, Chen Z W. Preferentially engineering FeN4 edge sites onto graphitic nanosheets for highly active and durable oxygen electrocatalysis in rechargeable Zn-air batteries[J]. Adv. Mater., 2020, 32(49):2004900.
doi: 10.1002/adma.v32.49 URL |
| [82] |
Han X P, Ling X F, Wang Y, Ma T Y, Zhong C, Hu W B, Deng Y D. Generation of nanoparticle, atomic-cluster, and single-atom cobalt catalysts from zeolitic imidazole frameworks by spatial isolation and their use in zinc-air batteries[J]. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2019, 58(16):5359-5364.
doi: 10.1002/anie.v58.16 URL |
| [83] |
Pan Y, Liu S J, Sun K A, Chen X, Wang B, Wu K L, Cao X, Cheong W-C, Shen R A, Han A J, Chen Z, Zheng L R, Luo J, Lin Y, Liu Y Q, Wang D S, Peng Q, Zhang Q, Chen C, Li Y D. A bimetallic Zn/Fe polyphthalocyanine-derived dingle-atom Fe-N4 catalytic site: a superior trifunctional catalyst for overall water splitting and Zn-air batteries[J]. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2018, 57(28):8614-8618.
doi: 10.1002/anie.v57.28 URL |
| [84] |
Chen G B, Liu P, Liao Z Q, Sun F F, He Y H, Zhong H X, Zhang T, Zschech E, Chen M W, Wu G, Zhang J, Feng X L. Zinc-mediated template synjournal of Fe-N-C electrocatalysts with densely accessible Fe-Nx active sites for efficient oxygen reduction[J]. Adv. Mater., 2020, 32(8):1907399.
doi: 10.1002/adma.v32.8 URL |
| [85] |
Arif Khan M, Sun C L, Cai J, Ye D X, Zhao K N, Zhang G B, Shi S S, Ali Shah L, Fang J H, Yang C, Zhao H B, Mu S C, Zhang J J. Potassium-ion activating formation of Fe-N-C moiety as efficient oxygen electrocatalyst for Zn-air batteries[J]. ChemElectroChem, 2021, 8(7):1298-1306.
doi: 10.1002/celc.v8.7 URL |
| [86] |
Ding S C, Lyu Z Y, Sarnello E, Xu M J, Fang L Z, Tian H Y, Karcher S, Li T, Pan X Q, Mccloy J, Ding G D, Zhang Q, Shi Q R, Du D, Li J C, Zhang X, Lin Y H. A MnOx enhanced atomically dispersed iron-nitrogen-carbon catalyst for the oxygen reduction reaction[J]. J. Mater. Chem. A, 2021, DOI: 10.1039/d1ta07219f.
doi: 10.1039/d1ta07219f |
| [87] |
Cheng Q Q, Yang L J, Zou L L, Zou Z Q, Chen C, Hu Z, Yang H. Single cobalt atom and N co-doped carbon nanofibers as highly durable electrocatalyst for oxygen reduction reaction[J]. ACS Catal., 2017, 7(10):6864-6871.
doi: 10.1021/acscatal.7b02326 URL |
| [88] |
Wu G, More K L, Johnston C M, Zelenay P. High-performance electrocatalysts for oxygen reduction derived from polyaniline, iron, and cobalt[J]. Science, 2011, 332(6028):443-447.
doi: 10.1126/science.1200832 URL |
| [89] |
Zhou Q Y, Cai J J, Zhang Z, Gao R, Chen B, Wen G B, Zhao L, Deng Y P, Dou H Z, Gong X F, Zhang Y L, Hu Y F, Yu A P, Sui X L, Wang Z B, Chen Z W. A gas-phase migration strategy to synthesize atomically dispersed Mn-N-C catalysts for Zn-air batteries[J]. Small Methods, 2021, 5(6):2100024.
doi: 10.1002/smtd.v5.6 URL |
| [90] |
Song P, Luo M, Liu X Z, Xing W, Xu W L, Jiang Z, Gu L. Zn single atom catalyst for highly efficient oxygen reduction reaction[J]. Adv. Funct. Mater., 2017, 27(28):1700802.
doi: 10.1002/adfm.v27.28 URL |
| [91] |
Zhang S A, Xue H, Li W l, Sun J, Guo N K, Song T S, Dong H L, Zhang J W, Ge X, Zhang W, Wang Q. Constructing precise coordination of nickel active sites on hierarchical porous carbon framework for superior oxygen reduction[J]. Small, 2021, 17(35):2102125.
doi: 10.1002/smll.v17.35 URL |
| [92] |
Shang H S, Zhou X Y, Dong J C, Li A, Zhao X, Liu Q H, Lin Y, Pei J J, Li Z, Jiang Z L, Zhou D N, Zheng L R, Wang Y, Zhou J, Yang Z K, Cao R, Sarangi R, Sun T T, Yang X, Zheng X S, Yan W S, Zhuang Z B, Li J, Chen W X, Wang D S, Zhang J T, Li Y D. Engineering unsymmetrically coordinated Cu-S1N3 single atom sites with enhanced oxygen reduction activity[J]. Nat. Commun., 2020, 11:3049.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-16848-8 URL |
| [93] |
Liang H W, Zhuang X D, Bruller S, Feng X L, Mullen K. Hierarchically porous carbons with optimized nitrogen doping as highly active electrocatalysts for oxygen reduction[J]. Nat. Commun., 2014, 5:4973.
doi: 10.1038/ncomms5973 URL |
| [94] |
Li Z Q, Jiang G P, Deng Y P, Liu G H, Ren D Z, Zhang Z, Zhu J B, Gao R, Jiang Y, Luo D, Zhu Y F, Liu D H, Jauhar A M, Jin H L, Hu Y F, Wang S, Chen Z W. Deep-breathing honeycomb-like Co-Nx-C nanopolyhedron bifunctional oxygen electrocatalysts for rechargeable Zn-air batteries[J]. iScience, 2020, 23(8):101404.
doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2020.101404 URL |
| [95] |
Guo C X, Zheng Y, Ran J R, Xie F X, Jaroniec M, Qiao S Z. Engineering high-energy interfacial structures for high-performance oxygen-involving electrocatalysis[J]. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2017, 56(29):8539-8543.
doi: 10.1002/anie.v56.29 URL |
| [96] |
Lin Y X, Yang L, Zhang Y K, Jiang H L, Xiao Z J, Wu C Q, Zhang G B, Jiang J, Song L. Defective carbon-CoP nanoparticles hybrids with interfacial charges polarization for efficient bifunctional oxygen electrocatalysis[J]. Adv. Energy Mater., 2018, 8(18):1703623.
doi: 10.1002/aenm.v8.18 URL |
| [97] |
Zhu J B, Xiao M L, Li G R, Li S, Zhang J, Liu G H, Ma L, Wu T P, Lu J, Yu A P, Su D, Jin H L, Wang S, Chen Z W. A triphasic bifunctional oxygen electrocatalyst with tunable and synergetic interfacial structure for rechargeable Zn-air batteries[J]. Adv. Energy Mater., 2020, 10(4):1903003.
doi: 10.1002/aenm.v10.4 URL |
| [98] |
Niu Y, Xiao M L, Zhu J B, Zeng T T, Li J D, Zhang W Y, Su D, Yu A P, Chen Z W. A “trimurti” heterostructured hybrid with an intimate CoO/CoxP interface as a robust bifunctional air electrode for rechargeable Zn-air batteries[J]. J. Mater. Chem. A, 2020, 8(18):9177-9184.
doi: 10.1039/D0TA01145B URL |
| [99] |
Yin H, Zhang C Z, Liu F, Hou Y L. Hybrid of iron nitride and nitrogen-doped graphene aerogel as synergistic catalyst for oxygen reduction reaction[J]. Adv. Funct. Mater., 2014, 24(20):2930-2937.
doi: 10.1002/adfm.v24.20 URL |
| [100] |
Dong Y Y, Deng Y J, Zeng J H, Song H Y, Liao S J. A high-performance composite ORR catalyst based on the synergy between binary transition metal nitride and nitrogen-doped reduced graphene oxide[J]. J. Mater. Chem. A, 2017, 5(12):5829-5837.
doi: 10.1039/C6TA10496G URL |
| [101] | Xiao M L, Zhang H, Chen Y T, Zhu J B, Gao L Q, Jin Z, Ge J J, Jiang Z, Chen S L, Liu C P, Xing W. Identification of binuclear Co2N5 active sites for oxygen reduction reaction with more than one magnitude higher activity than single atom CoN4 site[J]. Nano Energy, 2018, 46:396-403. |
| [102] | Xiao M L, Chen Y T, Zhu J B, Zhang H, Zhao X, Gao L Q, Wang X, Zhao J, Ge J J, Jiang Z, Chen S L, Liu C P, Xing W. Climbing the apex of the ORR volcano plot via binuclear site construction: electronic and geometric engineering[J]. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2019, 141(44):17763-17770. |
| [103] | Xiao M L, Zhu J B, Li S, Li G R, Liu W W, Deng Y P, Bai Z Y, Ma L, Feng M, Wu T P, Su D, Lu J, Yu A P, Chen Z W. 3D-Orbital occupancy regulated Ir-Co atomic pair towards Superior bifunctional oxygen electrocatalysis[J]. ACS Catal., 2021, 11(14):8837-8846. |
| [104] | Jin Z Y, Li P P, Meng Y, Fang Z W, Xiao D, Yu G H. Understanding the inter-site distance effect in single-atom catalysts for oxygen electroreduction[J]. Nat. Catal., 2021, 4(7):615-622. |
| [105] | Luo F, Zhu J B, Ma S X, Li M, Xu R Z, Zhang Q, Yang Z H, Qu K G, Cai W W, Chen Z W. Regulated coordination environment of Ni single atom catalyst toward high-efficiency oxygen electrocatalysis for rechargeable zinc-air batteries[J]. Energy Storage Mater., 2021, 35:723-730. |
| [1] | 刘思淼, 周景娇, 季世军, 文钟晟. FeNi-CoP/NC双功能催化剂的制备及电催化性能研究[J]. 电化学(中英文), 2023, 29(10): 211118-. |
| [2] | 李渊, 陈妙迎, 卢帮安, 张佳楠. 高活性和耐久性非铂氧还原催化剂的研究进展[J]. 电化学(中英文), 2023, 29(1): 2215002-. |
| [3] | 李家欣, 冯立纲. 析氧反应铁镍基预催化剂的表界面调控与进展[J]. 电化学(中英文), 2022, 28(9): 2214001-. |
| [4] | 秦雪苹, 朱尚乾, 张露露, 孙书会, 邵敏华. 酸性和碱性溶液中金属氮碳材料氧还原和氢析出反应的理论研究[J]. 电化学(中英文), 2021, 27(2): 185-194. |
| [5] | 张焰峰, 肖菲, 陈广宇, 邵敏华. 基于非贵金属氧还原催化剂的质子交换膜燃料电池性能[J]. 电化学(中英文), 2020, 26(4): 563-572. |
| [6] | 张雅琳,陈驰,邹亮亮,邹志青,杨辉. Fe-N共掺杂的碳纳米管串联空心球对氧还原反应的电催化[J]. 电化学(中英文), 2018, 24(6): 726-732. |
| [7] | 杨莉君,Dustin Banham, Elod Gyenge,叶思宇. Nafion含量与阴离子吸附对于铂单原子层核壳结构催化剂制备的影响[J]. 电化学(中英文), 2017, 23(2): 170-179. |
| [8] | 肖梅玲,祝建兵,刘长鹏,葛君杰,邢 巍. 包覆型非贵金属氧还原催化剂的研究进展[J]. 电化学(中英文), 2016, 22(2): 101-112. |
| [9] | 陈 驰,周志有*,张新胜,孙世刚. 铁、氮掺杂石墨烯/碳黑复合材料的制备及氧还原电催化性能[J]. 电化学(中英文), 2016, 22(1): 25-31. |
| [10] | 宋平, 阮明波, 刘京, 冉光钧, 徐维林. 燃料电池非铂基氧还原电催化剂的最新研究进展[J]. 电化学(中英文), 2015, 21(2): 130-137. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||