

草酸在Ti/IrO2-Ta2O5阳极圆柱形电解槽中的电催化氧化降解动力学
收稿日期: 2012-12-25
修回日期: 2013-03-19
网络出版日期: 2013-03-24
基金资助
国家自然科学基金项目(No. 21273097)和高等学校博士学科点专项科研基金项目(No. 20120061110015)资助
Electrocatalytic Oxidation Degradation Kinetics of Oxalic Acid in a Cylindrical Electrochemical Reactor with Ti/IrO2-Ta2O5 Anode
Received date: 2012-12-25
Revised date: 2013-03-19
Online published: 2013-03-24
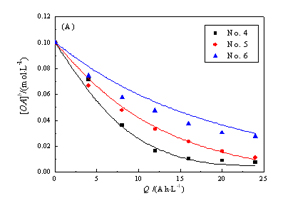
关键词: 电催化氧化; Ti/IrO2-TaO5阳极; 草酸; 理论模型
苏静 , 林海波 , 徐红 , 黄卫民 , 何亚鹏 . 草酸在Ti/IrO2-Ta2O5阳极圆柱形电解槽中的电催化氧化降解动力学[J]. 电化学, 2013 , 19(4) : 293 -299 . DOI: 10.61558/2993-074X.2114

Key words: electrochemical oxidation; Ti/IrO2-Ta2O5 ; anode; oxalic acid; theoretical model
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |