

Na2CO3对TiO2纳米管电极表面光电化学水分解反应的催化作用研究
收稿日期: 2012-06-04
修回日期: 2012-06-30
网络出版日期: 2012-07-05
基金资助
山东省自然科学基金(No. ZR2010EM026)和山东省优秀中青年科学家奖励基金(No. BS2011NJ009)资助
Sodium Carbonate Catalyzed Photoelectrochemical Water Splitting over TiO2 Nanotubes Photoanode
Received date: 2012-06-04
Revised date: 2012-06-30
Online published: 2012-07-05
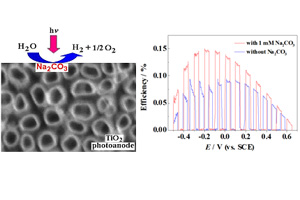
关键词: 光生空穴; 表面复合; 光电流; 阳极析氧; Mott-Schottky分析
孔德生 , 王静 , 张学迪 , 赵曦 , 王超 , 冯媛媛 , 李文娟 . Na2CO3对TiO2纳米管电极表面光电化学水分解反应的催化作用研究[J]. 电化学, 2013 , 19(1) : 71 -78 . DOI: 10.61558/2993-074X.2100

/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |