

甘氨酸修饰的Pt(111)电极上的氧还原
收稿日期: 2012-06-04
修回日期: 2012-06-30
网络出版日期: 2012-07-05
基金资助
国家自然基金面上项目(No. 21073176)资助
Oxygen Reduction Reaction on Glycin Modified Pt(111) Electrode
Received date: 2012-06-04
Revised date: 2012-06-30
Online published: 2012-07-05
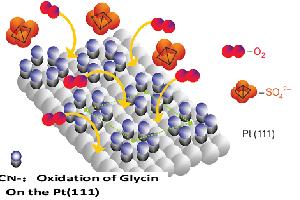
关键词: Pt(111)单晶电极; 氧还原; 甘氨酸修饰; 几何效应
李明芳 , 康婧 , 廖玲文 , 陈艳霞 , 叶深 . 甘氨酸修饰的Pt(111)电极上的氧还原[J]. 电化学, 2013 , 19(1) : 37 -42 . DOI: 10.61558/2993-074X.2096

/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |