

印染废水的电化学深度处理及回用研究
收稿日期: 2012-12-25
修回日期: 2013-03-18
网络出版日期: 2013-03-23
基金资助
国家科技支撑计划(No. 2011BAE07B09)和2012年浙江省大学生科技创新活动计划暨新苗人才计划(No. 2012R403063)资助
Advanced Treatment of Dyeing Wastewater for Reuse by Electrochemical Oxidation
Received date: 2012-12-25
Revised date: 2013-03-18
Online published: 2013-03-23
陈飞翔 , 杨初引 , 周明明 , 王家德 . 印染废水的电化学深度处理及回用研究[J]. 电化学, 2013 , 19(4) : 341 -344 . DOI: 10.61558/2993-074X.2119
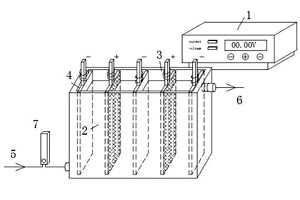
Key words: Dyeing wastewater; reuse; PbO2/Ti electrode
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |