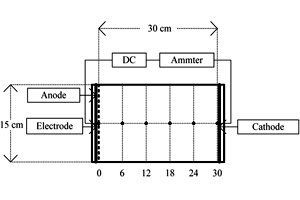
采用电动力学技术修复苯酚污染的粘性土壤,研究了苯酚的吸附特性,以及粘土中苯酚的最佳萃取剂和萃取条件,并讨论了不同pH、含水率、电场强度及不同添加物条件下苯酚的迁移特性. 实验得出,苯酚的吸附符合Freundlich等温式,最大吸附量362 mg·kg-1;用三氯甲烷做萃取剂,超声波20 min加恒温震荡30 min,从土壤中提取苯酚,萃取率可达到94.3%;土壤电动力学过程中苯酚向阳极迁移并在距离阳极0 ~ 6 cm处富集. 在pH值8.16,含水率为40%,电场强度为2 V·cm-1条件下,阳极添加0.1 mol·L-1 NaOH溶液,并向阴极添加0.05 mol·L-1 LAS溶液,苯酚的迁移效果达到最佳,在距阳极0 cm和6 cm处苯酚富集倍数分别达到139.0%和133.7%.
Using the electrokinetic technique to remediate phenol contaminated soil, the adsorption characteristics, the best extraction agent and extraction conditions of phenol in clay were studied. The migration characteristics of phenol under the conditions of different pH, different moisture contents, different electric-field intensities and different additives were discussed. It was found that the adsorption behavior of phenol followed Freundlich isotherm and the maximum adsorption was 362 mg·kg-1. Using chloroform as an extractant, with ultrasonic time of 20 min plus temperature shock time of 30 min to extract phenol from soil, the extraction rate could reach 94.3%. Phenol migrated to the anode and enriched within 0-6 cm from the anode in the soil electrodynamics process. The best migration effect of phenol was achieved under the conditions of pH=8.16, moisture content of 40%, electric-field intensity of 2 V·cm-1, along with the additions of 0.1 mol·L-1 NaOH solution and 0.05 mol·L-1 LAS solution into the anode and the cathode, respectively. The enrichment rates of phenol reached 139% and 133.7%, respectively, at the distances of 0 cm and 6 cm away from the anode.