

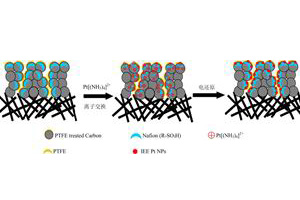
离子交换-电沉积法制备高Pt利用率多孔电极
收稿日期: 2012-06-04
修回日期: 2012-06-30
网络出版日期: 2012-07-05
基金资助
国家自然科学基金项目(No. 20676156, No. 51072239, No. 21176327)资助
Porous Electrodes with High Pt Utilization Obtained by Ion-Exchange/Electrodeposition
Received date: 2012-06-04
Revised date: 2012-06-30
Online published: 2012-07-05
陈四国, 丁 炜, 齐学强, 李 莉, 邓子华, 魏子栋 . 离子交换-电沉积法制备高Pt利用率多孔电极[J]. 电化学, 2013 , 19(1) : 53 -58 . DOI: 10.61558/2993-074X.2097

Key words: fuel cells; ion-exchange/electrodeposition; Pt utilization
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |