

FeCo合金纳米电催化剂制备及其性能研究
收稿日期: 2012-04-17
修回日期: 2012-05-03
网络出版日期: 2012-05-04
基金资助
新世纪优秀人才支持计划(No. NCET-10-0715),高等学校全国优秀博士学位论文作者专项资金(No. 201126)和浙江省重中之重学科开放基金项目(No. 20090503)资助
Preparation and Catalytic Properties of FeCo Alloy Nanocatalyst
Received date: 2012-04-17
Revised date: 2012-05-03
Online published: 2012-05-04
李明轩 , 欧洁连 , 陈声培 , 王鹏 , 许斌斌 , 孙世刚 . FeCo合金纳米电催化剂制备及其性能研究[J]. 电化学, 2013 , 19(2) : 125 -129 . DOI: 10.61558/2993-074X.3366
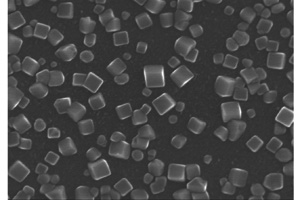
Key words: FeCo alloy; cube; electrocatalysis; nitrite reduction; oxygen reduction reaction
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |