

复合材料xLiFePO4·yLi3V2(PO4)3的合成及电化学性能(英文)
收稿日期: 2011-09-28
修回日期: 2011-10-28
网络出版日期: 2011-11-30
基金资助
This work was financially supported by National High Technology Research and Development Program of China (No. 2008AA03Z208)
Synthesis and electrochemical performance of xLiFePO4·yLi3V2(PO4)3 composites
Received date: 2011-09-28
Revised date: 2011-10-28
Online published: 2011-11-30
Supported by
This work was financially supported by National High Technology Research and Development Program of China (No. 2008AA03Z208)
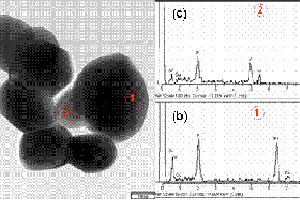
关键词: 锂离子电池; 复合物; 掺杂; xLiFePO4·yLi3V2(PO4)3
马平平 , 刘志坚 , 夏建华 , 陈宇 , 胡朴 , 卢志超 , 夏定国 . 复合材料xLiFePO4·yLi3V2(PO4)3的合成及电化学性能(英文)[J]. 电化学, 2012 , 18(1) : 31 -36 . DOI: 10.61558/2993-074X.2876

Key words: lithium ion batteries; composite; doping; xLiFePO4·yLi3V2(PO4)3
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |