

利用膨胀网作为双极板流道结构优化碱性水电解槽
收稿日期: 2023-12-28
修回日期: 2024-04-17
录用日期: 2024-05-07
网络出版日期: 2024-05-15
Optimization of Channel Structure of Alkaline Water Electrolyzer by Using an Expanded Mesh as a Bipolar Plate
Received date: 2023-12-28
Revised date: 2024-04-17
Accepted date: 2024-05-07
Online published: 2024-05-15
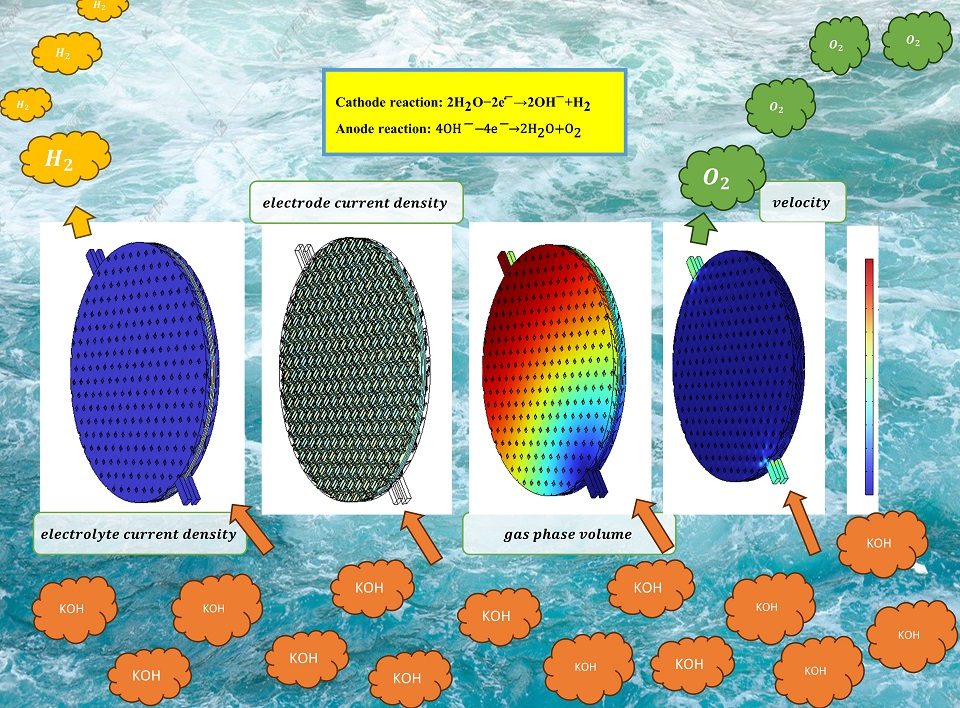
碱性水电解制氢是现今最为成熟的水电解制氢技术。电解槽由多个电解小室组成,单个电解小室由隔膜、电极、双极板和端板等组成。现有工业的双极板流道结构为凹凸结构,通过模具冲压成型制备,制备成本高且困难。凹凸结构电解小室存在电解液流动不均匀和电流密度低的问题,进而增加了碱性水电解制氢的能耗和成本。因而,本文首先根据现有工业的凹凸双极板流道结构搭建电化学和流动模型,分析电解小室电流密度、电解液流动和气泡分布情况。模型可靠性已通过与文献实验数据对照验证。其中,电化学电流密度决定了气体产率,气体在电解液中流动反过来影响电化学反应活性比表面积和欧姆电阻。结果表明,凹凸结构电解小室凹球底部流动速度几近为零,凸球表面电解液流速较大,流道结构中存在旋涡,电解液分布不均。接着,建模优化碱性水电解槽的流道结构,比较了凹凸结构、网状、菱形和膨胀网结构电解小室电化学和流动性能。结果表明,膨胀网结构电解小室电流密度最大,为3330 A/m2,电解液流速最大,为0.507 m/s。相同电流密度下,过电位最小,能耗最低。本文对碱性水电解槽流道结构的全面理解和优化提供一定的指导意义,为大规模电解槽设计提供理论基础。
熊海燕 , 朱振啸 , 高鑫 , 范晨铭 , 栾辉宝 , 李冰 . 利用膨胀网作为双极板流道结构优化碱性水电解槽[J]. 电化学, 2024 , 30(9) : 2312281 . DOI: 10.61558/2993-074X.3469
Alkaline water electrolysis (AWE) is the most mature technology for hydrogen production by water electrolysis. Alkaline water electrolyzer consists of multiple electrolysis cells, and a single cell consists of a diaphragm, electrodes, bipolar plates and end plates, etc. The existing industrial bipolar plate channel is concave-convex structure, which is manufactured by complicated and high-cost mold punching. This structure still results in uneven electrolyte flow and low current density in the electrolytic cell, further increasing in energy consumption and cost of AWE. Thereby, in this article, the electrochemical and flow model is firstly constructed, based on the existing industrial concave and convex flow channel structure of bipolar plate, to study the current density, electrolyte flow and bubble distribution in the electrolysis cell. The reliability of the model was verified by comparison with experimental data in literature. Among which, the electrochemical current density affects the bubble yield, on the other hand, the generated bubbles cover the electrode surface, affecting the active specific surface area and ohmic resistance, which in turn affects the electrochemical reaction. The result indicates that the flow velocity near the bottom of the concave ball approaches zero, while the flow velocity on the convex ball surface is significantly higher. Additionally, vortices are observed within the flow channel structure, leading to an uneven distribution of electrolyte. Next, modelling is used to optimize the bipolar plate structure of AWE by simulating the electrochemistry and fluid flow performances of four kinds of structures, namely, concave and convex, rhombus, wedge and expanded mesh, in the bipolar plate of alkaline water electrolyzer. The results show that the expanded mesh channel structure has the largest current density of 3330 A/m2 and electrolyte flow velocity of 0.507 m/s in the electrolytic cell. Under the same current density, the electrolytic cell with the expanded mesh runner structure has the smallest potential and energy consumption. This work provides a useful guide for the comprehensive understanding and optimization of channel structures, and a theoretical basis for the design of large-scale electrolyzer.

| [1] | Chu S, Majumdar A. Opportunities and challenges for a sustainable energy future[J]. Nature, 2012, 488(7411): 294-303. |
| [2] | Yang X, Nielsen C P, Song S, McElroy M B. Breaking the hard-to-abate bottleneck in China’s path to carbon neutrality with clean hydrogen[J]. Nature Energy, 2022, 7(10): 955-965. |
| [3] | Sachs J D, Schmidt-Traub G, Mazzucato M, Messner D, Nakicenovic N, Rockstr?m J. Six transformations to achieve the sustainable development goals[J]. Nat. Sustain., 2019, 2(9): 805-814. |
| [4] | Li Y B, Hu W K, Zhang F, Li Y. Collaborative operational model for shared hydrogen energy storage and park cluster: A multiple values assessment[J]. J. Energy Storage, 2024, 82: 110507. |
| [5] | Li J C, Xiao Y, Lu S Q. Optimal configuration of multi microgrid electric hydrogen hybrid energy storage capacity based on distributed robustness[J]. J. Energy Storage, 2024, 76: 109762. |
| [6] | Qazi U Y. Future of hydrogen as an alternative fuel for next-generation industrial applications; challenges and expected opportunities[J]. Energies, 2022, 15(13): 4741. |
| [7] | Prewitz M, Bardenhagen A, Beck R. Hydrogen as the fuel of the future in aircrafts - Challenges and opportunities[J]. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy, 2020, 45(46): 25378-25385. |
| [8] | Choi W, Kang S. Greenhouse gas reduction and economic cost of technologies using green hydrogen in the steel industry[J]. J. Environ. Manage., 2023, 335: 117569. |
| [9] | Ibrahim H, Ilinca A, Perron J. Energy storage systems—Characteristics and comparisons[J]. Renew. Sust. Energ. Rev., 2008, 12(5): 1221-1250. |
| [10] | Aneke M, Wang M. Energy storage technologies and real life applications - A state of the art review[J]. Appl. Energy, 2016, 179: 350-377. |
| [11] | Yu Z Y, Duan Y, Feng X Y, Yu X, Gao M R, Yu S H. Clean and affordable hydrogen fuel from alkaline water splitting: past, recent progress, and future prospects[J]. Adv. Mater., 2021, 33(31): e2007100. |
| [12] | Suleman F, Dincer I, Agelin-Chaab M. Environmental impact assessment and comparison of some hydrogen production options[J]. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy, 2015, 40(21): 6976-6987. |
| [13] | Kalamaras C M, Efstathiou A M. Hydrogen production technologies: Current state and future developments[J]. Conference Papers in Energy, 2013, 2013: 690627. |
| [14] | Acar C, Dincer I. Comparative assessment of hydrogen production methods from renewable and non-renewable sources[J]. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy, 2014, 39(1): 1-12. |
| [15] | Huang W T, Zhang B H, Ge L J, He J, Liao W L, Ma P L. Day-ahead optimal scheduling strategy for electrolytic water to hydrogen production in zero-carbon parks type microgrid for optimal utilization of electrolyzer[J]. J. Energy Storage, 2023, 68: 107653. |
| [16] | Liu Z M, Deng Y J, Wang P, Wang B H, Sun D L, Yu B. Study on the gas-liquid two-phase flow patterns for hydrogen production from electrolytic water[J]. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy, 2024, 60: 711-728. |
| [17] | Shiva Kumar S, Lim H. An overview of water electrolysis technologies for green hydrogen production[J]. Energy Rep., 2022, 8: 13793-13813. |
| [18] | Gambou F, Guilbert D, Zasadzinski M, Rafaralahy H. A comprehensive survey of alkaline electrolyzer modeling: Electrical domain and specific electrolyte conductivity[J]. Energies, 2022, 15(9): 3452. |
| [19] | Li Y Y, Deng X T, Gu J J, Zhang T, Guo B, Yang F Y, Ou Y M G. Comprehensive review and prospect of the modeling of alkaline water electrolysis system for hydrogen production[J]. Automotive Engineering, 2022, 44(4): 567-582. |
| [20] | Chandesris M, Médeau V, Guillet N, Chelghoum S, Thoby D, Fouda-Onana F. Membrane degradation in PEM water electrolyzer: Numerical modeling and experimental evidence of the influence of temperature and current density[J]. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy, 2015, 40(3): 1353-1366. |
| [21] | Siracusano S, Trocino S, Briguglio N, Pantò F, Aricò A S. Analysis of performance degradation during steady-state and load-thermal cycles of proton exchange membrane water electrolysis cells[J]. J. Power Sources, 2020, 468: 228390. |
| [22] | Du N Y, Roy C, Peach R, Turnbull M, Thiele S, Bock C. Anion-exchange membrane water electrolyzers[J]. Chem. Rev., 2022, 122(13): 11830-11895. |
| [23] | Emam A S, Hamdan M O, Abu-Nabah B A, Elnajjar E. Enhancing alkaline water electrolysis through innovative approaches and parametric study[J]. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy, 2024, 55: 1161-1173. |
| [24] | Daoudi C, Bounahmidi T. Overview of alkaline water electrolysis modeling[J]. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy, 2024, 49: 646-667. |
| [25] | Hu B, Liu M, Chen Q H, Zhou X W, Li H J, He M Z, Li Z Y, Zhang R, Huang Y D, Sherazi T A, Li N W. Porous polybenzimidazole membranes doped with KOH for alkaline water electrolysis[J]. J. Membr. Sci., 2024, 694: 122388. |
| [26] | Zhang T, Song L J, Yang F Y, Ouyang M G. Research on oxygen purity based on industrial scale alkaline water electrolysis system with 50Nm3 H2/h[J]. Appl. Energy, 2024, 360: 122852. |
| [27] | Liu Y, Amin M T, Khan F, Pistikopoulos E N. Safety analysis of proton exchange membrane water electrolysis system[J]. J. Environ. Chem. Eng., 2023, 11(5): 110772. |
| [28] | Wei Q, Fan L X, Tu Z K. Hydrogen production in a proton exchange membrane electrolysis cell (PEMEC) with titanium meshes as flow distributors[J]. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy, 2023, 48(93): 36271-36285. |
| [29] | de Groot M T, Kraakman J, Garcia Barros R L. Optimal operating parameters for advanced alkaline water electrolysis[J]. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy, 2022, 47(82): 34773-34783. |
| [30] | Phillips R, Edwards A, Rome B, Jones D R, Dunnill C W. Minimising the ohmic resistance of an alkaline electrolysis cell through effective cell design[J]. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy, 2017, 42(38): 23986-23994. |
| [31] | Zhang Y F. Study of influencing factors of cell voltage in filter-press type electrolyzer[D]. Hunan University, 2015. |
| [32] | Li J. Simulation study on flow characteristics in the unit of filter-press water electrolyzer[D]. China University of Petroleum, 2020. |
| [33] | Yu P, Wang F M, Shifa T A, Zhan X Y, Lou X D, Xia F, He J. Earth abundant materials beyond transition metal dichalcogenides: A focus on electrocatalyzing hydrogen evolution reaction[J]. Nano Energy, 2019, 58: 244-276. |
| [34] | Haverkort J W, Rajaei H. Voltage losses in zero-gap alkaline water electrolysis[J]. J. Power Sources, 2021, 497: 229864. |
| [35] | Liu L P, Wang J Y, Ren Z B, Wang F, Wang T, Guo H J. Ultrathin reinforced composite separator for alkaline water electrolysis: Comprehensive performance evaluation[J]. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy, 2023, 48(62): 23885-23893. |
| [36] | Olivier P, Bourasseau C, Bouamama P B. Low-temperature electrolysis system modelling: A review[J]. Renew. Sust. Energ. Rev., 2017, 78: 280-300. |
| [37] | Hammoudi M, Henao C, Agbossou K, Dubé Y, Doumbia M L. New multi-physics approach for modelling and design of alkaline electrolyzers[J]. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy, 2012, 37(19): 13895-13913. |
| [38] | Huang D J, Xiong B Y, Fang J K, Hu K W, Zhong Z Y, Ying Y H, Ai X M, Chen Z. A multiphysics model of the compactly-assembled industrial alkaline water electrolysis cell[J]. Appl. Energy, 2022, 314: 118987. |
| [39] | Hu S, Guo B, Ding S L, Yang F Y, Dang J, Liu B, Gu J J, Ma J G, Ouyang M G. A comprehensive review of alkaline water electrolysis mathematical modeling[J]. Appl. Energy, 2022, 327: 120099. |
| [40] | Zhang Z Z, Jin L M, Deng L A, Li W B, Liu M, Geng Z, Zhang C M. Three-dimensional simulation of two-phase flow distribution in spherical concave-convex shaped flow field for alkaline water electrolyzer[J]. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy, 2023, 48(86): 33401-33410. |
| [41] | Wang T, Wang J Y, Wang P J, Wang F, Liu L P, Guo H J. Non-uniform liquid flow distribution in an alkaline water electrolyzer with concave-convex bipolar plate (CCBP): A numerical study[J]. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy, 2023, 48(33): 12200-12214. |
| [42] | Wang T, Wang J Y, Wang P J, Ren Z B, Yan X P, Wang W, Guo W Q. Plate structure design guideline for commercial alkaline water electrolyzers (AWEs) with improved liquid flow uniformity: Multi-scale quantitative criteria and experimental validation[J]. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy, 2023, 49: 907-924. |
| [43] | Zhao P C, Wang J G, He W, Sun L M, Li Y. Alkaline zero gap bipolar water electrolyzer for hydrogen production with independent fluid path[J]. Energy Rep., 2023, 9: 352-360. |
| [44] | Zhao P C, Wang J G, Sun L M, Li Y, Xia H T, He W. Optimal electrode configuration and system design of compactly-assembled industrial alkaline water electrolyzer[J]. Energy Conv. Manag., 2024, 299: 117875. |
| [45] | Zouhri K, Lee S Y. Evaluation and optimization of the alkaline water electrolysis ohmic polarization: Exergy study[J]. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy, 2016, 41(18): 7253-7263. |
| [46] | Ding S L, Guo B, Hu S, Gu J J, Yang F Y, Li Y Y, Dang J, Liu B, Ma J G. Analysis of the effect of characteristic parameters and operating conditions on exergy efficiency of alkaline water electrolyzer[J]. J. Power Sources, 2022, 537: 231532. |
| [47] | Cha Q X. Introduction to the dynamics of electrode processes[M]. Bejing: Science Press, 2002. |
| [48] | Guo Y J. Structural design and performance optimization ofan alkaline water hydrogen electrolyzer[D]. Beijing University of Chemical Technology, 2020. |
| [49] | Le Bideau D, Mandin P, Benbouzid M, Kim M, Sellier M, Ganci F, Inguanta R. Eulerian two-fluid model of alkaline water electrolysis for hydrogen production[J]. Energies, 2020, 13(13): 3394. |
| [50] | Cao X P, Zhao N, Zhang S R, Zhou L L, Hu Y Q, Yun J. Investigation of the hydrogen bubble effect on the overpotential in an alkaline water electrolyzer[J]. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy, 2024, 49: 47-57. |
| [51] | Li D. Principles of Electrochemistry[M]. Beijing: Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics Press, 2008. |
| [52] | Gao L Y, Yang L, Wang C H, Dan G X, Huo X Y, Zhang M F, Li W, Zhang J L. Three-dimensional two-phase CFD simulation of alkaline electrolyzers[J]. J. Electrochem., 2023, 29(9): 25-40. |
| [53] | Buttler A, Spliethoff H. Current status of water electrolysis for energy storage, grid balancing and sector coupling via power-to-gas and power-to-liquids: A review[J]. Renew. Sust. Energ. Rev., 2018, 82: 2440-2454. |
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |