

基于电化学阻抗谱的致病菌检测传感器的研究进展
收稿日期: 2022-10-31
修回日期: 2023-01-05
录用日期: 2023-05-17
网络出版日期: 2023-05-24
Recent Advances in Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy-Based Pathogenic Bacteria Sensing
Received date: 2022-10-31
Revised date: 2023-01-05
Accepted date: 2023-05-17
Online published: 2023-05-24
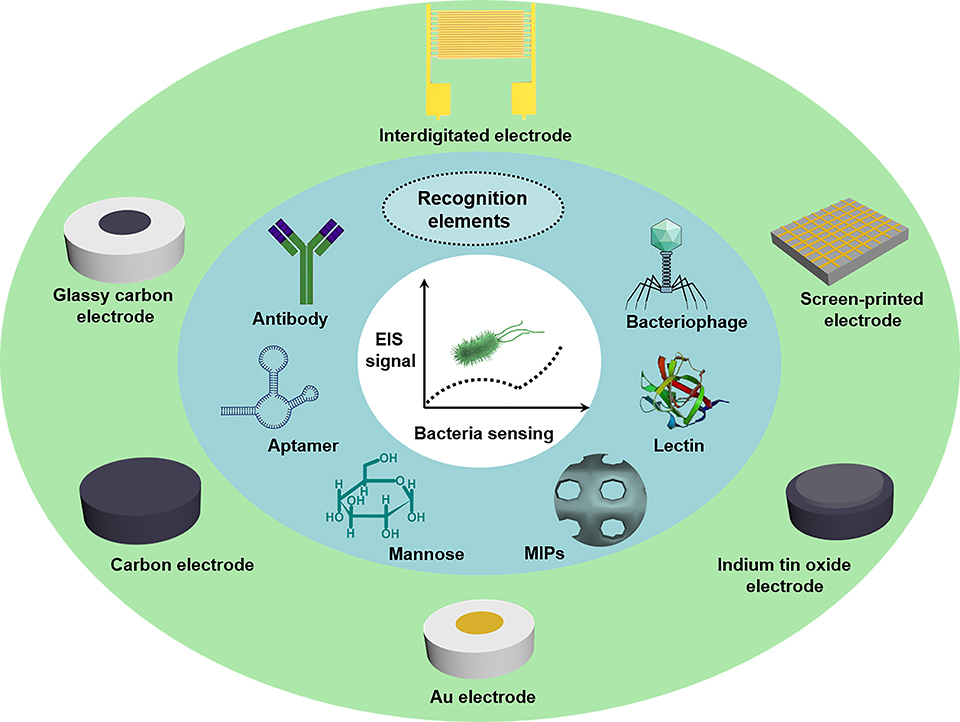
几千年来,致病菌对人类健康构成了巨大威胁。实现致病菌的实时监测可有效阻止致病菌的传播,从而降低对人类健康的威胁。迄今为止,已有电化学、光学、压电和量热等多种技术用于细菌的检测。其中,基于电化学阻抗技术的传感器由于其成本低、读取时间短、重现性好、设备便携等优点,在实时细菌检测中展现出了巨大的应用潜力。本文主要综述了近三年来电化学阻抗技术在细菌传感中的典型应用。众所周知,电极材料在基于电化学阻抗的传感器的构建中发挥着极其重要的作用,因为细菌生物识别元件的固定化,以及所制备的传感器的灵敏度、经济性和便携性都主要取决于电极材料。因此,为了向新入行的研究人员提供基于不同电极材料制备电化学阻抗传感器清晰的制备过程,我们尝试根据不同的电极平台对基于电化学阻抗技术的传感器进行分类。此外,还讨论了目前的难点、未来的应用方向和前景。我们希望通过本文的综述,能够为刚进入该领域的研究人员开展基于电化学阻抗技术,制备快速、灵敏、准确地检测多种致病菌的传感器研究提供指导。
陈涛 , 许元红 , 李景虹 . 基于电化学阻抗谱的致病菌检测传感器的研究进展[J]. 电化学, 2023 , 29(6) : 2218002 . DOI: 10.13208/j.electrochem.2218002
Pathogenic bacteria have been throwing great threat on human health for thousands of years. Their real-time monitoring is in urgent need as it could effectively halt the spread of pathogenic bacteria and thus reducing the risk to human health. Up till now, diverse technologies such as electrochemistry, optics, piezoelectricity and calorimetry have been developed for bacteria sensing. Therein, electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS)-based sensors show great potential in point-of-care bacterial analysis because of their low-cost, short read-out time, good reproducibility, and portable equipment construction. In this review, we will primarily summarize the typical applications of electrochemical impedance technology in bacteria sensing based on different electrodes in the last three years. As we know, the electrode materials play an extremely important role in the construction of EIS-based sensors because not only the immobilization of bio-recognition elements for bacteria, but also the sensitivity, economical efficiency and portability of the as-prepared sensors are mainly determined by the electrode materials. Therefore, in order to provide new researchers a clear preparation process for EIS-based sensors fabricated with different electrodes, we try to classify the EIS-based sensors according to the different electrode platforms. Moreover, present difficulties, future directions and perspectives for their applications are also discussed. It can provide guidance in future study of novel EIS-based sensors for rapid, sensitive and accurate sensing of diverse pathogenic bacteria.

/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |