

铜互连电镀中有机添加剂的合成与分析
收稿日期: 2022-08-11
修回日期: 2022-10-17
录用日期: 2022-12-07
网络出版日期: 2023-01-07
Synthesis and Evaluation of Organic Additives for Copper Electroplating of Interconnects
Received date: 2022-08-11
Revised date: 2022-10-17
Accepted date: 2022-12-07
Online published: 2023-01-07
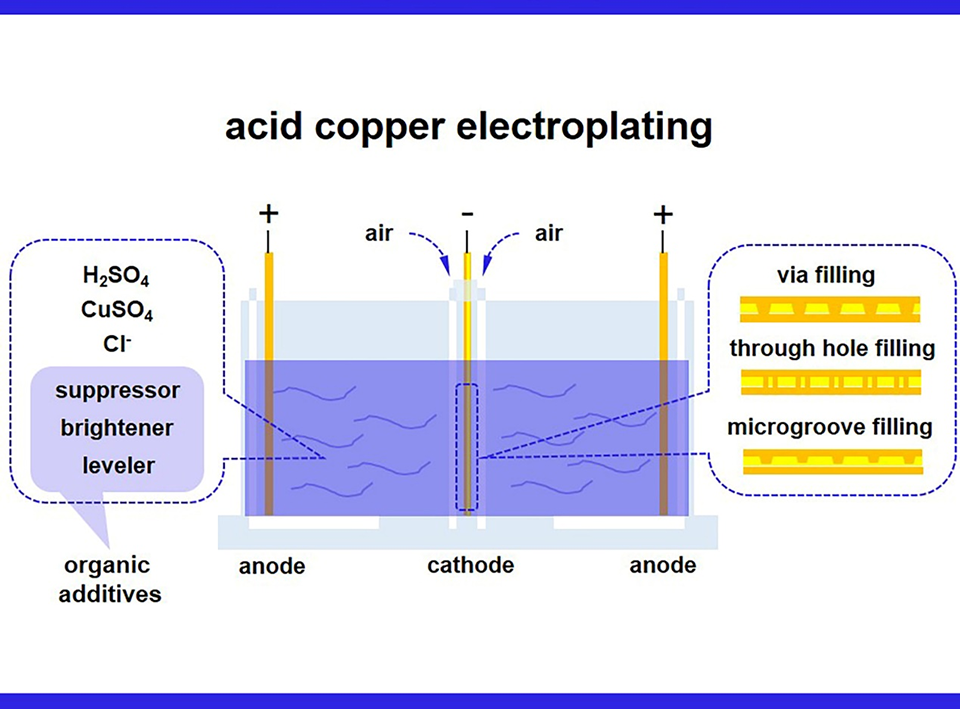
铜互连是保障电子设备的功能、性能、能效、可靠性以及制备良品率至关重要的一环。铜互连常通过在酸性镀铜液电镀铜实现,并广泛用于芯片、封装基材和印制电路板中。其中,有机添加剂在调控铜沉积完成沟槽填充、微孔填充以形成精密线路和实现层间互连方面起着决定性作用。添加剂主要由光亮剂、抑制剂和整平剂三组分组成,在恰当的浓度配比下,添加剂对于盲孔超级填充具有协同作用。目前,已报导的文献聚焦于代表性添加剂的超填充机理及其电化学行为,而对于添加剂的化学结构与制备方法鲜有深入研究。本文重点研究了各添加剂组分的制备工艺和快速电化学筛选方法,为电镀铜添加剂的未来发展提供理论指导。
翟悦晖 , 彭逸霄 , 洪延 , 陈苑明 , 周国云 , 何为 , 王朋举 , 陈先明 , 王翀 . 铜互连电镀中有机添加剂的合成与分析[J]. 电化学, 2023 , 29(8) : 2208111 . DOI: 10.13208/j.electrochem.2208111
Copper interconnects are essential to the functionality, performance, power efficiency, reliability, and fabrication yield of electronic devices. They are widely found in chips, packaging substrates and printed circuit boards, and are often produced by copper electroplating in an acidic aqueous solution. Organic additives play a decisive role in regulating copper deposition to fill microgrooves, and micro-vias to form fine lines and interlayer interconnects. Generally, an additive package consists of three components (brightener, suppressor, and leveler), which have a synergistic effect of super-filling on electroplating copper when the concentration ratio is appropriate. Many works of literature have discussed the mechanism of super filling and the electrochemical behavior of representative additive molecules; however, few articles discussed the chemical structure and preparation of the additives. Herein, this paper focuses on the preparation method and the rapid electrochemical screening of each additive component to provide an idea for the future development of copper electroplating additives.

Key words: acid copper electroplating; copper interconnect; suppressor; brightener; leveler
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |