

胺类添加剂对NCM811‖SiC电池热失控抑制效果研究
收稿日期: 2022-11-04
修回日期: 2022-12-04
录用日期: 2023-01-06
网络出版日期: 2023-01-06
Effect of Amine Additives on Thermal Runaway Inhibition of SiC||NCM811 Batteries
Received date: 2022-11-04
Revised date: 2022-12-04
Accepted date: 2023-01-06
Online published: 2023-01-06
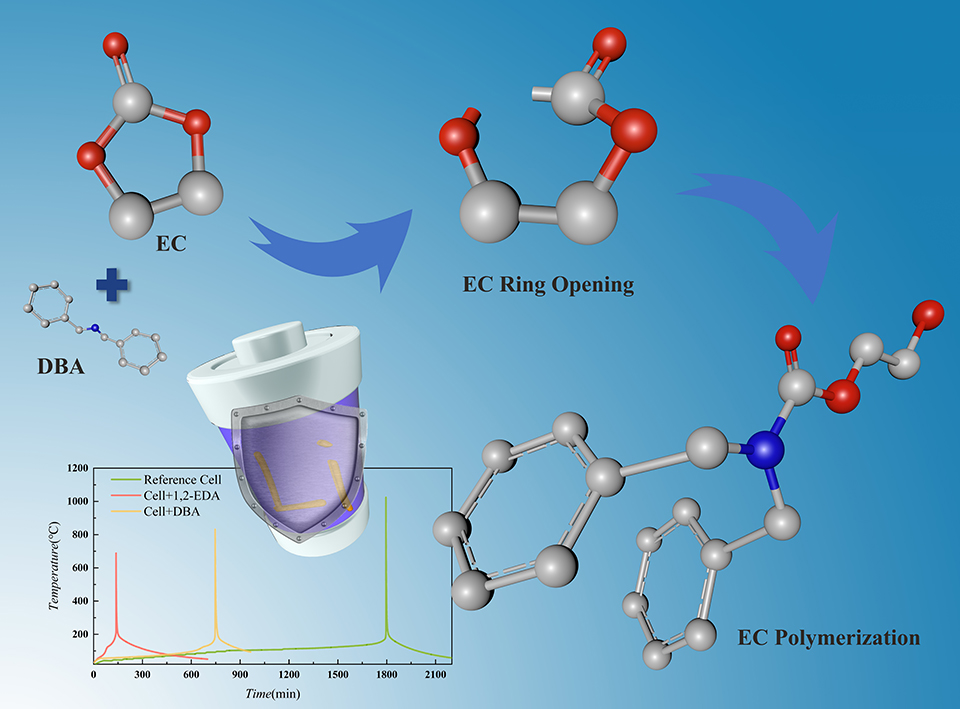
高镍三元电池的高能量密度是取代化石能源,推动清洁能源发展的核心优势,同时也是导致电池严重安全隐患的根本原因。初级胺类与次级胺类能与常见的含碳酸乙烯酯电解液发生开环聚合,从而形成正负极间隔离层,提高电池热安全性。本文基于胺类和电池组分间的化学反应,在电池材料层面和单体层面对电池的安全性展开了研究。在材料层面,利用差示扫描量热法测试锂离子电池中有无胺类添加剂对不同组分间的热稳定性影响。在单体层面,使用绝热加速量热仪对有无添加剂全电池的安全性进行测试,提取热失控特征温度。加入胺类添加剂后电池组分间部分化学反应被提前,同时总放热量明显减少,最大温升速率下降,电池热失控得到有效抑制。
侯博文 , 何龙 , 冯旭宁 , 张伟峰 , 王莉 , 何向明 . 胺类添加剂对NCM811‖SiC电池热失控抑制效果研究[J]. 电化学, 2023 , 29(8) : 2211141 . DOI: 10.13208/j.electrochem.2211141
The high energy density of NCM batteries with high nickel content is a key advantage in replacing fossil fuels and promoting clean energy development, at the same time, is also a fundamental cause of serious safety hazards in batteries. Primary and secondary amines can lead to ring-opening polymerization of common ethylene carbonate electrolytes, resulting in an isolation layer between the cathode and the anode, and improving the thermal safety of the battery. In this work, the safety of batteries is considered both at the material level and at the cell level, based on the chemical reactions between amines and the battery components. At the material level, the effect of the presence or absence of amine additives on the thermal stability of the different components of the lithium-ion battery was tested by differential scanning calorimetry. At the cell level, the safety of the whole battery with and without additives was tested by using accelerating rate calorimeter to extract thermal runaway (TR) characteristic temperatures. The addition of the amine resulted in an earlier onset of some of the chemical reactions between the battery components, as well as a significant reduction in total heat release and a decrease in the maximum temperature rise rate, such that TR, was effectively suppressed.

/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |