

电化学扫描隧道显微术:以Cu在Au(111)表面初始阶段电沉积为例
收稿日期: 2022-07-13
修回日期: 2022-09-07
录用日期: 2022-09-10
网络出版日期: 2022-09-11
基金资助
国家自然科学基金项目(22072123)
Electrochemical Scanning Tunneling Microscopy: Taking the Initial Stage of Cu Electrodeposition on Au(111) as an Example
Received date: 2022-07-13
Revised date: 2022-09-07
Accepted date: 2022-09-10
Online published: 2022-09-11
谭卓 , 李凯旋 , 毛秉伟 , 颜佳伟 . 电化学扫描隧道显微术:以Cu在Au(111)表面初始阶段电沉积为例[J]. 电化学, 2023 , 29(7) : 2216003 . DOI: 10.13208/j.electrochem.2216003
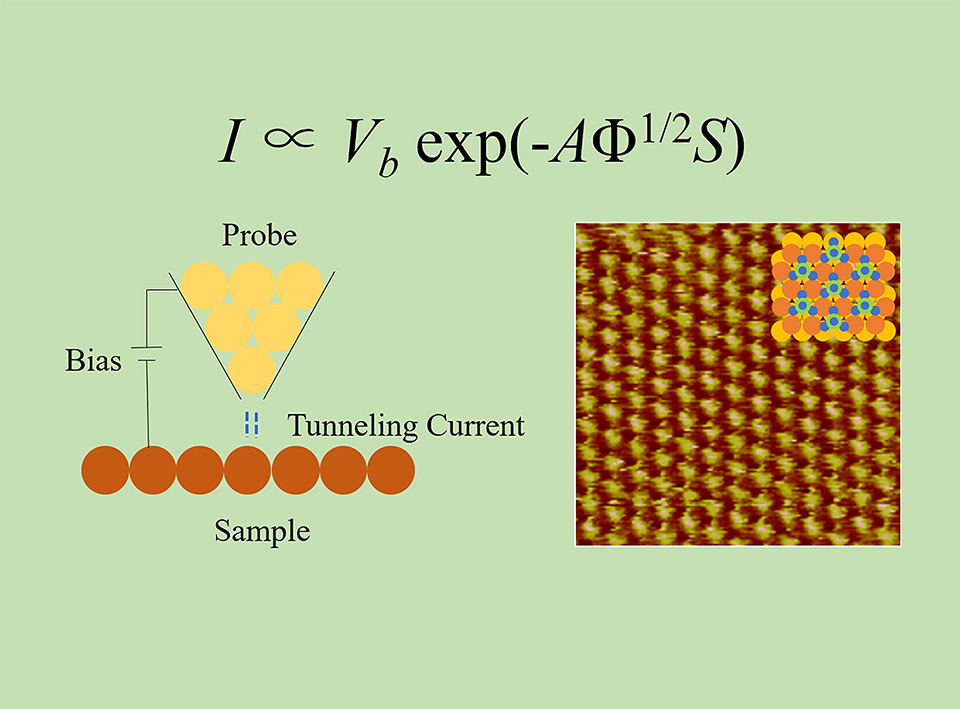
Electrochemical scanning tunneling microscopy (ECSTM) plays an important role in the field of electrochemistry, which can obtain potential-dependent structural information of electrode surface with high spatial resolution and observe some reaction processes in electrolyte solutions, and provide a powerful way to understand the interfacial structure and electrode processes from the perspective of high spatial resolution. In this article, the study of electrodeposition of Cu on Au (111) by ECSTM is taken as an example to introduce the experimental methods required for ECSTM and share our experience with other electrochemical groups. Firstly, the working principle of STM is introduced so that readers can understand the imaging principle of STM. Secondly, we describe the process in detail and the points for attention during ECSTM experiments, which include the cleanings of the electrochemical cell and O-ring, the preparation and encapsulation of the ECSTM tip, the preparation and cleaning of the working electrode, and the selections of the counter electrode and reference electrode. Thirdly, the ECSTM study on the initial stage of Cu electrodeposition on Au(111) has been taken to demonstrate the experimental procedure of ECSTM, and shown its ability to obtain image with high spatial resolution. We have analyzed the two interfacial structures obtained by ECSTM at two different potential regions according to the cyclic voltammetric curve of Cu UPD on Au (111) electrode. The high-resolution atomic image obtained at a relatively positive potential is assigned to the image of Au atoms. Further, it has been demonstrated that the ($\sqrt{3}$×$\sqrt{3}$)R30° structure can be observed after the completion of the submonolayer of Cu on Au(111) in the sulfuric acid solution. However, the ($\sqrt{3}$×$\sqrt{3}$)R30° structure obtained between the two pairs of current peaks of cyclic voltammetric curve should be assigned to the adsorption of sulfate anions, which occupy the centers of honeycomb lattice formed by Cu adatoms. The ECSTM images demonstrate the ability of this technique to achieve high-resolution imaging in electrochemical environments. The analysis shows that caution should be taken when analyzing ECSTM images due to the lack of chemical recognition ability and that it is important to combine ECSTM with other experimental techniques or theoretical methods to analyze the obtained data.
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |