

化学镀钴和超级化学镀填充的研究进展
Research Progress in Electroless Cobalt Plating and the Bottom-up Filling of Electroless Plating
Received date: 2022-04-02
Revised date: 2022-05-07
Online published: 2022-05-20
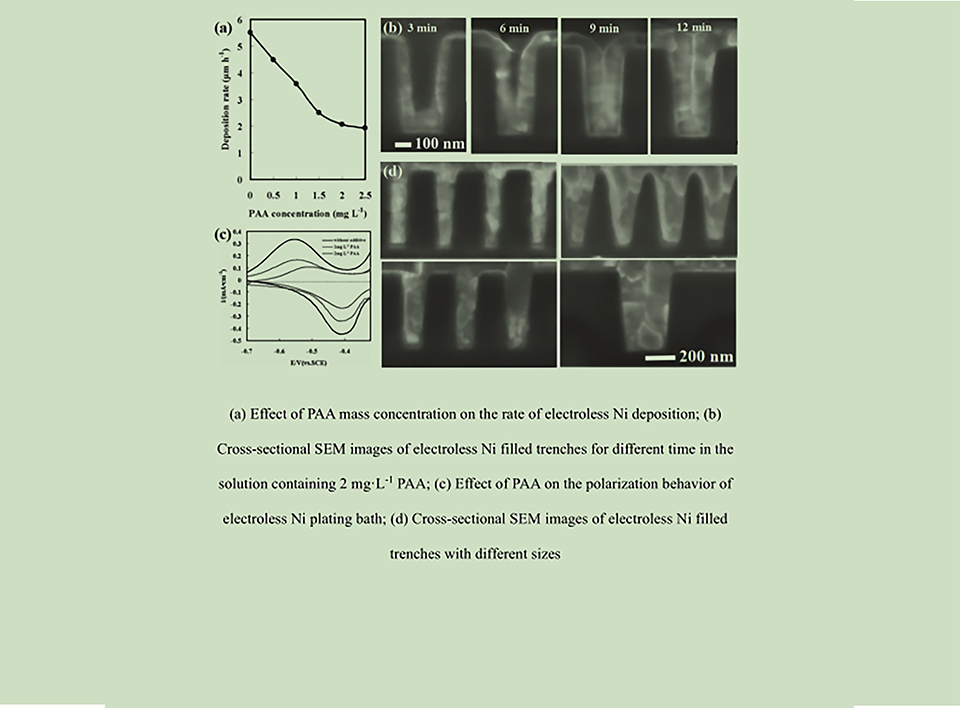
随着半导体集成度的不断提高,铜互连线的电阻率迅速提高。当互连线宽度接近7 nm时,铜互连线的电阻率与钴接近。IBM和美国半导体公司(ASE)已经使用金属钴取代铜作为下一代互连线材料。然而,钴种子层的形成和超级电镀钴填充7 nm微孔的技术工艺仍是一个很大的挑战。化学镀是在绝缘体表面形成金属种子层的一种非常简单的方法, 通过超级化学镀填充方式, 直径为几纳米的盲孔可以无空洞和无缝隙的方式完全填充。本文综述了化学镀钴的研究进展,并分析了还原剂种类对化学镀钴沉积速率和镀膜质量的影响。同时, 在长期从事超级化学填充研究的基础上, 作者提出了通过超级化学镀钴技术填充7 nm以及一下微盲孔的钴互连线工艺。
沈钰 , 李冰冰 , 马艺 , 王增林 . 化学镀钴和超级化学镀填充的研究进展[J]. 电化学, 2022 , 28(7) : 2213002 . DOI: 10.13208/j.electrochem.2213002
With the continuous improvement of semiconductor integration, the resistivity of copper interconnect lines increases rapidly. When the width of the interconnect line is close to 7 nm, the resistivity of copper becomes the same as that of cobalt. International Business Machines Corporation (IBM) and Advanced Semiconductor Incorporation (ASI) have used cobalt to replace copper as a next-generation interconnect material. However, the fabrication of the cobalt seed layer and the super filling of electroplating cobalt for the 7 nm via-holes have been still the large challenge. Electroless plating is a very simple method to form a seed layer on the surface of an insulator. By the bottom-up filling of electroless plating, via-holes with several nanometers could be filled completely. In this paper, the research progress in electroless cobalt plating is reviewed, and the effects of the reductant species on the deposition rate and the film quality of electroless cobalt plating are analyzed. Meanwhile, based on long-term and a lot of studies, a bottom-up filling of electroless cobalt plating for 7 nm via-hole in semiconductor cobalt interconnects is proposed.

/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |