

尖晶石钴氧化物的晶面调控与析氧活性研究
收稿日期: 2021-10-25
修回日期: 2021-11-30
网络出版日期: 2022-01-02
版权
Facet Dependent Oxygen Evolution Activity of Spinel Cobalt Oxides
Received date: 2021-10-25
Revised date: 2021-11-30
Online published: 2022-01-02
Copyright
张丽桦 , 揣宏媛 , 刘海 , 范群 , 况思宇 , 张生 , 马新宾 . 尖晶石钴氧化物的晶面调控与析氧活性研究[J]. 电化学, 2022 , 28(2) : 2108481 . DOI: 10.13208/j.electrochem.210848
Water splitting is a promising technology to produce clean hydrogen if powered by renewable energies, where oxygen evolution is the rate determining step at an anode. Here we adjust the different crystal planes of the cobalt oxides catalyst to expose more effective active sites through a hydrothermal process, so as to improve the reaction activity for oxygen evolution. The samples were well characterized by TEM, SEM and XRD. Among the three synthetic crystal planes (100), (111) and (110) of spinel cobalt oxides, the (100) crystal plane has the highest intrinsic activity. Combining in-situ infrared and DFT calculations, we observed that the oxygen evolution reaction reached the lowest energy barrier on the (100) plane of the cobalt oxide crystal. Further XPS analysis showed that the highest Co3+/Co2+ ratio was observed on the surface of the nanocube samples, indicating that Co3+ is a more active site for oxygen evolution catalytic activity.
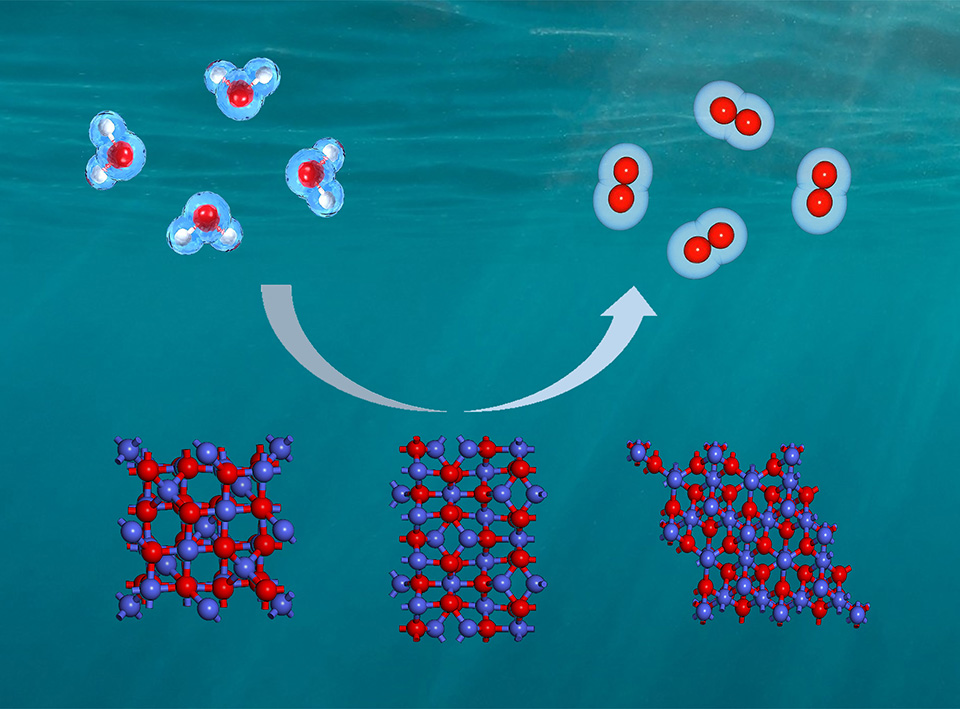
Key words: water splitting; oxygen evolution; spinel cobalt oxide; facet dependent; nanocubes
| [1] | Jamesh M I, Sun X M. Recent progress on earth abundant electrocatalysts for oxygen evolution reaction (OER) in alkaline medium to achieve efficient water splitting - A review[J]. J. Power Sources, 2018, 400:31-68. |
| [2] | Jiang H, Gu J X, Zheng X S, Liu M, Qiu X Q, Wang L B, Li W Z, Chen Z F, Ji X B, Li J. Defect-rich and ultrathin N doped carbon nanosheets as advanced trifunctional metal-free electrocatalysts for the ORR, OER and HER[J]. Energy Environ. Sci., 2019, 12(1):322-333. |
| [3] | Jahan M, Liu Z L, Loh K P. A Graphene oxide and coppercentered metal organic framework composite as a tri-functional catalyst for HER, OER, and ORR[J]. Adv. Funct. Mater., 2013, 23(43):5363-5372. |
| [4] | Zhang L H, Fan Q, Li K, Zhang S, Ma X B. First-row transition metal oxide oxygen evolution electrocatalysts: regulation strategies and mechanistic understandings[J]. Sustain. Energy Fuels, 2020, 4(11):5417-5432. |
| [5] | Jamesh M I, Harb M. Tuning the electronic structure of the earth-abundant electrocatalysts for oxygen evolution reaction (OER) to achieve efficient alkaline water splitting - A review[J]. J. Energy Chem., 2021, 56:299-342. |
| [6] | Zhang S, Fan Q, Xia R, Meyer T J. CO2 reduction: from homogeneous to heterogeneous electrocatalysis[J]. Accounts Chem. Res., 2020, 53(1):255-264. |
| [7] | Liu H, Su Y Q, Kuang S Y, Hensen E J M, Zhang S, Ma X B. Highly efficient CO2 electrolysis within a wide operation window using octahedral tin oxide single crystals[J]. J. Mater. Chem. A, 2021, 9(12):7848-7856. |
| [8] | Karmakar A, Karthick K, Sankar S S, Kumaravel S, Madhu R, Kundu S. A vast exploration of improvising synthetic strategies for enhancing the OER kinetics of LDH structures: a review[J]. J. Mater. Chem. A, 2021, 9(3):1314-1352. |
| [9] | Duan Y, Sun S N, Sun Y M, Xi S B, Chi X, Zhang Q H, Ren X, Wang J X, Ong S J H, Du Y H, Gu L, Grimaud A, Xu Z C J. Mastering surface reconstruction of metastable spinel oxides for better water oxidation[J]. Adv. Mater., 2019, 31(12):1807898. |
| [10] | Sun Y M, Liao H B, Wang J R, Chen B, Sun S N, Ong S J H, Xi S B, Diao C Z, Du Y H, Wang J O, Breese M B H, Li S Z, Zhang H, Xu Z C J. Author Correction: Covalency competition dominates the water oxidation structure-activity relationship on spinel oxides[J]. Nat. Catal., 2020, 3(11):959. |
| [11] | Reier T, Oezaslan M, Strasser P. Electrocatalytic oxygen evolution reaction (OER) on Ru, Ir, and Pt Catalysts: A comparative study of nanoparticles and bulk materials[J]. ACS Catal., 2012, 2(8):1765-1772. |
| [12] | Acedera R A E, Gupta G, Mamlouk M, Balela M D L. Solution combustion synjournal of porous Co3O4 nanoparticles as oxygen evolution reaction (OER) electrocatalysts in alkaline medium[J]. J. Alloy. Compd., 2020, 836:154919. |
| [13] | Wang C X, Shi P H, Cai X D, Xu Q J, Zhou X J, Zhou X L, Yang D, Fan J C, Min Y L, Ge H H, Yao W F. Synergistic effect of Co3O4 nanoparticles and graphene as catalysts for peroxymonosulfate-based orange II degradation with high oxidant utilization efficiency[J]. J. Phys. Chem. C, 2016, 120(1):336-344. |
| [14] | Xiao Z, Huang Y C, Dong C L, Xie C, Liu Z J, Du S Q, Chen W, Yan D F, Tao L, Shu Z W, Zhang G H, Duan H G, Wang Y Y, Zou Y Q, Chen R, Wang S Y. Operando identification of the dynamic behavior of oxygen vacancyrich Co3O4 for oxygen evolution reaction[J]. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2020, 142(28):12087-12095. |
| [15] | Peng Y, Hajiyani H, Pentcheva R. Influence of Fe and Ni Doping on the OER Performance at the Co3O4 (001) Surface: Insights from DFT+ U Calculations[J]. ACS Catal., 2021, 11(9):5601-5613. |
| [16] | Xu L, Jiang Q Q, Xiao Z H, Li X Y, Huo J, Wang S Y, Dai L M. Plasma-engraved Co3O4 nanosheets with oxygen vacancies and high surface area for the oxygen evolution reaction[J]. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2016, 128(17):5363-5367. |
| [17] | Zhang Y X, Ding F, Deng C, Zhen S Y, Li X Y, Xue Y F, Yan Y M, Sun K N. Crystal plane-dependent electrocatalytic activity of Co3O4 toward oxygen evolution reaction[J]. Catal. Commun., 2015, 67:78-82. |
| [18] | Liu L, Jiang Z Q, Fang L, Xu H T, Zhang H J, Gu X, Wang Y. Probing the crystal plane effect of Co3O4 for enhanced electrocatalytic performance toward efficient overall water splitting[J]. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter., 2017, 9(33):27736-27744. |
| [19] | Liu Q F, Chen Z P, Yan Z, Wang Y, Wang E D, Wang S, Wang S D, Sun G Q. Crystal-plane-dependent activity of spinel Co3O4 towards water splitting and the oxygen reduction reaction[J]. ChemElectroChem, 2018, 5(7):1080-1086. |
| [20] | Zhu K Y, Zhu X F, Yang W S. Application of in situ techniques for the characterization of NiFe-based oxygen evolution reaction (OER) electrocatalysts[J]. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2019, 58(5):1252-1265. |
| [21] | Xiao X L, Liu X F, Zhao H, Chen D F, Liu F Z, Xiang J H, Hu Z B, Li Y D. Facile shape control of Co3O4 and the effect of the crystal plane on electrochemical performance[J]. Adv. Mater., 2012, 24(42):5762-5766. |
| [22] | Zhang J J, Wang H H, Zhao T J, Zhang K X, Wei X, Li X H, Hirano S I, Chen J S. Oxygen vacancy engineering of Co3O4 nanocrystals through coupling with metal support for water oxidation[J]. ChemSusChem, 2017, 10(14):2875-2879. |
| [23] | He D, Song X Y, Li W Q, Tang C Y, Liu J C, Ke Z J, Jiang C Z, Xiao X H. Active electron density modulation of Co3O4-based catalysts enhances their oxygen evolution performance[J]. Angew. Chem. In.t Ed., 2020, 132(17):6996-7002. |
| [24] | Kumar K, Canaff C, Rousseau J, Arrii-Clacens S, Napporn T W, Habrioux A, Kokoh K B. Effect of the oxide-carbon heterointerface on the activity of Co3O4/NRGO nano-composites toward ORR and OER[J]. J. Phys. Chem. C, 2016, 120(15):7949-7958. |
| [25] | Tang D, Ma Y, Liu Y, Wang K K, Liu Z, Li W Z, Li J. Amorphous three-dimensional porous Co3O4 nanowire network toward superior OER catalysis by lithium-induced[J]. J. Alloy Compd., 2021, 893:162287. |
| [26] | Zhou X M, Xia Z M, Tian Z M, Ma Y Y, Qu Y Q. Ultrathin porous Co3O4 nanoplates as highly efficient oxygen evolution catalysts[J]. J. Mater. Chem. A, 2015, 3(15):8107-8114. |
| [27] | McCrory C C L, Jung S, Peters J C, Jaramillo T F. Bench-marking heterogeneous electrocatalysts for the oxygen evolution reaction[J]. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2013, 135(45):16977-16987. |
| [28] | Ma T Y, Dai S, Jaroniec M, Qiao S Z. Metal-organic framework derived hybrid Co3O4-carbon porous nanowire arrays as reversible oxygen evolution electrodes[J]. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2014, 136(39):13925-13931. |
| [29] | Song K, Cho E, Kang Y M. Morphology and active-site engineering for stable round-trip efficiency Li-O2 batteries: A search for the most active catalytic site in Co3O4[J]. ACS Catal., 2015, 5(9):5116-5122. |
| [30] | Yao Y C, Hu S L, Chen W X, Huang Z Q, Wei W C, Yao T, Liu R R, Zang K T, Wang X Q, Wu G, Yuan W J, Yuan T W, Zhu B Q, Liu W, Li Z J, He D S, Xue Z G, Wang Y, Zheng X S, Dong J C, Chang C R, Chen Y X, Hong X, Luo J, Wei S Q, Li W X, Strasser P, Wu Y E, Li Y D. Engineering the electronic structure of single atom Ru sites via compressive strain boosts acidic water oxidation electrocatalysis[J]. Nat. Catal., 2019, 2(4):304-313. |
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |