

玻碳电极界面的阻抗谱数学表达及定量分析
收稿日期: 2020-08-24
修回日期: 2020-10-16
网络出版日期: 2020-11-10
基金资助
国家自然科学基金重点项目(21431001);广西自然科学基金(2020GXNSFBA297001)
Mathematical Expression and Quantitative Analysis of Impedance Spectrum on the Interface of Glassy Carbon Electrode
Received date: 2020-08-24
Revised date: 2020-10-16
Online published: 2020-11-10
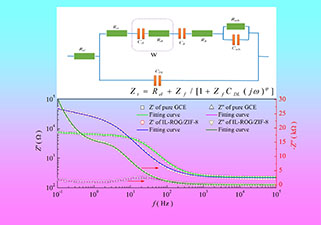
玻碳电极(GCE)是各类电化学传感器常用的基础电极,其界面特征直接影响检测性能。本文详细考察了电极体系的电化学过程,针对GCE传感界面,探讨了一个等效电路中电解质电阻、电荷输运电阻、扩散阻抗、电化学(氧化/还原)反应阻抗、表面吸附阻抗和双电层电容等电学元件的物理意义,并给出了对应的数学模型。通过改变模型中5个参数值,模拟了不同状态下的阻抗谱,分析了电极系统各参数对GCE阻抗谱的贡献规律。最后,采用该数学模型对裸GCE和修饰GCE在铁氰化钾溶液中的阻抗谱进行分析,拟合结果与实验数据吻合度高;基于拟合获得参数,定量对比分析了修饰前后电极表面的特征变化。
程蕾 , 闫普选 , 樊友军 , 邹华红 , 梁宏 . 玻碳电极界面的阻抗谱数学表达及定量分析[J]. 电化学, 2021 , 27(5) : 518 -528 . DOI: 10.13208/j.electrochem.200821
Glassy carbon electrode (GCE) is a common basic electrode for various electrochemical sensors, and the detection properties are determined by its interfacial characteristics. In this paper, we established an equivalent circuit including electrolyte resistance (Rel), charge transport resistance (Rct), diffusion impedance (Rdi, Cdi), electrochemical (oxidation/reduction) reaction impedance (RR, CR), surface adsorption impedance (Rads , Cads), double-layer capacitance (CDL), and derived the mathematical expression for the equivalent circuit. The Rel and CDL are contributed by inactive ions in electrolyte to produce non-faradaic impedance, while the Rct and RR are contributed by the active ions of redox reaction in electrolyte to produce faradaic impedance. The Rct directly corresponds to the electrode potential (E) of the reaction, which represents the difficulty of electrode reaction. When the potential E is the only state variable in the impedance spectrum of electrode reaction, that is, there is only one time constant in the impedance spectrum, the Rct can represent the whole Faraday impedance of the system. However, when the electrode reaction is also affected by other variables such as diffusion, surface film or surface adsorption ion coverage, the Faraday impedance of the system also includes the impedance produced by the diffusion impedance and the changes of the surface film (RR, CR) and the coverage of the surface absorbed ions caused by electrochemical reaction (Rads, Cads). The impedance spectrum of the electrode system in different states were simulated by changing the five parameters of the mathematical expression. The contribution of different factors to the impedance spectrum of GCE was revealed. Finally, the impedance spectra of bare/modified GCE in potassium ferricyanide solution were analyzed by the mathematical model. The fitting results are in good agreement with the experimental data. Based on the parameters obtained by fitting, the changes of the electrode surface characteristic before and after modifications were quantitatively compared and analyzed. The charge transport resistance increases from 5827.8 Ω to 25104.3 Ω, and the diffusion conductance of Fe3+/Fe2+ ions on the electrode surface also increases by an order of magnitude. However, there is no significant difference with the double-layer capacitance and the frequency dispersion coefficient. The surface of the modified electrode remains electrically neutral. The aggregation state and oxidation-reduction mechanism of Fe3+/Fe2+ on the electrode surface are the same as those on the bare GCE surface.

/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |