

液态金属电极的电化学储能应用
收稿日期: 2020-07-16
修回日期: 2020-08-07
网络出版日期: 2020-08-20
基金资助
国家重点研发计划(2018YFB0905600);国家自然科学基金项目(U1766216);国家自然科学基金项目(51774148);国家自然科学基金项目(51804128)
Liquid Metal Electrodes for Electrochemical Energy Storage Technologies
Received date: 2020-07-16
Revised date: 2020-08-07
Online published: 2020-08-20
李浩秒 , 周浩 , 王康丽 , 蒋凯 . 液态金属电极的电化学储能应用[J]. 电化学, 2020 , 26(5) : 663 -682 . DOI: 10.13208/j.electrochem.200652
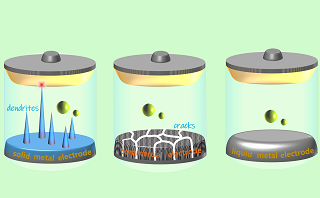
Electrochemical energy storage technologies (ESTs) with low cost, long lifespan and high safety are of great importance for efficient integration of renewable energy into the grid. Liquid metal electrodes (LMEs) possessing the merits of high electronic conductivity, easy manufacture and amorphous structure is of great application value in the field of energy storage batteries. During charge-discharge processing, the LMEs could avoid the issues of structural deformation and dendrite growth in solid metal electrodes, which could effectively extend the cycle life of the LME based batteries. Moreover, LME based batteries are easy to be scaled up and less expensive, which are well-positioned to satisfy the demands of grid-scale energy storage. In this paper, the state-of-the-art overview of LMEs in batteries including liquid metal batteries (LMBs), sodium-sulfur (Na||S) and ZEBRA (Na||NiCl2) batteries is presented. The materials systems, reaction mechanisms and novel designing in LMBs are emphatically discussed. Besides the LMEs, the developments of the molten salts electrolytes and solid state electrolytes, and the multi-field coupled flows inside LMBs are summarized. The challenges for the applications of LMEs in the batteries, such as high temperature sealing and corrosion, are discussed. Finally, the prospects of the application of LMEs in the field of the ESTs are also described.
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |