

四丁基六氟磷酸铵作为锂离子电池阻燃添加剂的研究
收稿日期: 2016-04-19
修回日期: 2016-05-26
网络出版日期: 2016-08-11
基金资助
本项目由国家973项目(No. 2015CB251102),国家自然科学基金项目(No. U1305246, No. 21321062)资助
Tetrabutylammonium Hexafluorophosphate as Flame Retardant Additive for Lithium Ion Batteries
Received date: 2016-04-19
Revised date: 2016-05-26
Online published: 2016-08-11
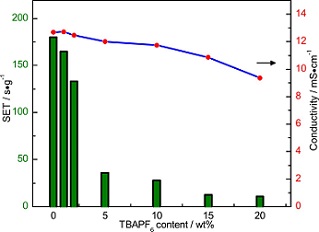
近年来关于锂离子电池造成的安全问题甚至事故的报道屡见不鲜,锂离子电池的安全问题已经成为人们关注的焦点. 我们用四丁基六氟磷酸铵(TBAPF6)作为锂离子电池电解液阻燃添加剂,研究发现添加了TBAPF6的电解液具有明显的阻燃效果,同时电解液电导率下降并不明显. LiCoO2/Graphite全电池在添加了TBAPF6的电解液中可逆容量会略有降低,但具有更优异的循环稳定性. 主要是由于TBAPF6添加量的增加会影响石墨电极的库伦效率,延长活化时间. 通过对LiCoO2/Graphite全电池绝热加速量热仪(ARC)测试,表明添加TBAPF6对电池的燃烧有明显的抑制作用. 在TBAPF6添加量至5%时,电池在300 oC内自放热速率不超过0.1oC/min,电池的安全性显著提高.
赵青 , 张倩 , 范镜敏 , 郑明森 , 董全峰 . 四丁基六氟磷酸铵作为锂离子电池阻燃添加剂的研究[J]. 电化学, 2017 , 23(4) : 435 -440 . DOI: 10.13208/j.electrochem.160419

/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |