

哌啶型离子液体混合电解液在Li/LiCoO2电池中的性能研究
收稿日期: 2016-02-18
修回日期: 2016-03-04
网络出版日期: 2016-03-14
基金资助
贵州省科学技术基金项目(黔科合J字[2012]2284) 和贵阳市科技计划项目(筑科合同{2012101}3-8号)资助
Performance of Piperidine Ionic Liquid Based Mixed Electrolyte in Li/LiCoO2 Cell
Received date: 2016-02-18
Revised date: 2016-03-04
Online published: 2016-03-14
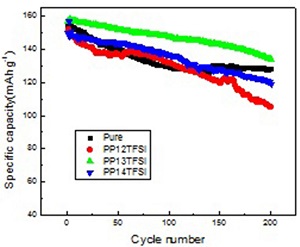
合成并考察了N-甲基-N-乙(丙,丁)基哌啶-二( 三氟甲基磺酰) 亚胺三种离子液体( PP12(3,4)TFSI )作为电解液添加剂的影响. 使用热分析和电化学技术研究了离子液体混合电解液的热稳定性和电化学性能.实验表明,哌啶型离子液体可以提高有机电解液的热稳定性,并且侧链的长短对 LiCoO2 电极的电化学性能有重要的影响.当以PP13TFSI配成的混合电解液,在3.0~4.35 V之间、电流密度为150 mA•g-1时, LiCoO2 电极的首次放电容量为156.6 mAh•g-1,200周循环后容量为133.9 mAh•g-1,容量保持率为85.5%,远远优于在传统有机电解液中的循环性能.
程琥 , 聂晓燕 , 申叶丹 . 哌啶型离子液体混合电解液在Li/LiCoO2电池中的性能研究[J]. 电化学, 2017 , 23(1) : 59 -63 . DOI: 10.13208/j.electrochem.160218
The N-methyl-N-ethyl (propyl, butyl) piperidinium bis (trifluo romethanesulfonyl) imide (PP12(3,4)TFSI) ionic liquids were prepared, and their influences on the performances of Li/LiCoO2 cells were investigated. The electrochemical performance and thermostability of ionic liquids based mixed electrolytes were characterized by electrochemical methods and thermogravimetric analysis. The results showed that the piperidine ionic liquids could improve the thermostability of organic electrolyte, and the size of their side chain had played an important role on the electrochemical performance of Li/LiCoO2 cell. The Li/LiCoO2 cell used the electrolyte mixed with PP13TFSI exhibited the best electrochemical performance among the three ionic liquids. The initial discharge capacity reached 156.9 mAh·g-1 at the rate of 150 mA·g-1 and 3.0 ~ 4.35 V. The discharge capacity upon 200 cycles was 133.9 mAh·g-1, and the capacity retention was 85.5%. The cycle performance was much better than that in conventional organic electrolytes.

Key words: ionic liquid; LiCoO2; electrolyte; electrochemical performance
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |