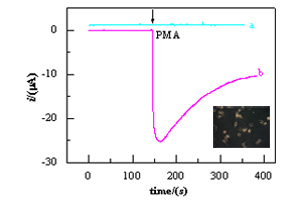
将辣根过氧化物酶(HRP)固定到凹凸棒石粘土(以下简称凹土,Attapulgite)表面,制得了HRP-凹土纳米复合物(HRP-Attapulgite),采用电化学阻抗、紫外光谱和红外光谱技术表征了HRP固定化过程. HRP-Attapulgite电化学性质测试表明,凹土能促进HRP的直接电子转移,其循环伏安曲线有一对良好的氧化还原峰,峰电位分别为Epc = -370 mV, Epa = -300 mV, 式量电位E0′ = -335 mV;凹土表面HRP的H2O2响应电流与浓度(0.3 ~ 75 μmol·L-1)呈线性关系. 该电极还可用于巨噬细胞中微量H2O2的测定.
The nanostructured attapulgite clay was employed as a support matrix for immobilizing horseradish peroxidase (HRP). FTIR and electrochemical methods demonstrated that HRP had been effectively assembled on attapulgite surface with the formation of HRP-attapulgite nanocomposites. The HRP-attapulgite hybrid was deposited on the glassy carbon (GC) electrode forming the HRP-attapulgite/GC electrode. Cyclic voltammetric results showed a pair of well-defined redox peaks, which were ascribed to direct electron transfer (DET) of HRP, with the formal potential E0′ = -335 mV (vs. SCE) in the phosphate buffer solution (PBS, pH 7.0). The dependence of E0′ on solution pH indicated that DET reaction of HRP was coupled with proton transfer. The developed electrode revealed a good electrocatalytical activity toward the reduction of H2O2. The electrocatalyic current was linear to the concentration of H2O2 in the concentration range of 0.3 to 75 μmol·L-1 with high sensitivity ((53 ± 2) μA·(mmol·L-1)-1·cm-2) and low detection limit ((0.10 ± 0.05) μmol·L-1). Moreover, the HRP-attapulgite/GC electrode was used to detect the level cellular H2O2 released from the Macrophages cells (RAW 264.7). Therefore, an electrochemical approach for detection of cellular H2O2 based on HRP-attapulgite hybrid was developed. This study has not only established a novel approach to detect cellular H2O2, but also provided a general route for fabricating attapulgite-based biosensing platform via assembling enzymes/proteins on attapulgite surface, expanded the scope of attapulgite applications to the field of bioelectroanalytical chemistry and cellular biology.