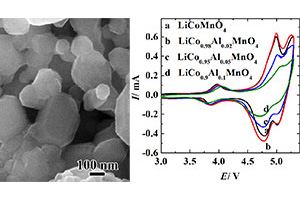
采用固相法合成掺杂镁和铝尖晶石LiCoMnO4材料,研究镁和铝掺杂量对尖晶石LiCoMnO4电极的初始容量、放电平台以及循环性能的影响. 利用扫描电子显微镜、粉末X-射线衍射仪观察分析材料形貌及结构. 结果表明,所合成材料的粒径分布均匀,结晶性较佳. LiCoMnO4电极初始容量为87.0 mAh.g-1,少量镁或铝掺杂使电极初始容量有所增加,LiCo0.98Mg0.02MnO4和LiCo0.98Al0.02MnO4电极初始容量分别为91.3和93.6 mAh.g-1,提高了其5 V放电平台的比例,过量掺杂则其容量降低. 此外,掺杂Al显著改善了LiCoMnO4电极的循环性能,而掺杂镁对电极的循环性能其影响不明显.
游美玲
,
童庆松
,
李秀华
,
林忞
,
黄行康
,
杨勇
. 锂离子正极材料LiCo1-xMgxMnO4与LiCo1-xAlxMnO4 (x = 0, 0.02, 0.05, 0.1)的制备及其电化学性能[J]. 电化学, 2014
, 20(1)
: 22
-27
.
DOI: 10.13208/j.electrochem.121122
The Al-doped and Mg-doped LiCoMnO4 materials were synthesized through solid-state reaction. The effects of doping amounts of Mg and Al on the initial capacities, discharge plateaus, and cycle performances were investigated. The morphologies and structures of the as-prepared materials were studied by scanning electron microscopy and powder X-ray diffraction. The results indicate that the as-prepared samples were composed of uniform, well-crystallized particles. The pristine LiCoMnO4 possessed an initial capacity of 87.0 mAh·g-1, while LiCo0.98Mg0.02MnO4 and LiCo0.98Al0.02MnO4 delivered 91.3 and 93.6 mAh·g-1, respectively. The proper doping amount increased the capacity and the ratio of discharge plateau at 5 V, while over-doping decreased the discharge capacity of LiCoMnO4. In addition, Al doping significantly improved the cycle performance of LiCoMnO4, while no apparent influence with Mg doping.
Zhecheva E, Stoyanova R, Alcantara R, et al. EPR studies of Li deintercalation from LiCoMnO4 spinel-type electrode active material[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2006, 159(2): 1389-1394.
Huang X K, Lin M, Tong Q S, et al. Synthesis of LiCoMnO4 via a sol-gel method and its application in high power LiCoMnO4/Li4Ti5O12 lithium-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2012, 202: 352-356.
Zhang R G(张仁刚), Zhao S X(赵世玺), Xia J L(夏君磊), et al. Study on modification of spinel LiMn2O4 by overcoating[J]. Journal of Electrochemistry (电化学), 2002, 8(3): 269-274.
Zhou D Q(周大桥). Preparation and performance of Co and La Co-doped Li-rich lithium Manganate[J]. Journal of Electrochemistry(电化学), 2009, 15(1): 74-78.
Pasero D, de Souza S, Reeves N, et al. Oxygen content and electrochemical activity of LiCoMnO4-δ[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry, 2005, 15(41): 4435-4440.
Strobel P,Tillier J, Diaz A, et al. Search for new manganese-cobalt oxides as positive electrode materials for lithium batteries[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2007, 174(2): 910-915.
Mandal S, Rojas R M, Amarilla J M, et al. High temperature Co-doped LiMn2O4-based spinels. Structural, electrical, and electrochemical characterization[J]. Chemistry of Materials, 2002, 14(4): 1598-1605.
Ohzuku T, Takeda S, Iwanaga M. Solid-state redox potentials for Li[Me1/2Mn3/2]O4 (Me:3d-transition metal) having spinel-framework structures: a series of 5 volt materials for advanced lithium-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 1999, 81: 90-94.
Zhecheva E, Stoyanova R. Effect of allied and alien ions on the EPR spectrum of Mn-containing lithium-manganese spinel oxides [J]. Solid State Communications, 2005, 135(7): 405-410.
Kawai H, Nagata M, Tukamoto H, et al. A new lithium cathode LiCoMnO4: Toward practical 5 V lithium batteries[J]. Electrochemical and Solid-State Letters, 1998, 1(5): 212-214.
Stoyanova R K, Zhecheva E N, Gorova M Y. EPR evidence on short-range Co-Mn order in LiCoMnO4 spinels[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry, 2000, 10: 1377-1381.
Zhecheva E, Stoyanova R, Gorova M, et al. Co/Mn distribution and electrochemical intercalation of Li into Li[Mn2-yCoy]O4 spinels, 0< y< 1[J]. Solid State Ionics, 2001(1/2), 140:19-33.
Amdouni N, Gendron F, Mauger A, et al. LiMn2-yCoyO4 (0 ≤ y ≤ 1) intercalation compounds synthesized from wet-chemical route[J]. Materials Science and Engineering: B, 2006, 129(1/3): 64-75.
Kawai H, Nagata M, Tukamotob H, et al. A novel cathode Li2CoMn3O8 for lithium ion batteries operating over 5 volts[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry Communication, 1998, 8(4):837-839.
Rojas R M, Amarilla J M, Pascual, L, et al. Combustion synthesis of nanocrystalline LiNiYCo1-2YMn1+YO4 spinels for 5V cathode materials[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2006, 160(1): 529-535.
Alcantara R, Jaraba M, Lavela P, et al. Electrochemical, 6Li MAS NMR, and X-ray and neutron diffraction study of LiCoxFeyMn2-(x+y)O4 spinel oxides for high-voltage cathode materials[J]. Chemical Materials, 2003, 15(12): 1210-1216.
Lin Y(林永), Zhao K(赵锟), Wang M L(王曼丽). Study on synthesis of spinel-LiMn2O4 nanoparticles and its electrochemical impedance spectroscopies[J]. Chemical Research and Application(化学研究与应用), 2011, 23(8): 975-979.