

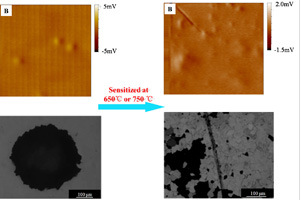
敏化处理304不锈钢局部腐蚀行为的扫描微电极法研究
收稿日期: 2013-01-31
修回日期: 2013-03-28
网络出版日期: 2013-04-05
基金资助
国家自然科学基金项目(No. 21021002)资助
Localized Corrosion Behavior of Sensitized 304 Stainless Steel by Scanning Reference Electrode Technique
Received date: 2013-01-31
Revised date: 2013-03-28
Online published: 2013-04-05
叶陈清 , 胡融刚 , 侯瑞青 , 王小平 , 杜荣归 , 林昌健 . 敏化处理304不锈钢局部腐蚀行为的扫描微电极法研究[J]. 电化学, 2013 , 19(6) : 507 -511 . DOI: 10.13208/j.electrochem.130217
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |