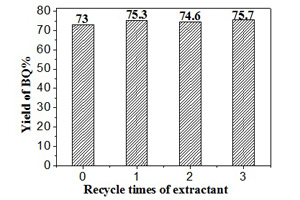
在H型阳离子交换膜电解槽中,以H2SO4电解质、阳极和阴极铅电极,研究苯酚电解氧化合成对苯醌. 讨论电流密度、电解质浓度、电解液中对苯醌浓度和萃取剂等电解条件对对苯醌收率和电流效率的影响. 经优选工艺条件为:电流密度4 A·dm-2,H2SO4电解质浓度1 mol·L-1,氯仿萃取剂. 通入3.2 Ah电量,对苯醌收率可达68%,电流效率为24.7%. 而在萃取剂存在下,对苯醌收率可提高至73%,电流效率为26%. 实验结果表明氯仿萃取剂可循环套用.
The benzoquinone was prepared from phenol by electrooxidation in an H-type cell with cation exchange membrane, in which lead plates were used both as an anode and a cathode, while H2SO4 was used as a supporting electrolyte. The effects of current density, concentration of sulphuric acid, concentrations of benzoquinone in electrolyte and extractant on the yields and efficiencies of electrolysis were investigated. Under the optimized conditions of current density being 4 A·dm-2, concentration of sulphuric acid 1 mol·L-1, passed charge 3.2 A·h, the yield and current efficiency of benzoquinone could reach 68% and 24.7%, respectively, without using chloroform as an extractant. However, the yield and current efficiency of benzoquinone could be increased to 73% and 26%, respectively, in the presence of chloroform extractant which could be recycled in the preparation of benzoquinone.