

碳纳米管负载Ni2P作为染料敏化太阳能电池对电极的性能研究
收稿日期: 2011-11-24
修回日期: 2012-02-16
网络出版日期: 2012-02-21
基金资助
国家973计划(No. 2009CB220100),国家自然科学基金(No. 51001063)和天津市应用基础及前沿技术研究计划(No. 11JCZDJC23300)资助
Carbon Nanotubes with Ni2P Nanoparticles as a Counter Electrode in Dye-sensitized Solar Cells
Received date: 2011-11-24
Revised date: 2012-02-16
Online published: 2012-02-21
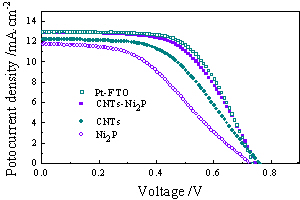
窦衍叶 , 晏南富 , 李国然 , 高学平 . 碳纳米管负载Ni2P作为染料敏化太阳能电池对电极的性能研究[J]. 电化学, 2012 , 18(4) : 301 -305 . DOI: 10.61558/2993-074X.2920

/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |