高能量密度、功率密度和温度稳定性的全固态薄膜锂离子电池是微电子器件的理想电源. 开发新型的大比容量正极薄膜材料是解决问题的关键之一. 与LiCoO2正极相比,层状结构的LiNi0.5Mn0.5O2有更高的可逆比容量和结构稳定性. 本文应用脉冲激光沉积法制备LiNi0.5Mn0.5O2沉积薄膜,研究了衬底材料、温度对薄膜的微观结构、表面形貌及组分的影响. 由LiNi0.5Mn0.5O2电极组装半电池,研究了薄膜的电化学性能与晶体结构、表面形貌及组分间的关系,表征了LiNi0.5Mn0.5O2沉积薄膜不同充电截止电压的循环稳定性及倍率性能,讨论了LiNi0.5Mn0.5O2薄膜的结构特点.
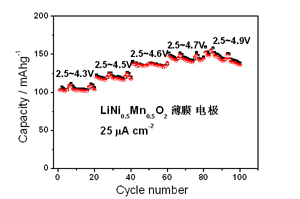
The all-solid-state thin-film Li-ion batteries with high energy density, power density and temperature stability are the ideal power sources for microelectronic devices. Developing new thin-film cathodes with large specific capacity is the key to their practical applications. The LiNi0.5Mn0.5O2 with a layered structure has a higher reversible capacity and better structural stability compared with traditional LiCoO2 cathode material. In this work, the LiNi0.5Mn0.5O2 thin film cathodes were prepared by pulsed laser deposition. The effects of substrate material and temperature on the microstructure, surface morphology and composition of the thin films were investigated. Rate capability and cycle performance of LiNi0.5Mn0.5O2 thin-film electrodes at different voltage windows were investigated and their correlations with the crystal structure, surface morphology and composition of the thin films are discussed. It was shown that the LiNi0.5Mn0.5O2 thin-film electrodes prepared on the Au substrates exhibited a pure layered phase, while those on the stainless steel substrates exhibited mixed phases, which is due to the severe diffusion between the film and the substrate. The reversible specific capacity of the LiNi0.5Mn0.5O2 thin-film electrode reached 210 mAh?g-1 between 2 and 5 V at a current density of 2 μA?cm-2, which agrees well with literature report. The excellent cycling stability was obtained at a voltage up to 4.7 V, indicating good structural stability of the film also confirmed with the XRD data. However, the relatively low rate capability could be due to the Li/Ni intermixing in the layered structure, while the capacity fade observed when the charge voltage was further increased to 4.9 V could be due to the formation of solid electrolyte interface induced by the electrolyte decomposition at such a high voltage.