

收稿日期: 2011-09-04
修回日期: 2011-09-15
网络出版日期: 2011-10-21
基金资助
国家自然科学基金(20973151,20901065)资助
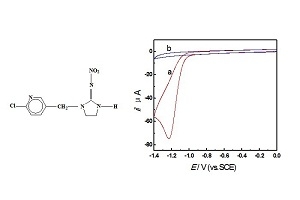
Electrochemical Behavior of Imidacloprid
Received date: 2011-09-04
Revised date: 2011-09-15
Online published: 2011-10-21
王杰琼 , 张旺 , 陈铭 , 刁国旺 . 吡虫啉电化学性能研究[J]. 电化学, 2012 , 18(1) : 68 -72 . DOI: 10.61558/2993-074X.2882
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |