

核电站结构材料的锌离子注入电化学研究
收稿日期: 2010-09-28
修回日期: 2010-12-30
网络出版日期: 2011-05-05
基金资助
国家自然科学基金(50971059), 中央高校基本科研业务费专项资金(10QX42)
Electrochemical Studies of Zinc Injection into the Structure Materials of Nuclear Power Plants
Received date: 2010-09-28
Revised date: 2010-12-30
Online published: 2011-05-05
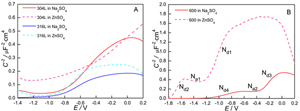
张胜寒 , 檀玉 , 梁可心 . 核电站结构材料的锌离子注入电化学研究[J]. 电化学, 2011 , 17(2) : 212 -216 . DOI: 10.61558/2993-074X.2833

/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |