

基于单细胞尺度的纳米移液管递送研究
收稿日期: 2024-04-29
修回日期: 2024-08-07
录用日期: 2024-08-09
网络出版日期: 2024-08-21
Precision Delivery Using Nanopipette for Single-Cell Studies
Received date: 2024-04-29
Revised date: 2024-08-07
Accepted date: 2024-08-09
Online published: 2024-08-21
张鹤 , Md Maksudur Rahman , 陶洋 , Joseph W Sampson , 任航 . 基于单细胞尺度的纳米移液管递送研究[J]. 电化学, 2024 , 30(11) : 2414002 . DOI: 10.61558/2993-074X.3488
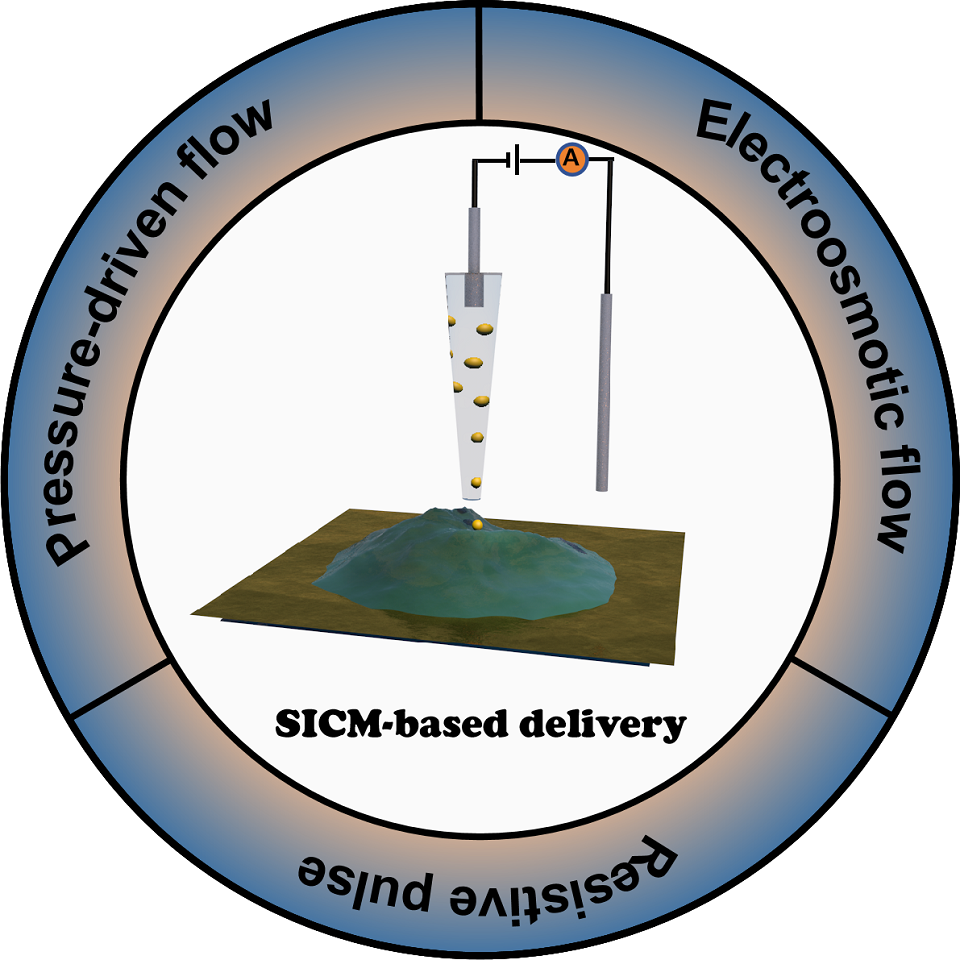
Nanopipette based scanning probe technique is a versatile tool in non-contact imaging in biology. In addition to the topographic imaging, its capability of localized delivery of bio-active molecules is emerging. In this mini review, we introduce the applications of nanopipette in single-cell researches with a focus on localized delivery. The working principles of three delivery modes including resistive pulse, pressure-driven flow, and electroosmotic flow-driven delivery are summarized and compared. Their applications in single-cell researches are reviewed. The current technical challenges in scanning ion conductance microscopy-based delivery, and their growing influence in medicine and pharmacologic researches are also discussed.
| [1] | Zhang L W, Vertes A. Single-cell mass spectrometry approaches to explore cellular heterogeneity[J]. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2018, 57(17): 4466-4477. |
| [2] | Altschuler S J, Wu L F. Cellular heterogeneity: Do differences make a difference[J] Cell, 2010, 141(4): 559-563. |
| [3] | Huang K, Wang Y H, Zhang H, Wang T Y, Liu X H, Liu L, Jiang H, Wang X M. Application and outlook of electrochemical technology in single-cell analysis[J]. Biosens. Bioelectron., 2023, 242: 115741. |
| [4] | Chinese society of electrochemistry. The top ten scientific questions in electrochemistry[J]. J. Electrochem., 2024, 30(1): 2024121. |
| [5] | Polcari D, Dauphin-Ducharme P, Mauzeroll J. Scanning electrochemical microscopy: A comprehensive review of experimental parameters from 1989 to 2015[J]. Chem. Rev., 2016, 116(22): 13234-13278. |
| [6] | Ushiki T, Nakajima M, Choi M, Cho S J, Iwata F. Scanning ion conductance microscopy for imaging biological samples in liquid: a comparative study with atomic force microscopy and scanning electron microscopy[J]. Micron, 2012, 43(12): 1390-1398. |
| [7] | Lazenby R A, White R J. Advances and perspectives in chemical imaging in cellular environments using electrochemical methods[J]. Chemosensors, 2018, 6(2): 24. |
| [8] | Zhu C, Huang K X, Siepser N P, Baker L A. Scanning ion conductance microscopy[J]. Chem. Rev., 2021, 121(19): 11726-11768. |
| [9] | Kempaiah R, Vasudevamurthy G, Subramanian A. Scanning probe microscopy based characterization of battery materials, interfaces, and processes[J]. Nano Energy, 2019, 65: 103925. |
| [10] | Page A, Perry D, Unwin P R. Multifunctional scanning ion conductance microscopy[J]. Proc. Math. Phys. Eng. Sci., 2017, 473(2200): 20160889. |
| [11] | Mirkin M V. High resolution studies of heterogeneous processes with the scanning electrochemical microscope[J] Mikrochim. Acta, 1999, 130(3): 127-153. |
| [12] | Kai T H, Zoski C G, Bard A J. Scanning electrochemical microscopy at the nanometer level[J]. Chem. Commun., 2018, 54(16): 1934-1947. |
| [13] | Amemiya S, Guo J, Xiong H, Gross D A. Biological applications of scanning electrochemical microscopy: Chemical imaging of single living cells and beyond[J]. Anal. and Bioanal. Chem., 2006, 386(3): 458-471. |
| [14] | Bergner S, Vatsyayan P, Matysik F M. Recent advances in high resolution scanning electrochemical microscopy of living cells-a review[J]. Anal. Chim. Acta., 2013, 775: 1-13. |
| [15] | Conzuelo F, Schulte A, Schuhmann W. Biological imaging with scanning electrochemical microscopy[J]. Proc. Math. Phys. Eng. Sci., 2018, 474(2218): 20180409. |
| [16] | Wu J N, Gao Y F, Pan N, Lu L P, Wang X Y. An isolated single-particle-based SECM tip interface for single-cell NO sensing[J]. Biosens. Bioelectron., 2023, 223: 115048. |
| [17] | Nebel M, Grutzke S, Diab N, Schulte A, Schuhmann W. Visualization of oxygen consumption of single living cells by scanning electrochemical microscopy: The influence of the faradaic tip reaction.[J]. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2013, 52(24): 6335-6338. |
| [18] | Happel P, Thatenhorst D, Dietzel I D. Scanning ion conductance microscopy for studying biological samples[J]. Sensors, 2012, 12(11): 14983-15008. |
| [19] | Muhammed Y, Lazenby R A. Scanning ion conductance microscopy revealed cisplatin-induced morphological changes related to apoptosis in single adenocarcinoma cells[J]. Anal. Methods, 2024, 16(4): 503-514. |
| [20] | Hansma P K, Drake B, Marti O, Gould S A, Prater C B. The scanning ion-conductance microscope[J]. Science, 1989, 243(4891): 641-643. |
| [21] | Korchev Y E, Milovanovic M, Bashford C L, Bennett D C, Sviderskaya E V, Vodyanoy I, Lab M J. Specialized scanning ion-conductance microscope for imaging of living cells[J]. J. Microsc.-Oxf., 1997, 188: 17-23. |
| [22] | Song Y, Zhang S T, Cao C, Yan J, Li M, Li X Y, Chen F, Gu N. Imaging structural and electrical changes of aging cells using scanning ion conductance microscopy[J]. Small Methods, 2023, 8(8): e2301315. |
| [23] | Gesper A, Thatenhorst D, Wiese S, Tsai T, Dietzel I D. Patrick H. Long-term, long-distance recording of a living migrating neuron by scanning ion conductance microscopy[J]. Scanning, 2015, 37(3): 226-231. |
| [24] | Huang K X, Zhou L S, Alanis K, Hou J H, Baker L A. Imaging effects of hyperosmolality on individual tricellular junctions[J]. Chem. Sci., 2020, 11(5): 1307-1315. |
| [25] | Tognoni E. High-speed multifunctional scanning ion conductance microscopy: Innovative strategies to study dynamic cellular processes[J]. Curr. Opin. Electrochem., 2021, 28: 100738. |
| [26] | Navikas V, Leitao S M, Grussmayer K S, Descloux A, Drake B, Yserentant K, Werther P, Herten D P, Wombacher R, Radenovic A, Fantner G E. Correlative 3D microscopy of single cells using super-resolution and scanning ion-conductance microscopy[J]. Nat. Commun., 2021, 12(1): 4565. |
| [27] | Sanchez D, Johnson N, Li C, Novak P, Rheinlaender J, Zhang Y, Korchev Y E. Noncontact measurement of the local mechanical properties of living cells using pressure applied via a pipette[J]. Biophys. J., 2008, 95(6): 3017-3027. |
| [28] | McKelvey K, Edwards M A, White H S. Resistive pulse delivery of single nanoparticles to electrochemical interfaces[J]. J. Phys. Chem. Lett., 2016, 7(19): 3920-3924. |
| [29] | Babakinejad B, Jonsson P, Lopez Cordoba A, Actis P, Novak P, Takahashi Y, Shevchuk A, Anand U, Anand P, Drews A, Ferrer-Montiel A, Klenerman D, Korchev Y E. Local delivery of molecules from a nanopipette for quantitative receptor mapping on live cells[J]. Anal. Chem., 2013, 85(19): 9333-9342. |
| [30] | Lan W J, Holden D A, Liu J, White H S. Pressure-driven nanoparticle transport across glass membranes containing a conical-shaped nanopore[J]. J. Phys. Chem. C, 2011, 115(38): 18445-18452. |
| [31] | Saha-Shah A, Weber A E, Karty J A, Ray S J, Hieftje G M, Baker L A. Nanopipettes: Probes for local sample analysis[J]. Chem. Sci., 2015, 6(6): 3334-3341. |
| [32] | Oh K W. 6-Lab-on-chip (LOC) devices and microfluidics for biomedical applications[M]. Woodhead: Elsevler, 2012: 150-171. |
| [33] | Delgado A V, Gonzalez-Caballero F, Hunter R J, Koopal L K, Lyklema J. Measurement and interpretation of electrokinetic phenomena[J]. Pure. Appl. Chem., 2005, 77(10): 1753-1805 |
| [34] | Bruckbauer A, James P, Zhou D, Yoon J W, Excell D, Korchev Y, Jones R, Klenerman D. Nanopipette delivery of individual molecules to cellular compartments for single-molecule fluorescence tracking[J]. Biophys. J., 2007, 93(9): 3120-3131. |
| [35] | Seger R A, Actis P, Penfold C, Maalouf M, Vilozny B, Pourmand N. Voltage controlled nano-injection system for single-cell surgery[J]. Nanoscale, 2012, 4(19): 5843-5846. |
| [36] | Kolmogorov V, Erofeev A, Vaneev A, Gorbacheva L, Kolesov D, Klyachko N, Korchev Y, Gorelkin P. Scanning ion-conductance microscopy for studying mechanical properties of neuronal cells during local delivery of glutamate[J]. Cells, 2023, 12(20): 2428. |
| [37] | Page A, Kang M, Armitstead A, Perry D, Unwin P R. Quantitative visualization of molecular delivery and uptake at living cells with self-referencing scanning ion conductance microscopy-scanning electrochemical microscopy[J]. Anal. Chem., 2017, 89(5): 3021-3028. |
| [38] | Howorka S, Siwy Z. Nanopore analytics: Sensing of single molecules[J]. Chem. Soc. Rev., 2009, 38(8): 2360-2384. |
| [39] | Wang Y X, Cai H J, Mirkin M V. Delivery of single nanoparticles from nanopipettes under resistive-pulse control[J]. ChemElectroChem, 2014, 2(3): 343-347. |
| [40] | Pandey P, Sesena-Rubfiaro A, Khatri S, He J. Development of multifunctional nanopipettes for controlled intracellular delivery and single-entity detection[J]. Faraday Discuss., 2022, 233(0): 315-335. |
| [41] | Chau C C, Maffeo C M, Aksimentiev A, Radford S E, Hewitt E W, Actis P. Single molecule delivery into living cells[J]. Nat. Commun., 2024, 15(1): 4403. |
| [42] | Liu Y, Xu C, Chen X W, Wang J H, Yu P, Mao L Q. Voltage-driven counting of phospholipid vesicles with nanopipettes by resistive-pulse principle[J]. Electrochem. Commun., 2018, 89: 38-42. |
| [43] | Terejanszky P, Makra I, Furjes P, Gyurcsanyi R E. Calibration-less sizing and quantitation of polymeric nanoparticles and viruses with quartz nanopipets[J]. Anal. Chem., 2014, 86(10): 4688-4697. |
| [44] | Holden D A, Watkins J J, White H S. Resistive-pulse detection of multilamellar liposomes[J]. Langmuir, 2012, 28(19): 7572-7577. |
| [45] | Actis P, Maalouf M M, Kim H J, Lohith A, Vilozny B, Seger R A, Pourmand N. Compartmental genomics in living cells revealed by single-cell nanobiopsy[J]. ACS Nano, 2014, 8(1): 546-553. |
| [46] | Ando T. High-speed atomic force microscopy and its future prospects[J]. Biophys. Rev., 2018, 10(2): 285-292. |
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |