

碳酸酯类电解液中纳米银电极界面过程的原位拉曼光谱研究
收稿日期: 2023-01-26
修回日期: 2023-03-03
录用日期: 2023-03-12
网络出版日期: 2023-03-14
An In-Situ Raman Spectroscopic Study on the Interfacial Process of Carbonate-Based Electrolyte on Nanostructured Silver Electrode
Received date: 2023-01-26
Revised date: 2023-03-03
Accepted date: 2023-03-12
Online published: 2023-03-14
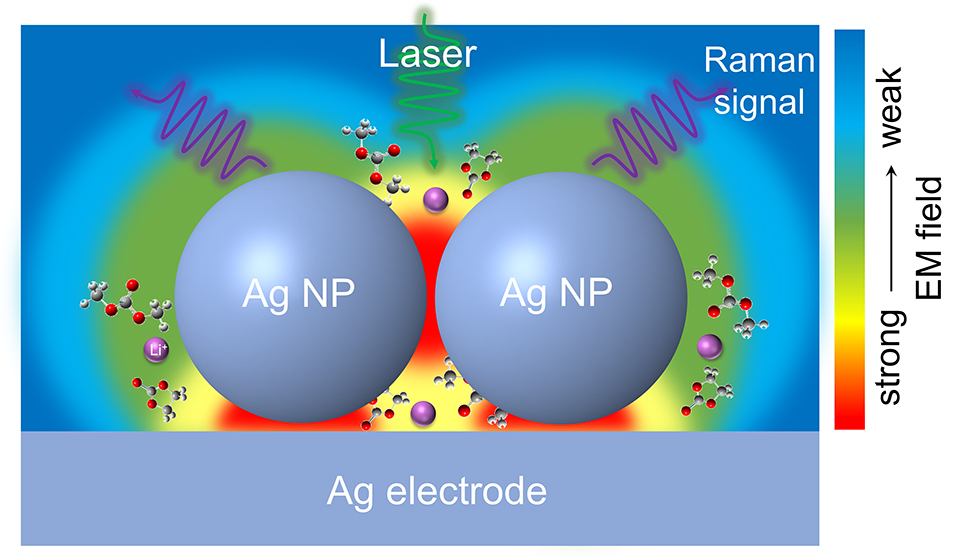
锂电池体系中负极表面固态电解质界面相(SEI)对锂电池性能起到至关重要的作用。然而,SEI结构和化学组成复杂,其形成机理至今仍未完全阐明,阻碍了锂电池的发展和应用。本文从方法学角度出发,采用表面增强拉曼光谱(SERS)“借力”策略,通过优化银纳米粒子的结构并借助其外来表面局域等离激元共振作用,开展以EC-DMC为溶剂的碳酸酯类电解液体系中SEI成膜过程的原位研究。为了确保可靠的原位SERS测试,我们设计了一种三电极体系气密拉曼电池。我们利用原位SERS方法,在纳米银电极上获得了SEI成膜过程的组成和结构信息。研究表明,SEI随电位变化呈现出双层结构,其中内层由薄且致密的无机组分构成,外层由疏松的有机组分构成。同时,研究发现LEMC是EC还原的主要成分,而不是LEDC,且金属锂参与的化学反应在形成稳定SEI中的起到关键作用。此外,锂发生沉积后,由于锂与银的合金效应导致其介电常数发生变化,从而削无法进一步增强SEI的拉曼信号。本文为深入理解负极表面SEI的形成及演变过程提供依据,并为今后开展锂电池体系相关界面过程的原位研究提供借鉴。
谷宇 , 胡元飞 , 王卫伟 , 尤恩铭 , 唐帅 , 苏建加 , 易骏 , 颜佳伟 , 田中群 , 毛秉伟 . 碳酸酯类电解液中纳米银电极界面过程的原位拉曼光谱研究[J]. 电化学, 2023 , 29(12) : 2301261 . DOI: 10.13208/j.electrochem.2301261
The solid-electrolyte interphase (SEI) plays a key role in anodes for rechargeable lithium-based battery technologies. However, a thorough understanding in the mechanisms of SEI formation and evolution remains a major challenge, hindering the rapid development and wide applications of Li-based batteries. Here, we devise a borrowing surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) activity strategy by utilizing a size optimized Ag nanosubstrate to in-situ monitor the formation and evolution of SEI, as well as its structure and chemistry in an ethylene carbonate-based electrolyte. To ensure a reliable in-situ SERS investigation, we designed a strict air-tight Raman cell with a three-electrode configuration. Based on the potential-dependent spectroscopic information, we revealed that the SEI formed in an EC-based electrolyte presents a double-layer structure, comprising a thin inorganic inner layer and an organic-rich outer layer. We also identified that LEMC, rather than LEDC, is the major component of EC reduction, and the critical role of metallic Li in the formation of stable SEI is preliminary explored. Nevertheless, identifying the SEI compositions is only feasible before Li deposition on the Ag surface. After the formation of Li-Ag alloys, the subsequent evolution of SEI could not be detected due to the change in the dielectric constant of Ag after the lithiation. Our work provides a real-time spectroscopic method for investigating interfacial processes of anodes, which is beneficial to the understanding of SEI formation and evolution and thus provides guidance for the development of rationally designed SEI in Li-based batteries.

| [1] | Atkins D, Ayerbe E, Benayad A, Capone F G, Capria E, Castelli I E, Cekic-Laskovic I, Ciria R, Dudy L, Edstr?m K, Johnson M R, Li H, Lastra J M G, De Souza M L, Meunier V, Morcrette M, Reichert H, Simon P, Rueff J P, Sottmann J, Wenzel W, Grimaud A. Understanding battery interfaces by combined characterization and simulation approaches: Challenges and perspectives[J]. Adv. Energy Mater., 2021, 12(17): 2102687. |
| [2] | Yu X, Manthiram A. Electrode-electrolyte interfaces in lithium-based batteries[J]. Energy Environ. Sci., 2018, 11(3): 527-543. |
| [3] | Yan C, Xu R, Xiao Y, Ding J F, Xu L, Li B Q, Huang J Q. Toward critical electrode/electrolyte interfaces in rechargeable batteries[J]. Adv. Funct. Mater., 2020, 30(23): 1909887. |
| [4] | Peled E. The electrochemical behavior of alkali and alkaline earth metals in nonaqueous battery systems—the solid electrolyte interphase model[J]. J. Electrochem. Soc., 1979, 126(12): 2047-2051. |
| [5] | Peled E, Menkin S. Review—SEI: Past, present and future[J]. J. Electrochem. Soc., 2017, 164(7): A1703-A1719. |
| [6] | Xu R, Yan C, Huang J Q. Competitive solid-electrolyte interphase formation on working lithium anodes[J]. Trends Chem., 2021, 3(1): 5-14. |
| [7] | Gu Y, Wang W W, Li Y J, Wu Q H, Tang S, Yan J W, Zheng M S, Wu D Y, Fan C H, Hu W Q, Chen Z B, Fang Y, Zhang Q H, Dong Q F, Mao B W. Designable ultra-smooth ultra-thin solid-electrolyte interphases of three alkali metal anodes[J]. Nat. Commun., 2018, 9(1): 1339. |
| [8] | Cheng X B, Zhang R, Zhao C Z, Zhang Q. Toward safe lithium metal anode in rechargeable batteries: A review[J]. Chem. Rev., 2017, 117(15): 10403-10473. |
| [9] | Aurbach D, Zaban A. Impedance spectroscopy of lithium electrodes. 1. General behavior in propylene carbonate solutions and the correlation to surface-chemistry and cycling efficiency[J]. J. Electroanal. Chem., 1993, 348(1-2): 155-179. |
| [10] | Peled E, Golodnitsky D, Ardel G. Advanced model for solid electrolyte interphase electrodes in liquid and polymer electrolytes[J]. J. Electrochem. Soc., 1997, 144(8): L208-L210. |
| [11] | Gu Y, Wang W W, Yan J W, Wu D Y, Dong Q F, Mao B W. Surface electrochemistry approaches for understanding and creating smooth solid-electrolyte interphase and lithiophilic interfaces for lithium metal anodes[J]. Curr. Opin. Electrochem., 2021, 26: 100671. |
| [12] | Wu H, Jia H, Wang C, Zhang J G, Xu W. Recent progress in understanding solid electrolyte interphase on lithium metal anodes[J]. Adv. Energy Mater., 2020, 11(5): 2003092. |
| [13] | Wang A P, Kadam S, Li H, Shi S Q, Qi Y. Review on modeling of the anode solid electrolyte interphase (SEI) for lithium-ion batteries[J]. npj Comput. Mater., 2018, 4(1): 15. |
| [14] | Wang W W, Gu Y, Yan H, Li S, He J W, Xu H Y, Wu Q H, Yan J W, Mao B W. Evaluating solid-electrolyte interphases for lithium and lithium-free anodes from nanoindentation features[J]. Chem, 2020, 6(10): 2728-2745. |
| [15] | Wang W W, Gu Y, Wang J H, Chen Z B, Yin X T, Wu Q H, Yan J W, Mao B W. Probing mechanical properties of solid-electrolyte interphases on Li nuclei by in situ AFM[J]. J. Electrochem. Soc., 2022, 169(2): 020563. |
| [16] | Wang W W, Gu Y, Yan H, Li K X, Chen Z B, Wu Q H, Kranz C, Yan J W, Mao B W. Formation sequence of solid electrolyte interphases and impacts on lithium deposition and dissolution on copper: An in situ atomic force microscopic study[J]. Faraday Discuss., 2022, 233: 190-205. |
| [17] | Lin D C, Liu Y Y, Li Y B, Li Y Z, Pei A, Xie J, Huang W, Cui Y. Fast galvanic lithium corrosion involving a Kirkendall-type mechanism[J]. Nat. Chem., 2019, 11(4): 382-389. |
| [18] | Ding S Y, Yi J, Li J F, Ren B, Wu D Y, Panneerselvam R, Tian Z Q. Nanostructure-based plasmon-enhanced Raman spectroscopy for surface analysis of materials[J]. Nat. Rev. Mater., 2016, 1(6): 16021. |
| [19] | Panneerselvam R, Liu G K, Wang Y H, Liu J Y, Ding S Y, Li J F, Wu D Y, Tian Z Q. Surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy: Bottlenecks and future directions[J]. Chem. Commun., 2018, 54(1): 10-25. |
| [20] | Wu D Y, Li J F, Ren B, Tian Z Q. Electrochemical surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy of nanostructures[J]. Chem. Soc. Rev., 2008, 37(5): 1025-1041. |
| [21] | Weiling M, Pfeiffer F, Baghernejad M. Vibrational spectroscopy insight into the electrode|electrolyte interface/interphase in lithium batteries[J]. Adv. Energy Mater., 2022, 12(46): 2202504. |
| [22] | Shen Y F, Chen Y L, Wang S X, Zhu Y, Wang W C, Wu M X, Chen Z D. Electrochemical SERS study of Benzotriazole and 3-mercapto-1-propanesulfonate in acidic solution on copper electrode[J]. J. Electrochem., 2022, 28(6): 2104451. |
| [23] | Peng H Y, Wang J Z, Liu J, Yu H H, Lin J D, Wu D Y, Tian Z Q. Investigation on electrochemical processes of p-aminothiophenol on gold electrode of nanostructures[J]. J. Electrochem., 2022, 28(4): 2106281. |
| [24] | Li J F, Huang Y F, Ding Y, Yang Z L, Li S B, Zhou X S, Fan F R, Zhang W, Zhou Z Y, Wu D Y, Ren B, Wang Z L, Tian Z Q. Shell-isolated nanoparticle-enhanced Raman spectroscopy[J]. Nature, 2010, 464(7287): 392-395. |
| [25] | Su M, Dong J C, Li J F. In-situ Raman spectroscopic study of electrochemical reactions at single crystal surfaces[J]. J. Electrochem., 2020, 26(1): 54-60. |
| [26] | Wang X, Huang S C, Huang T X, Su H S, Zhong J H, Zeng Z C, Li M H, Ren B. Tip-enhanced Raman spectroscopy for surfaces and interfaces[J]. Chem. Soc. Rev., 2017, 46(13): 4020-4041. |
| [27] | Li H, Mo Y J, Pei N, Xu X X, Huang X J, Chen L Q. Surface-enhanced Raman scattering study on passivating films of Ag electrodes in lithium batteries[J]. J. Phys. Chem. B, 2000, 104(35): 8477-8480. |
| [28] | Gogoi N, Melin T, Berg E J. Elucidating the step-wise solid electrolyte interphase formation in lithium-ion batteries with operando Raman spectroscopy[J]. Adv. Mater. interfaces, 2022, 9(22): 2200945. |
| [29] | Tang S, Gu Y, Yi J, Zeng Z, Ding S Y, Yan J W, Wu D Y, Ren B, Tian Z Q, Mao B W. An electrochemical surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopic study on nanorod-structured lithium prepared by electrodeposition[J]. J. Raman Spectrosc., 2016, 47(9): 1017-1023. |
| [30] | Johnson L, Li C, Liu Z, Chen Y, Freunberger S A, Ashok P C, Praveen B B, Dholakia K, Tarascon J M, Bruce P G. The role of LiO2 solubility in O2 reduction in aprotic solvents and its consequences for Li-O2 batteries[J]. Nat. Chem., 2014, 6(12): 1091-1099. |
| [31] | Wang J W, Zhang Y L, Guo L M, Wang E K, Peng Z Q. Identifying reactive sites and transport limitations of oxygen reactions in aprotic lithium-O2 batteries at the stage of sudden death[J]. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2016, 55(17): 5201-5205. |
| [32] | Hy S, Felix F, Rick J, Su W N, Hwang B J. Direct in situ observation of Li2O evolution on Li-rich high-capacity cathode material, Li[Nixli(1-2x)/3mn(2-x)/3]O2 (0 ≤ x ≤ 0.5)[J]. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2014, 136(3): 999-1007. |
| [33] | Gajan A, Lecourt C, Torres Bautista B E, Fillaud L, Demeaux J, Lucas I T. Solid Electrolyte interphase instability in operating lithium-ion batteries unraveled by enhanced-Raman spectroscopy[J]. ACS Energy Lett., 2021, 6(5): 1757-1763. |
| [34] | Nanda J, Yang G, Hou T, Voylov D N, Li X, Ruther R E, Naguib M, Persson K, Veith G M, Sokolov A P. Unraveling the nanoscale heterogeneity of solid electrolyte interphase using tip-enhanced Raman spectroscopy[J]. Joule, 2019, 3(8): 2001-2019. |
| [35] | Zhang W L, Lu Y, Wan L, Zhou P, Xia Y C, Yan S S, Chen X X, Zhou H Y, Dong H, Liu K. Engineering a passivating electric double layer for high performance lithium metal batteries[J]. Nat. Commun., 2022, 13(1): 2029. |
| [36] | Tian Z Q, Ren B, Li J F, Yang Z L. Expanding generality of surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy with borrowing SERS activity strategy[J]. Chem. Commun., 2007, (34): 3514-3534. |
| [37] | Li J F, Zhang Y J, Ding S Y, Panneerselvam R, Tian Z Q. Core-shell nanoparticle-enhanced Raman spectroscopy[J]. Chem. Rev., 2017, 117(7): 5002-5069. |
| [38] | Sharma B, Frontiera R R, Henry A I, Ringe E. Van Duyne R P. SERS: Materials, applications, and the future[J]. Mater. Today, 2012, 15(1-2): 16-25. |
| [39] | Hutter E, Fendler J H. Exploitation of localized surface plasmon resonance[J]. Adv. Mater., 2004, 16(19): 1685-1706. |
| [40] | Uzayisenga V, Lin X D, Li L M, Anema J R, Yang Z L, Huang Y F, Lin H X, Li S B, Li J F, Tian Z Q. Synthesis, characterization, and 3D-FDTD simulation of Ag@SiO2 nanoparticles for shell-isolated nanoparticle-enhanced Raman spectroscopy[J]. Langmuir, 2012, 28(24): 9140-9146. |
| [41] | Qiu Z, Zhang M, Wu D Y, Ding S Y, Zuo Q Q, Huang Y F, Shen W, Lin X D, Tian Z Q, Mao B W. Raman spectroscopic investigation on TiO2-N719 dye interfaces using Ag@TiO2 nanoparticles and potential correlation strategies[J]. ChemPhysChem, 2013, 14(10): 2217-2224. |
| [42] | Li J F, Rudnev A, Fu Y, Bodappa N, Wandlowski T. In situ SHINERS at electrochemical single-crystal electrode/electrolyte interfaces: Tuning preparation strategies and selected applications[J]. ACS Nano, 2013, 7(10): 8940-8952. |
| [43] | Patnaik P. Handbook of inorganic chemicals[M]. New York: McGraw-Hill, 2003. |
| [44] | Johnson P B, Christy R W. Optical constants of the noble metals[J]. Phys. Rev. B, 1972, 6(12): 4370-4379. |
| [45] | Zwilling M, Schmidt P C, Weiss A. Experimental and theoretical studies of optical properties on alloys of the intermetallic systems Li2Ag2-xInx and Li2Cd2-xInx[J]. Appl. Phys., 1978, 16(3): 255-269 |
| [46] | Huang Y F, Zhang M, Zhao L B, Feng J M, Wu D Y, Ren B, Tian Z Q. Activation of oxygen on gold and silver nanoparticles assisted by surface plasmon resonances[J]. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2014, 53(9): 2353-2357. |
| [47] | Qian J, Xu W, Bhattacharya P, Engelhard M, Henderson W A, Zhang Y, Zhang J G. Dendrite-free Li deposition using trace-amounts of water as an electrolyte additive[J]. Nano Energy, 2015, 15: 135-144. |
| [48] | Xu K. Nonaqueous liquid electrolytes for lithium-based rechargeable batteries[J]. Chem. Rev., 2004, 104(10): 4303-4417. |
| [49] | Aurbach D. Nonaqueous electrochemistry[M]. Marcel Dekker, 1999. |
| [50] | Yang G, Ivanov I N, Ruther R E, Sacci R L, Subjakova V, Hallinan D T, Nanda J. Electrolyte solvation structure at solid-liquid interface probed by nanogap surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy[J]. ACS Nano, 2018, 12(10): 10159-10170. |
| [51] | Aurbach D, Markovsky B, Shechter A, Ein-Eli Y, Cohen H. A Comparative Study of synthetic graphite and Li electrodes in electrolyte solutions based on ethylene carbonate-dimethyl carbonate mixtures[J]. J. Electrochem. Soc., 1996, 143(12): 3809. |
| [52] | Wang L, Menakath A, Han F, Wang Y, Zavalij P Y, Gaskell K J, Borodin O, Iuga D, Brown S P, Wang C, Xu K, Eichhorn B W. Identifying the components of the solid-electrolyte interphase in Li-ion batteries[J]. Nat. Chem., 2019, 11(9): 789-796. |
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |