

多活性中心双金属硫化物促进多硫化锂转化构建高性能锂硫电池
收稿日期: 2022-07-30
修回日期: 2022-08-23
录用日期: 2022-09-15
网络出版日期: 2022-09-19
Bimetallic Compound Catalysts with Multiple Active Centers for Accelerated Polysulfide Conversion in Li-S Batteries
#W. H. and J. X. contributed equally to this work.
Received date: 2022-07-30
Revised date: 2022-08-23
Accepted date: 2022-09-15
Online published: 2022-09-19
Supported by
National Key R&D Program of China(2021YFF0500600);National Natural Science Foundation of China(51932005);National Natural Science Foundation of China(52022041);All-Solid-State Lithium Battery Electrolyte Engineering Research Centre(XMHT20200203006);China Postdoctoral Science Foundation(2022M710041)
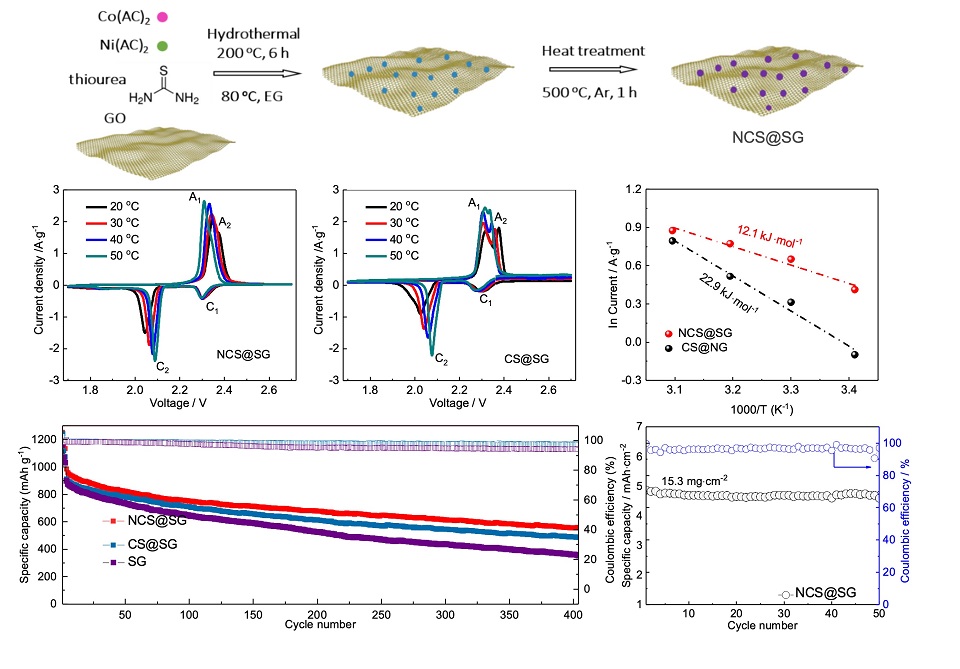
锂硫电池是极具应用潜力的下一代高能量密度电池体系之一。然而,其充放电中间产物多硫化锂的“穿梭效应”不仅消耗大量电解液,还导致硫活性物质利用率低、循环寿命短,是锂硫电池产业化进程中的主要瓶颈之一。引入催化剂加速硫活性物质转化速率,减少多硫化锂在电解液中的累积浓度,是抑制穿梭效应的有效解决策略。高效的催化剂应具备丰富的催化活性位点,以确保高效吸附多硫化锂并加速其向不溶的充放电产物转化。本文制备出硫掺杂石墨烯表面原位负载的双金属硫化物NiCo2S4(NCS@SG)并将其作为催化剂应用于锂硫电池的中间层。相比于单金属硫化物(CoS),NiCo2S4催化剂具有多活性中心催化位点,可以更好地吸附多硫化锂并促进其向放电产物快速转化。应用上述中间层后,电池的充放电比容量、库仑效率和循环稳定性得到了明显提升。当硫的负载达到15.3 mg·cm-2时,经过50次循环后,具有NCS@SG中间层的电池获得了高达93.9%的容量保持率。上述结果表明,设计双金属基催化剂是优化锂硫电池催化剂活性和反应效率的重要方向。
化五星 , 夏静怡 , 胡忠豪 , 李欢 , 吕伟 , 杨全红 . 多活性中心双金属硫化物促进多硫化锂转化构建高性能锂硫电池[J]. 电化学, 2023 , 29(3) : 2217006 . DOI: 10.13208/j.electrochem.2217006
Practical applications of lithium-sulfur (Li-S) batteries are hindered mainly by the low sulfur utilization and severe capacity fading derived from the polysulfide shuttling. Catalysis is an effective remedy to those problems by promoting the conversion of polysulfides to reduce their accumulation in the electrolyte, which needs the catalyst to have efficient adsorption ability to soluble polysulfides and high activity for their conversion. In this work, we have proposed a bimetallic compound of NiCo2S4 anchored onto sulfur-doped graphene (NCS@SG) to fabricate a catalytic interlayer for Li-S batteries. Compared to CoS, the NiCo2S4 demonstrated much higher catalytic activity toward sulfur reduction reaction due to its multiple anchoring and catalytic active sites derived from the coordination of the bimetallic centers. As a result, the NCS@SG interlayer dramatically improved the specific capacity, rate performance, and cycling stability of Li-S batteries. Especially, when the areal sulfur loading of the NCS@SG battery increased to 15.3 mg·cm-2, the high-capacity retention of 93.9 % could be achieved over 50 cycles.

/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |