

质子交换膜燃料电池阴极催化层疏水性优化
Hydrophobicity Optimization of Cathode Catalyst Layer for Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cell
Received date: 2022-07-06
Revised date: 2022-07-14
Accepted date: 2022-07-20
Online published: 2022-07-21
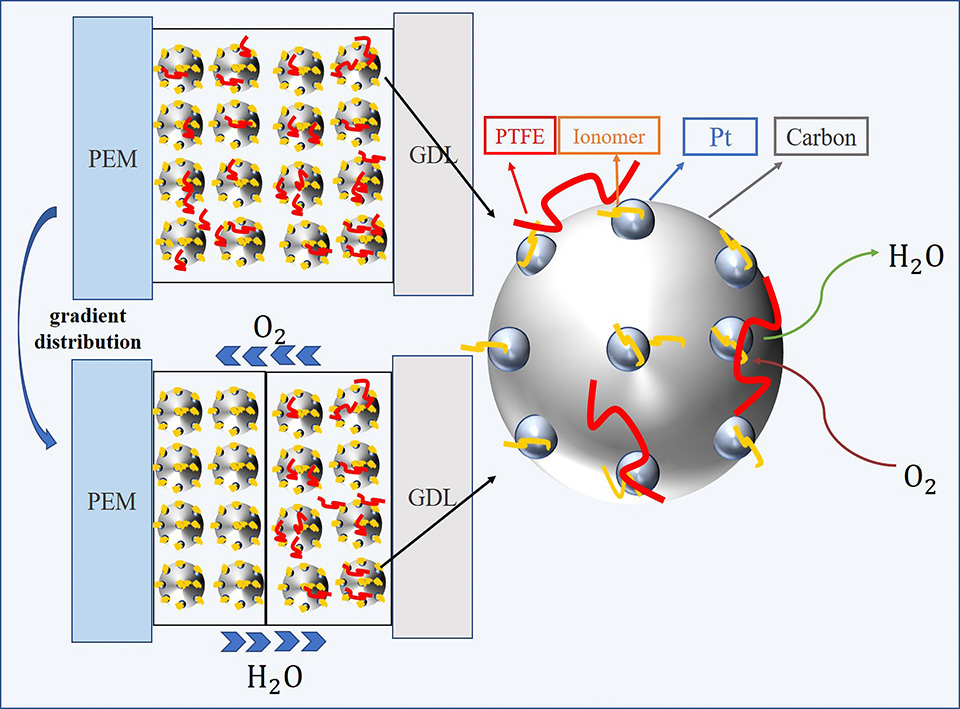
本文采用CCM法(catalyst coated membrane)技术,结合单电池极化曲线、电化学阻抗谱、极限电流法和表面接触角等多种表征技术,系统研究了直接聚四氟乙烯(PTFE)分子添加以及PTFE修饰的疏水性碳(PTFE@XC72)等不同疏水化方法对质子交换膜燃料电池(PEMFC)的阴极催化层电化学性能、氧气传输阻抗和质子传输阻抗的影响。在此基础上,通过构建PTFE梯度化疏水性结构来进一步优化PEMFC的性能。结果表明,与添加PTFE@XC72相比,直接添加适量的PTFE分子对膜电极(MEA)性能提升效果更为显著,这主要与该疏水结构可在维持高速质子传导的同时,极大降低催化层的氧气传输阻抗有关。当直接添加的PTFE与催化层中碳载体的质量比为0.1时,MEA呈现最好的性能。在添加PTFE@XC72的MEA中,由于额外的碳颗粒导致催化层厚度增加,延长了反应物质的传输路径,从而使得质子传输阻抗和氧气传输阻抗均上升。在此基础上,通过在催化层不同位置直接添加PTFE构建梯度化疏水性结构。结果表明,当适量PTFE靠近催化层与气体扩散层界面分布时,MEA呈现最好的性能,峰值功率密度比未经疏水性处理的膜电极高接近20%,氧气传输阻抗大幅降低。
陈浩杰 , 唐美华 , 陈胜利 . 质子交换膜燃料电池阴极催化层疏水性优化[J]. 电化学, 2023 , 29(9) : 2207061 . DOI: 10.13208/j.electrochem.2207061
Hydrophobicity of the cathode catalyst layers (CCLs) crucially determines the performance of proton exchange membrane fuel cells (PEMFCs) by affecting the transports of oxygen and liquid water. In this regard, polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is usually used as a hydrophobic additive to facilitate the oxygen and water transports in CCLs. So far, there remains lacking systematic effort to optimize the addition methods of PTFE in CCLs and the mechanisms behind. In this work, the effects of the approaches for PTFE addition and the distribution of PTFE on the mass transport of oxygen and the proton conduction in CCLs were studied by using a number of electrochemical characterization methods and contact angle tests. It was found that direct adding PTFE molecules is a better way than adding the PTFE-modified carbons to improve the electrochemical properties of CCLs, since the latter causes an increase in the proton transport resistance, whereas the direct molecule addition results in the obviously improved oxygen transport without affecting the proton conduction. In addition, the gradient distribution of PTFE in CCLs, more specifically, adding PTFE near the interface between CCL and gas diffusion layer (GDL), yielded higher catalyst utilization than the homogeneous distribution of PTFE due to the lower oxygen transport resistance.

| [1] | Alaswad A, Baroutaji A, Achour H, Carton J, Al Makky A, Olabi A G. Developments in fuel cell technologies in the transport sector[J]. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy, 2016, 41(37): 16499-16508. |
| [2] | Chen W H, Chen S L. Effect of ink solvents on low-Pt loading proton exchange membrane fuel cell performance[J]. Acta Phys.-Chim. Sin., 2019, 35(5): 517-522. |
| [3] | Liu Q S, Lan F C, Chen J Q, Zeng C J, Wang J F. A review of proton exchange membrane fuel cell water management: Membrane electrode assembly[J]. J. Power Sources, 2022, 517: 230723. |
| [4] | Wu C W, Zhang W, Han X, Zhang Y X, Ma G J. A systematic review for structure optimization and clamping load design of large proton exchange membrane fuel cell stack[J]. J. Power Sources, 2020, 476: 228724. |
| [5] | Wang Y, Diaz D F R, Chen K S, Wang Z, Adroher X C. Materials, technological status, and fundamentals of PEM fuel cells - A review[J]. Mater. Today, 2020, 32: 178-203. |
| [6] | Wang X R, Ma Y, Gao, J, Li T, Jiang G Z, Sun Z Y. Review on water management methods for proton exchange membrane fuel cells[J]. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy, 2021, 46(22): 12206-12229. |
| [7] | Avcioglu G S, Ficicilar B, Bayrakceken A, Eroglu I. High performance PEM fuel cell catalyst layers with hydrophobic channels[J]. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy, 2015, 40(24): 7720-7731. |
| [8] | Chi B, Hou S Y, Liu G Z, Deng Y J, Zeng J H, Song H Y, Liao S J, Ren J W. Tuning hydrophobic-hydrophilic balance of cathode catalyst layer to improve cell performance of proton exchange membrane fuel cell (PEMFC) by mixing polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE)[J]. Electrochim. Acta, 2018, 277: 110-115. |
| [9] | Chi B, Ye Y K, Lu X Y, Jiang S J, Du L, Zeng J H, Ren J W, Liao S J. Enhancing membrane electrode assembly performance by improving the porous structure and hydrophobicity of the cathode catalyst layer[J]. J. Power Sources, 2019, 443: 227284. |
| [10] | Wang M, Chen M, Yang Z Y, Liu G C, Lee J K, Yang W, Wang X D. High-performance and durable cathode catalyst layer with hydrophobic C@PTFE particles for low-Pt loading membrane assembly electrode of PEMFC[J]. Energy Conv. Manag., 2019, 191: 132-140. |
| [11] | Cai X, Lin R, Wang H, Liu S C, Zhong D. One simple method to improve the mass transfer of membrane electrode assembly to realize operation under wide humidity[J]. J. Power Sources, 2021, 506: 230185. |
| [12] | Roh C W, Choi J, Lee H. Hydrophilic-hydrophobic dual catalyst layers for proton exchange membrane fuel cells under low humidity[J]. Electrochem. Commun., 2018, 97: 105-109. |
| [13] | Qiu Y L, Zhang H M, Zhong H X, Zhang F X. A novel cathode structure with double catalyst layers and low Pt loading for proton exchange membrane fuel cells[J]. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy, 2013, 38 (14): 5836-5844. |
| [14] | Deng R Y, Xia Z X, Sun R L, Wang S L, Sun G Q. Nanostructured ultrathin catalyst layer with ordered platinum nanotube arrays for polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells[J]. J. Energy Chem., 2020, 43: 33-39. |
| [15] | Yakovlev Y V, Lobko Y V, Vorokhta M, Nováková J, Mazur M, Matolínová I, Matolín V. Ionomer content effect on charge and gas transport in the cathode catalyst layer of proton-exchange membrane fuel cells[J]. J. Power Sources, 2021, 490: 229531. |
| [16] | Xue Q, Li J K, Yang Z Y. Synergistically improving the activity, antipoisonous ability, and long-term stability of Pt to methanol oxidation through developing favorable graphene-based supports[J]. Langmuir, 2017, 33(4): 872-880. |
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |