

电加热微电极传热模式的结构依赖性研究
收稿日期: 2022-03-21
修回日期: 2022-04-27
录用日期: 2022-04-28
网络出版日期: 2022-05-07
Dependence of Heat Transfer Model on the Structure of Electrically Coil-Heated Microelectrodes
Received date: 2022-03-21
Revised date: 2022-04-27
Accepted date: 2022-04-28
Online published: 2022-05-07
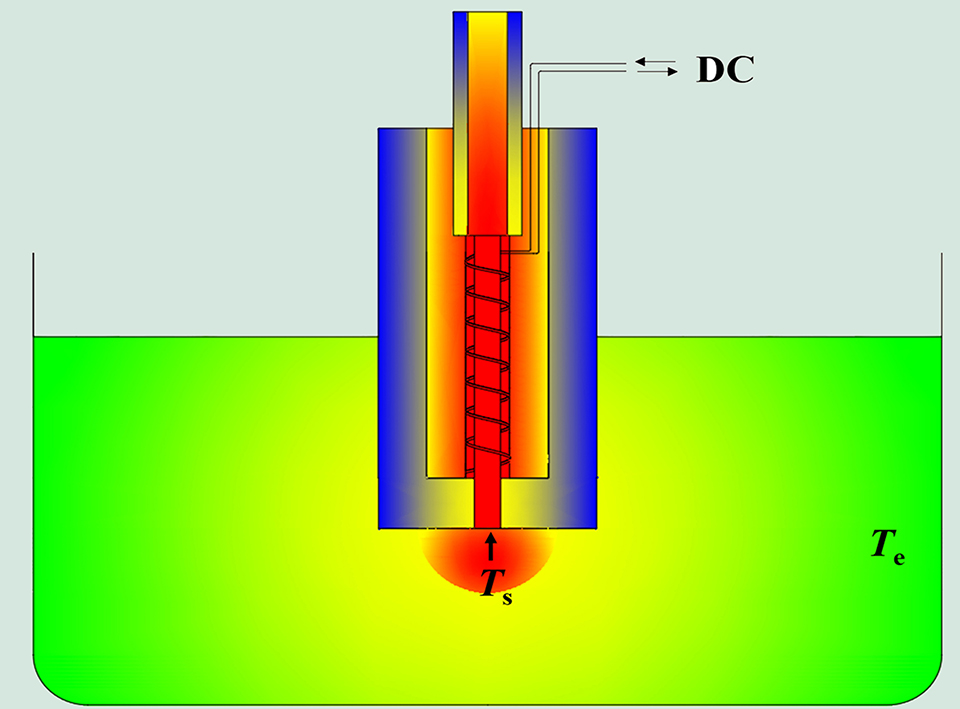
近年来,电加热微电极在电分析化学中得到了广泛的关注。研究表明,在高温下促进质量传输和反应动力学通常会导致电流信号增加。然而,目前还没有关于微电极内部传热的研究,这对于微传感器的设计和操作是必要的。本文利用有限元模拟软件(COMSOL)来分析影响表面温度(Ts)的因素,这对线圈加热的微盘电极的加热能力至关重要。电极表面和加热铜线底部之间的距离也与Ts(R2 = 1)有良好的线性关系。考虑到成本,25 mm长的金丝足以获得相对较高的Ts。此外,当电极材料为金且金盘直径为0.2 mm时,可以获得最高的Ts。本文还研究了不同温度下加热铜线直径与电流的关系。仿真结果有望为电加热微传感器的设计和实际应用提供重要帮助。
李炬 , 杨森 , 孙建军 . 电加热微电极传热模式的结构依赖性研究[J]. 电化学, 2023 , 29(9) : 2203211 . DOI: 10.13208/j.electrochem.2203211
Electrically heated microelectrodes have gained much attention in electroanalytical chemistry in recent years. It has been shown that the promotion of mass transport and reaction kinetics at high-temperatures often results in increased current signals. However, there is no study about the heat transfer inner the microelectrodes which is necessary for the design and operation for microsensors. This report introduces a finite element software (COMSOL) to analyze the factors that influence the surface temperature (Ts), which is crucial for the heating ability of micro-disk electrodes with coils. Distances between the electrode surface and the bottom of the heated copper wire also have a good linear relationship with Ts (R2 = 1). Considering the cost, 25-mm length of the gold wire is enough to obtain a relatively high Ts. In addition, the highest Ts can be obtained when the electrode material is gold and the diameter of the gold disk is 0.2 mm. The relationship of diameters of heated copper wires with currents to obtain different temperatures has also been studied. It is expectable that the simulation results can be used to significantly help the design and operation of electrically heated microsensors in practical applications.

/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |