

基于电化学分子探针合理设计的高选择性长程活体分析
收稿日期: 2021-10-06
修回日期: 2021-12-04
网络出版日期: 2021-12-18
版权
Rational Design of Electrochemical Molecular Probes for Highly Selective and Long-Term Measurement In Vivo
Received date: 2021-10-06
Revised date: 2021-12-04
Online published: 2021-12-18
Copyright
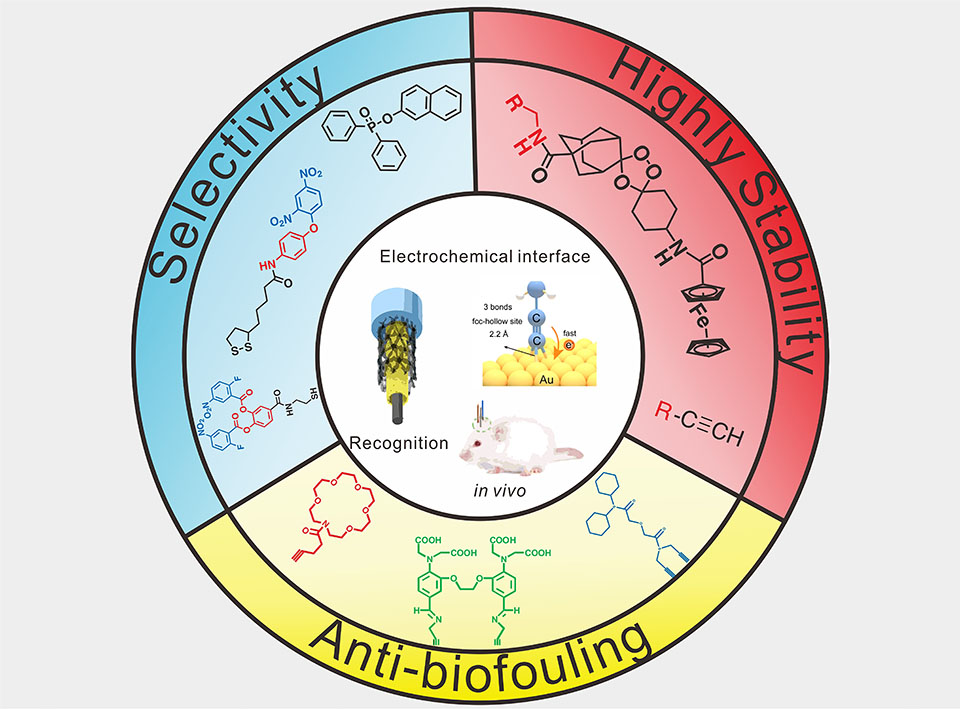
发展脑内化学物质的高选择性长期稳定的传感分析方法,对于准确获取脑生理病理过程的动力学信息,精准区分复杂的脑疾病分子机制具有重要的研究意义。本文从三个方面综述了基于新型电化学探针分子设计的脑内高选择性长程活体分析方面的研究进展:(1)通过设计并合成新型的O2·-、H2Sn、Ca2+、K+等的特异性有机分子探针,合理将特异性化学信号转换为高选择性的电化学信号,建立了系列高选择性的非电化学活性分子的活体电化学分析策略;(2)系统研究了传统Au-S键、Au-Se键、Au-C≡C键三种分子组装方式的界面电化学行为差异,优化并建立了基于Au-C≡C功能化的高稳定性电化学传感界面,发展了高选择性、长期稳定的Fe2+实时活体分析方法;(3)通过合理地将高稳定分子组装策略和抗生物污染界面相结合,制备了高选择性高稳定性的可逆型Ca2+微电极阵列,实现了脑中风模型下鼠脑中不同脑区Ca2+长达60天的实时追踪,以及癫痫模型下不同脑区四种离子(Ca2+、Na+、K+及pH)的动态实时成像及动力学分析。最后,该综述针对目前脑活体分析时神经递质、氨基酸等重要生理物质的多脑区实时分析的难点及移动清醒动物的无线传感分析策略进行了简要的展望。
王越 , 张立敏 , 田阳 . 基于电化学分子探针合理设计的高选择性长程活体分析[J]. 电化学, 2022 , 28(3) : 2108451 . DOI: 10.13208/j.electrochem.210845
Designing electrochemical interfaces for in vivo analysis of neurochemicals with high selectivity and long-term stability is vital for monitoring dynamic variation and dissecting the complex mechanisms of pathogenesis in living animals. This review focuses on the development of electrochemical interfaces based on rational design of molecular probes for in vivo measurement with high selectivity and high stability from three aspects: (1) Specific recognition probes were rationally designed and created to remarkably improve the selectivity of in vivo analysis in a complicated brain environment. (2) The Au-C≡C functionalized surface was developed to remarkably enhance the stability of molecular assembly, and employed for real-time mapping and accurate quantification in the brains. (3) Combined with the Au-C≡C functionalized molecular probe, the new type anti-biofouling microfiber array was established to achieve long-term and real-time monitoring dynamic changes in the brain. At last, some perspectives are highlighted in the further development of the efficient electrochemical interfaces for in vivo detection in the brain.

Key words: electrochemical interface; recognition molecule; high stability; in vivo; brain
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |