

电解耦合臭氧化体系处理酸性废水的氧化效能
收稿日期: 2021-04-19
修回日期: 2021-05-25
网络出版日期: 2021-08-13
版权
Oxidative Efficiency of Ozonation Coupled with Electrolysis for Treatment of Acid Wastewater
Received date: 2021-04-19
Revised date: 2021-05-25
Online published: 2021-08-13
Copyright
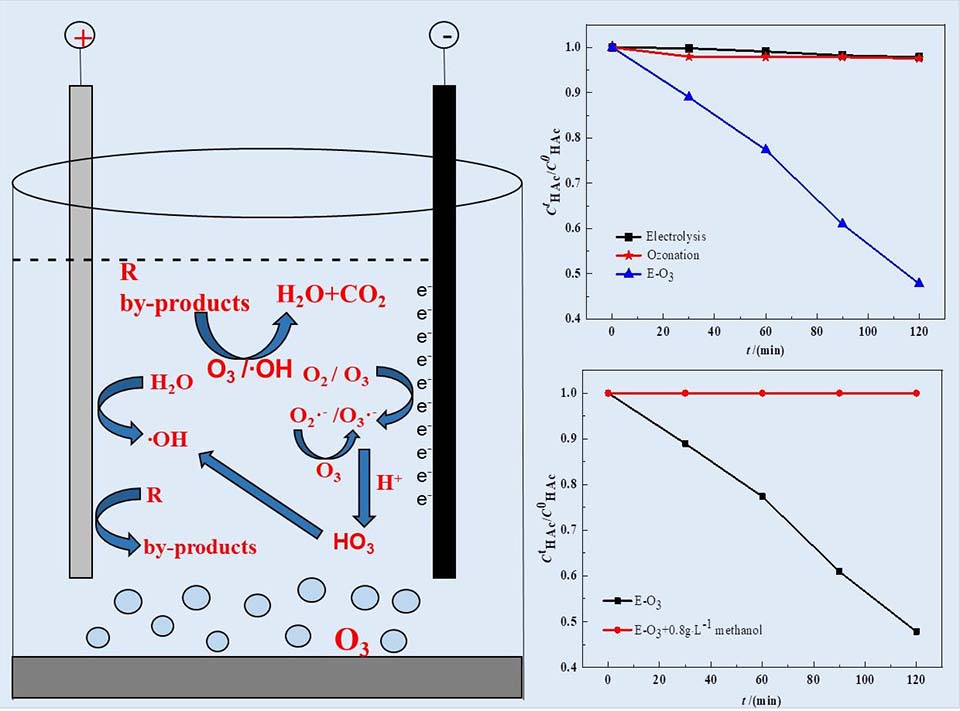
建立能有效处理酸性废水的臭氧类高级氧化技术(AOPs-O3)是一个有待解决的难点。已有报道表明,臭氧氧化与电解结合(电解臭氧化,E-O3)可以有效降解中性溶液中的污染物。本文研究了E-O3在酸性溶液中降解乙酸(HAc,臭氧惰性物)的效率,发现E-O3在pH小于3时仍具有较高的氧化效率,如在pH为1.0时处理100 mg·L-1 乙酸溶液2小时后E-O3的效率达到52.2%,而相同条件下电解和臭氧氧化的效率分别只有2.2%和3.5%。尽管酸度增加会降低E-O3的氧化效率,但在pH等于0时其仍有相对较高的氧化效率。芳族化合物苯乙酮在pH等于1.0条件下也能被E-O3有效地降解并矿化。机理解析表明,溶解臭氧或氧气可以从阴极获得电子,从而产生高活性的氧化物种,如羟基自由基。在预处理了一种实际酸性废水中E-O3也具有较好的效率。本研究为酸性废水的有效(预)处理提供了一种新方法。
胡泽友 , 项丰云 , 毛佶强 , 丁亚磊 , 童少平 . 电解耦合臭氧化体系处理酸性废水的氧化效能[J]. 电化学, 2022 , 28(1) : 2104191 . DOI: 10.13208/j.electrochem.210419
Establishment of an ozone-based advanced oxidation process (AOPs-O3) for effective treatment of acid wastewater is an important and difficult task. The process of ozonation coupled with electrolysis (electrolysis-ozonation, E-O3) has been reported to effectively degrade pollutants in neutral solution. We studied the efficiency of E-O3 for degradation of acetic acid (HAc, an ozone inert chemical) in acid solution and found that E-O3 had high oxidative efficiency at pH less than 3. For example, 52.2% of 100 mg·L-1 HAc could be removed by E-O3 in 120 min at pH 1.0, but only 2.2% and 3.5% by electrolysis and ozonation, respectively. Although the efficiency of E-O3 decreased with the increase of acidity of solution, it still remained relatively high even at pH 0. An aromatic compound of acetophenone could also be effectively degraded by E-O3 at pH 1.0. The results indicate that electrons can transfer from cathode to dissolved ozone or oxygen in acidic solution, thus resulting in generation of reactive species, e.g. hydroxyl radicals. A real acidic wastewater was also effectively pretreated by E-O3. This study provides a promising AOPs-O3 for treatment of acid wastewaters.

Key words: electrolysis; ozone; acetic acid; efficiency; acid wastewater
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |