

Fe3O4磁性纳米颗粒催化电化学降解土霉素的研究
收稿日期: 2021-07-14
修回日期: 2021-08-05
网络出版日期: 2021-08-09
基金资助
国家自然科学基金项目(21925404);杭州市科技发展计划项目(20150533B09)
Electrochemical Degradation of Oxytetracycline Catalyzed by Fe3O4 Magnetic Nanoparticles
Received date: 2021-07-14
Revised date: 2021-08-05
Online published: 2021-08-09
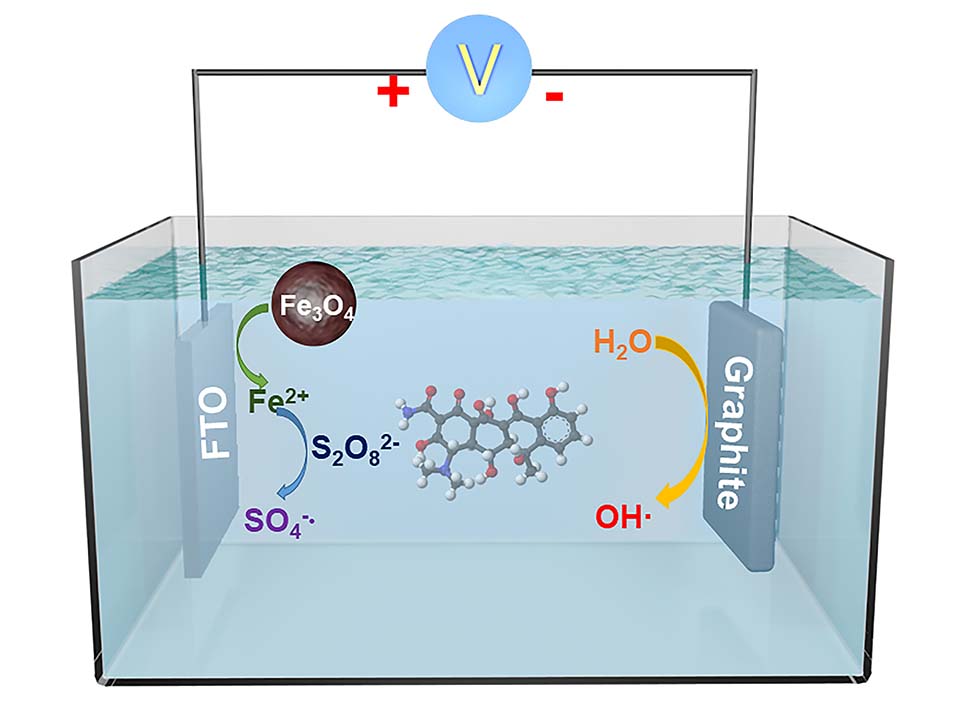
本研究以Fe3O4作为催化剂,活化过氧化二硫酸盐电化学氧化体系,改善土霉素(OTC)的降解为主要内容。通过场发射扫描电子显微镜(SEM)、 X射线衍射(XRD)表征,证明水热法成功制备了150 nm左右的Fe3O4磁性纳米颗粒。通过对比实验证明,同时加入Fe3O4与施加电流时表现出优秀的OTC降解能力,经证明在过硫酸盐(PDS)浓度为4.0 mmol·L-1,溶液初始pH值为7,电流密度j为30 mA·cm-2, Fe3O4磁性纳米颗粒用量为0.1 g·L-1,初始OTC浓度为70 mg·L-1的条件时,60 min内OTC降解率可达88.75%,一级动力学模拟曲线的速率常数可以达到0.06069。此外, Fe3O4连续循环5次后,依然具有良好的稳定性。Fe3O4与电流的存在分别可以促进SO4 ·-和·OH的生成。经自由基猝灭实验证明, SO4 ·-和·OH均负责抗生素降解。
关键词: 电化学氧化; 土霉素降解; Fe3O4磁性纳米颗粒; 稳定性
应方 , 许珊珊 , 许燕冰 , 梁苗苗 , 李剑锋 . Fe3O4磁性纳米颗粒催化电化学降解土霉素的研究[J]. 电化学, 2022 , 28(4) : 2107141 . DOI: 10.13208/j.electrochem.210714
The purpose of this study is to optimize the electrochemical degradation of oxytetracycline (OTC) in water using a low cost and simple preparation method. In this paper, the Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles were used as catalysts to activate the electrochemical oxidation system of peroxydisulfates (PDS) which acted as electrolytes to provide active free radicals in order to improve the degradation of OTC under the condition of applying current. As one of the tetracycline antibiotics (TCs), OTC is one of the most used antibiotics in the world, therefore, it is necessary to study the effective degradation of OTC. By means of field emission scanning electron microscopy (FESEM), X-ray diffraction (XRD) and other characterization methods, it was proved that the Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles at about 150 nm were successfully prepared by a simple hydrothermal method. Firstly, it is suggested that the application of electric current and the presence of Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles are necessary for the effective degradation of OTC. Secondly, the optimal reaction experiment confirmed an excellent OTC degradation ability by combination of Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles and current. The optimal reaction conditions were as follows: the concentration of PDS was 4.0 mmol·L-1, the initial pH value of the solution was 7, and the current density j was 30 mA·cm-2. When the dosage of Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles was 0.1 g·L-1 and the initial OTC concentration was 70 mg·L-1, the degradation rate of OTC could reach 88.75% within 60 min and the rate constant of the first-order kinetics simulation curve could reach 0.06069. In addition, the variation of UV-vis characteristic peak of OTC during the degradation process revealed that the change of OTC concentration was not due to simple physical adsorption, but through the complete degradation of active free radicals. In addition, after the continuous circulation of Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles for 5 times, the degradation rate of OTC could still reach more than 68%, proving that Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles have good catalytic stability. The presence of Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles and the application of electric current could promote the formations of SO4·- and ·OH, respectively. The radical quenching experiments showed that both SO4 ·- and ·OH were active free radicals degraded by antibiotics. This work uses a low-cost catalyst to enhance an electrochemical degradation of OTC. The experimental operation is simple, the degradation rate is fast, and the energy consumption is low. It is promising to practical applications.

/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |