

ANiN(A = Li, Na, Mg, Ca)的结构、热力学、弹性和电子性质的第一性原理研究
收稿日期: 2021-03-05
修回日期: 2021-04-15
网络出版日期: 2021-04-20
Structural, Dynamic, Elastic and Electronic Properties of ANiN (A = Li, Na, Mg, Ca): First-Principles Calculations
Received date: 2021-03-05
Revised date: 2021-04-15
Online published: 2021-04-20
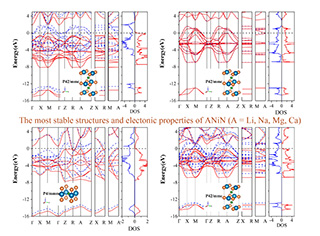
三元过渡金属氮化物ANiN (A = Li, Na, Mg, Ca)是潜在的可充放电池的电极材料。物理性质,比如热稳定性、电子能隙以及弹性稳定性等,对于这些材料的电池应用都是非常重要的。本文使用第一原理方法,对比研究了ANiN这些材料的结构、动力学、弹性和电子结构性质。对状态方程和声子谱的计算被用来确定体系的稳定结构。对最稳定结构的弹性常数的计算表明,这些稳定结构都满足 Born-Huang的稳定性判据,意味着它们的弹性稳定性。对体系电子结构的计算表明,LiNiN和CaNiN是半金属(half-metals),MgNiN是磁性材料,而NaNiN是通常的金属。这些材料的磁学性质都通过Stoner理论进行了解释。最后,电荷密度的计算被用来很好地说明了这些材料中的Ni-N成键的特征,表明成键特点主要是离子性的,但明显地混合了共价性。
关键词: ANiN (A = Li, Na, Mg, Ca); 结构稳定性; 电子性质; 第一性原理计算
黄夏敏 , 张丽红 , 吴顺情 , 杨勇 , 朱梓忠 . ANiN(A = Li, Na, Mg, Ca)的结构、热力学、弹性和电子性质的第一性原理研究[J]. 电化学, 2021 , 27(3) : 339 -350 . DOI: 10.13208/j.electrochem.210302
Ternary transition metal nitrides ANiN (A = Li, Na, Mg, Ca) are potential electrode materials for rechargeable batteries. The physical properties, such as the thermodynamic stability, the electronic band gap as well as the elastic stability, are important for their battery applications. Here, comparative studies are performed for the structural, dynamic, elastic and electronic properties of ANiN by the first-principles method. The calculations on the cohesive energy versus unit-cell volume and phonon spectra are employed to determine the most stable structures of ANiN. The calculated elastic constants of the most stable structures indicate that the Born-Huang criterion for the elastic stability can all be satisfied, showing the elastic stability of the materials. The electronic structures calculations suggest that LiNiN and CaNiN are half-metals, MgNiN is magnetic metal, while NaNiN is a common metal. The magnetization of the materials is understood by the Stoner theory. Furthermore, the charge density plots have been used to illustrate the bonding between Ni and N atoms, which is mainly ionic mixed with covalent.

/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |