

基于硅基硼掺金刚石电极的电化学-原位核磁共振波谱电解池的设计、制备与可行性研究
收稿日期: 2020-07-22
修回日期: 2020-08-24
网络出版日期: 2021-06-28
基金资助
国家重点研发计划项目(2017YFA0206500);国家自然科学基金项目(21974117)
版权
Design and Fabrication of the Electrolytic Cell with Silicon-Based Boron-Doped Diamond Electrode and Its Feasibility for in-Situ Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Study
Received date: 2020-07-22
Revised date: 2020-08-24
Online published: 2021-06-28
Copyright
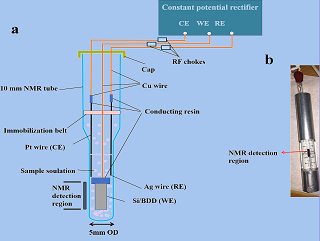
电化学与核磁共振波谱联用技术(EC-NMR)可以实时监测电化学反应过程,从分子水平阐释反应机理,是一种非常有前景的无损在线检测技术。本文首次报道以硅基硼掺金刚石(Si/BDD)作为工作电极的原位EC-NMR三电极单室电解池的设计和制作。研究表明,由于尺寸12.5 mm × 1.2 mm × 0.5 mm的Si/BDD电极在核磁检测区的体积较小且电极材料厚度较薄,因此该电极对射频场的阻碍较小,对磁场均匀性破坏也相应较小。运用自制的EC-NMR电解池并以经典的对苯二酚(QH 2)电氧化生成对苯二醌(Q)作为模型体系,原位研究了该电化学反应的整个动态过程。在1.2 V恒电位下电解0.1 mol·L-1 QH2 64分钟,监测到位于位于6.83 ppm处的Q特征峰逐渐生成,反应过程中核磁谱峰未发生裂分或明显的展宽。结果表明,应用本文所设计并制备的原位EC-NMR电解池,可有效对电化学反应物和产物进行定性、定量分析,将可在后续的电化学原位核磁波谱研究中发挥重要作用。
关键词: 硅基硼掺金刚石; 原位电化学核磁波谱联用技术; EC-NMR电解池; 电氧化; 对苯二酚
彭浩 , 孙惠军 , 周志有 , 申琳璠 , 黄龙 , 曹烁晖 , 孙世刚 . 基于硅基硼掺金刚石电极的电化学-原位核磁共振波谱电解池的设计、制备与可行性研究[J]. 电化学, 2021 , 27(3) : 332 -338 . DOI: 10.13208/j.electrochem.200722
In-situ EC-NMR technique can be used to monitor the electrochemical reaction process in real-time and to explain the reaction mechanism at the molecular level, which is a promising and non-destructive online detection technology. This article for the first time reports the design and production of in-situEC-NMR three-electrode single-chamber electrolytic cell using silicon-based boron-doped diamond (Si/BDD) as the working electrode. Research shows that the geometric size of Si/BDD electrode being 12.5 mm 1.2 mm 0.5 mm in the NMR detection zone is small and the thickness of the electrode material is thin, which accounts for the less hindrance to the radio frequency field, and correspondingly the less damage to the uniformity of the magnetic field. The developed EC-NMR electrolytic cell was tested, and a classic electrochemical reaction of electrooxidation from hydroquinone (QH2) to benzoquinone (Q) was used as a model system to study the entire dynamic process in-situ. After electrolysis of 0.1 mol·L-1 QH2 at a constant potential of 1.2 V for 64 min, it is detected that the characteristic peak intensity of QH2 at 6.58 ppm was gradually decreased, and the characteristic Q peak at 6.83 ppm was gradually generated. The NMR spectrum peak did not split or broaden significantly during the reaction. The results demonstrate that the in-situ EC-NMR electrolytic cell designed and prepared in this paper can be effectively used for the qualitative and quantitative analyses of the reactants and products in electrochemical reactions, which thus will play an important role in the subsequent researches on electrochemical in-situ NMR spectroscopy.

/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |