

电化学方法调控荧光碳点的研究
收稿日期: 2020-06-30
修回日期: 2020-08-02
网络出版日期: 2020-08-19
Electrochemical Engineering of Carbon Nanodots
Received date: 2020-06-30
Revised date: 2020-08-02
Online published: 2020-08-19
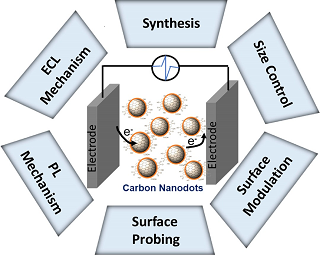
作为零维碳基发光纳米材料,碳点是对现有发光纳米材料的重要补充. 精准控制粒径及表面结构对实现碳点的性质调控及其应用至关重要. 本文介绍了本课题组在利用电化学方法研究荧光碳点方面的进展. 重点展示了利用电化学方法实现对碳点粒径的控制,对表面氧化程度的调节以及对其发光机理的研究. 电化学方法可对只有几纳米厚度的材料表面进行有效的控制,可操作性强且经济环保. 通过对碳点的粒径及表面的调控,作者也进一步揭示了碳点的发光与表面结构的相关性. 这些工作为碳点的合成及其性质调控提供了可循的规律,有利于推动碳点在生物医生成像、传感检测、催化及能源转化等领域的应用.
包蕾 , 庞代文 . 电化学方法调控荧光碳点的研究[J]. 电化学, 2020 , 26(5) : 639 -647 . DOI: 10.13208/j.electrochem.200644
Carbon nanodots (CNDs), as zero-dimensional carbonaceous fluorescent nanomaterials, are valuable add-ons to the current cohorts of fluorescent nanoparticles. The fine control over the size and the surface is the key to gain designated photophysical properties of CNDs as well as empowers CNDs in many applications. Herein, a series of electrochemical strategies to manipulate the size and the surface of CNDs and to identify the surface structures was presented. Accordingly, the understandings on the originals of photoluminescence as well as the pathways of electrochemiluminescence of CNDs were revealed. These studies demonstrated that electrochemical methods were easy to operate, cost-effective and efficient in altering thin layers of the surface on CNDs within a few nanometers. The key findings in the luminescence mechanism provided guidelines for the rational design of CNDs with suitable features, which could promote applications of CNDs in bioimaging, sensing and catalytic conversion.

/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |