

惰性小分子电催化还原反应的电解液调控
收稿日期: 2020-05-04
修回日期: 2020-06-11
网络出版日期: 2020-06-28
基金资助
国家自然科学基金项目(21925503);国家自然科学基金项目(21871149);国家重点研发计划纳米科技专项(2017YFA0206700);中央高校基本科研业务费专项资金项目资助
Electrolyte Tailoring for Electrocatalytic Reduction of Stable Molecules
Received date: 2020-05-04
Revised date: 2020-06-11
Online published: 2020-06-28
李金翰 , 程方益 . 惰性小分子电催化还原反应的电解液调控[J]. 电化学, 2020 , 26(4) : 474 -485 . DOI: 10.13208/j.electrochem.200442
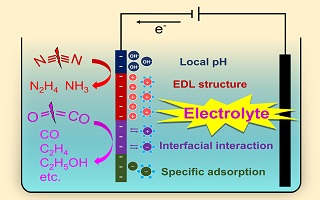
Reduction of stable molecules such as CO2 and N2 is important process in electrochemical energy conversion and storage technologies for electrofuels production. However, for the inert nature of CO2/N2 molecule and competitive proton reduction in conventional aqueous electrolytes, selective electrochemical carbon/nitrogen fixation suffers from high overpotential, low reaction rate and low selectivity. While addressing these issues has witnessed substantial advances in electrocatalysts, much less attention has been placed on the electrolytes, which play an important role in regulating the local environment and thus the performance of catalysts under operating conditions. Rational design of electrolytes has received increasing interest to boost the activity and selectivity of stable molecule electrocatalysis. In this review, we overview recent progress in mechanistic understanding and strategies development in tailoring electrolytes for electrocatalytic CO2 and N2 reduction. We highlight the ion effect, local environment, and interface structure of electrocatalysts and electrolytes based on experimental and computational studies on representative examples. Particular discussion is provided on the effect of local pH modulation, electrolyte concentrating, selective ionic adsorption and nonaqueous electrolyte.
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |