

离子液体凝胶聚合物电解质的三元组分相互作用研究
收稿日期: 2019-11-20
修回日期: 2020-01-05
网络出版日期: 2020-02-14
基金资助
国家自然基金项目(No. 21878061)和国家自然科学基金项目(No. 51604102)资助
The Interaction of Ternary Components of Ionic Liquid Gel Polymer Electrolytes for Lithium Metal Batteries
Received date: 2019-11-20
Revised date: 2020-01-05
Online published: 2020-02-14
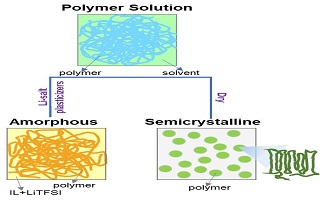
采用Raman光谱、傅里叶转换红外光谱和X-射线衍射光谱研究N-甲基-N-丙基哌啶双三氟甲磺酸亚胺离子液体(PP13TFSI)和双三氟甲磺酸亚胺锂盐(LiTFSI)对PVDF-HFP聚合物聚合方式的影响,结果表明,PP13TFSI、LiTFSI和PVDF-HFP是共混存在的,同时加入PP13TFSI和LiTFSI会使聚合物的聚合方式由晶体结构转变为无定形结构. 通过对电解质及其各组分的线性扫描伏安曲线和热重曲线分析可知,溶剂N-甲基吡咯烷酮(NMP)容易残留在凝胶聚合物电解质(ILGPE)中,这会降低ILGPE的电化学稳定性和热稳定性. 作者对固态LiFePO4|ILGPE|Li电池的倍率性能进行了研究,实验结果表明其具有较好的倍率性能,当电池倍率由C/10增大至2C,然后再回到C/10时,其容量可以恢复到原来的90.9%左右. 该研究结果对理解PP13TFSI和LiTFSI在ILGPE中的作用机理具有重要的意义.
关键词: 离子液体聚合物电解质; 电化学稳定性; 热稳定性
潘晓娜 , 刘丽来 , 王治璞 , 王丹 , 李云 , 杨培霞 , 张锦秋 , 安茂忠 . 离子液体凝胶聚合物电解质的三元组分相互作用研究[J]. 电化学, 2020 , 26(3) : 406 -412 . DOI: 10.13208/j.electrochem.191120
Ionically conductive gel polymer electrolyte is an excellent candidate due to its inflammable, nonvolatile and high thermal stability as compared to commercial liquid electrolytes which are usually flammable, volatile, and containing toxic organic solution as solvent, The synthesis and application of ionic gel polymer electrolytes in lithium ion/metal batteries have been previously reported. However, the interaction effects of N-methyl-N-propylpiperidinium bis(trifluoromethanesulfonyl)imide (PP13TFSI) ionic liquid (as plasticizer) and lithium bis(trifluoromethanesulfonyl)imide (LiTFSI) on PVDF-HFP polymer remain unclear. In this work, the molecular structure of ionic liquid gel polymer electrolyte (ILGPE) composed of PP13TFSI, LiTFSI and PVDF-HFP was studied by Raman spectroscopy and Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR). Meanwhile, X-ray diffraction (XRD) analysis was performed to qualify the crystallization of PVDF-HFP polymer in the ILGPE with or without PP13TFSI or/and LiTFSI to investigate ionic liquid or/and LiTFSI impact on PVDF-HFP polymer. The results showed that PP13TFSI, LiTFSI and PVDF-HFP were physical-blending without chemical reaction, but with molecular coordination with PVDF-HFP polymer chain. In addition, the crystallization of PVDF-HFP could be changed by additions of PP13TFSI and LiTFSI at the same time, and the ionic conductivity could be improved with increasing amorphous phase in polymer matrix. The electrochemical stability window and thermal stability of ILGPE became worse with the N-methyl-2-pyrrolidone (NMP) residue inside the ILGPE. The LiFePO4/Li battery with the optimized ILGPE (the weight ratio of ionic liquid, LiTFSI, and PVDF-HFP polymer was 3/1/1) showed a good C-rate capability at room temperature. In summary, PP13TFSI and LiTFSI could coordinate with PVDF-HFP polymer chain, and no chemical reaction took place among the three compounds during preparing ILGPE. Furthermore, it is necessary to remove NMP solvent from ILGPE during drying process to improve the electrochemical stability window and thermal stability of ILGPE.

/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |