

氮化钴电催化还原二氧化碳为一氧化碳
收稿日期: 2018-10-08
修回日期: 2018-12-16
网络出版日期: 2019-08-28
Electrocatalytic Reduction of Carbon Dioxide to Carbon Monoxide using Cobalt Nitride
Received date: 2018-10-08
Revised date: 2018-12-16
Online published: 2019-08-28
Supported by
This work was financially supported by the National Key Projects for Fundamental Research and Development of China (2016YFB0600901), and National Nature Science Foundation of China (21701180).
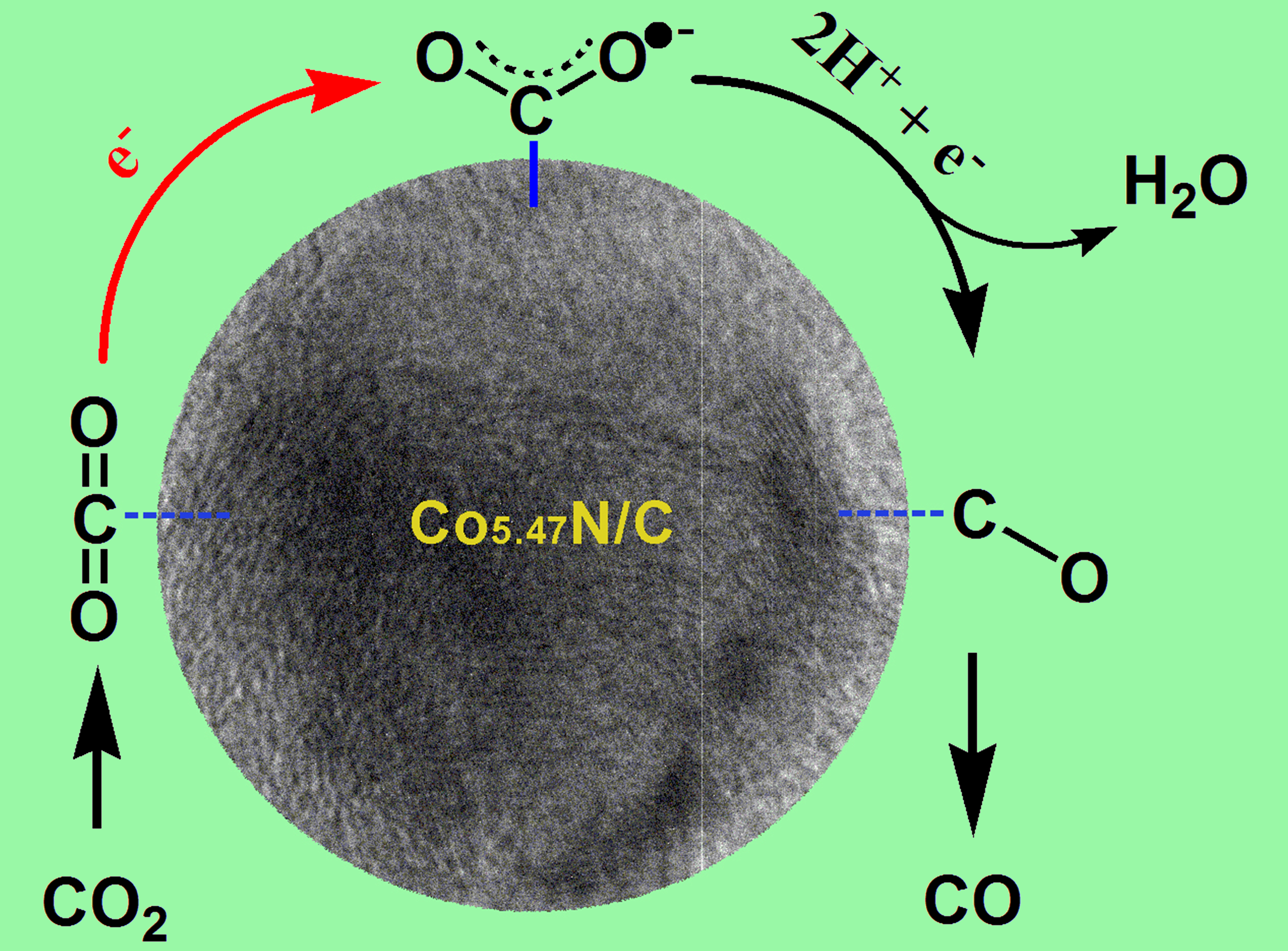
电催化还原二氧化碳是一种潜在的解决全球变暖的途径,但是仍有许多挑战. 本文报道了使用氮化钴在水溶液中电催化还原二氧化碳为一氧化碳. 通过对比不同煅烧温度及气氛合成的催化剂表明氮掺杂对催化活性的提高至关重要. 其中700-Co5.47N/C展现了最高的催化活性,在较低的电势-0.7 V(vs. RHE)下,一氧化碳的电流密度达到9.78 mA·cm-2. 另外,通过改变电解电压,CO/H2 的比例能在1:3到3:2之间调节. 91 mV·dec-1的Tafel 斜率表明形成表面吸附的CO2·-中间体是CO2表面还原的决速步骤,而氮化策略可以增加表面碱性位点的数量,从而稳定还原的中间体,提高反应效率和产物选择性.
马 晨 , 侯朋飞 , 康 鹏 . 氮化钴电催化还原二氧化碳为一氧化碳[J]. 电化学, 2019 , 25(4) : 467 -476 . DOI: 10.13208/j.electrochem.180941
Electrocatalytic reduction of carbon dioxide (CO2) is a promising method to alleviate global warming issues, although it still faces many challenges. Herein, we report cobalt nitride for electrocatalytic reduction of CO2 to carbon monoxide (CO) in an aqueous electrolyte. A comparison of catalysts with different preparation temperatures and atmospheres suggests that nitrogen doping is critical to improve catalytic activity. For the most active catalyst of 700-Co5.47N/C, the CO current density reached 9.78 mA·cm-2 at potential of -0.7 V vs. RHE. In addition, the CO/H2 ratio could be adjusted from 1:3 to 3:2 by changing applied potential. Tafel slope of 91 mV·dec-1 indicates that forming a surface adsorbed CO2·- intermediate became the rate-determining step and nitriding strategy increased CO2 selectivity by providing more base sites.

Key words: cobalt nitride; carbon dioxide electroreduction; carbon monoxide; syngas
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |