

新型单丝电极交流探头在3.5wt.% NaCl中的电化学响应规律研究
收稿日期: 2019-03-11
修回日期: 2019-04-17
网络出版日期: 2019-04-18
基金资助
基金国家自然科学基金项目(51671163);基金国家自然科学基金项目(51731008)
Electrochemical Response of A Single Wire-Electrode AC Probe in 3.5wt.% NaCl
Received date: 2019-03-11
Revised date: 2019-04-17
Online published: 2019-04-18
邹振文 , 郑大江 , 王子明 , 宋光铃 . 新型单丝电极交流探头在3.5wt.% NaCl中的电化学响应规律研究[J]. 电化学, 2020 , 26(3) : 317 -327 . DOI: 10.13208/j.electrochem.190321
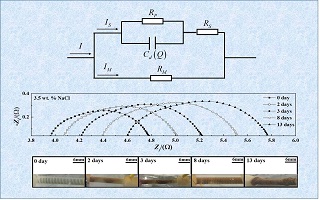
In this paper, a recently developed single wire-electrode AC probe technology which does not need a reference or counter electrode was employed to investigate the electrochemical corrosion and sacrificial anode protection behaviors of steel and zinc in 3.5wt.% NaCl. With this simple, fast, reliable and stable probe, the instantaneous corrosion rate and accumulated corrosion loss of carbon steel in 3.5wt.% NaCl were measured, and the results revealed that both were greater than those of zinc. Furthermore, the observed different corrosion behaviors between carbon steel and zinc during the immersion could be caused by their different surface films. With the galvanic couple of carbon steel-zinc, the protection efficiency offered by the anode zinc was found to be above 95%, and it increased initially and then decreased with immersion time.
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |