

Pt-Cu合金纳米枝晶的合成及其氧还原催化性能
收稿日期: 2018-09-28
修回日期: 2018-10-15
网络出版日期: 2018-10-29
基金资助
获国家重点研发项目(No. 2016YFB0101201)和国家自然科学基金项目(No. 21533005, No. 21503134)资助
Facile Synthesis of Pt-Cu Alloy Nanodendrites as High-Performance Electrocatalysts for Oxygen Reduction Reaction
Received date: 2018-09-28
Revised date: 2018-10-15
Online published: 2018-10-29
Supported by
This work was funded by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (No. 2016YFB0101201) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No.21533005 and No. 21503134)
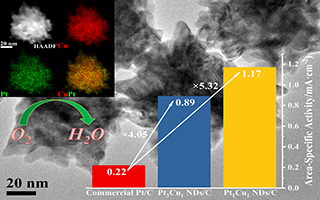
罗柳轩 , 魏光华 , 沈水云 , 朱凤鹃 , 柯长春 , 闫晓晖 , 章俊良 . Pt-Cu合金纳米枝晶的合成及其氧还原催化性能[J]. 电化学, 2018 , 24(6) : 733 -739 . DOI: 10.13208/j.electrochem.180856

Key words: Pt; alloy; electrocatalysts; nanodendrites; oxygen reduction reaction
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |