

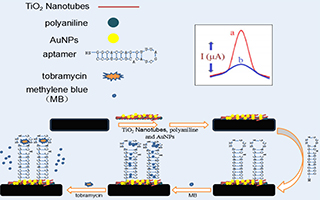
基于AuNPs/PANI/TNTs纳米复合材料的电化学检测妥布霉素的适配体传感器
收稿日期: 2018-06-12
修回日期: 2018-07-14
网络出版日期: 2019-12-28
An Aptasensor Based on AuNPs/PANI/TNTs Nanocomposite for Electrochemical Detection of Tobramycin
Received date: 2018-06-12
Revised date: 2018-07-14
Online published: 2019-12-28
Supported by
The project was supported financially by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 21201043).
农永玲 , 乔妮娜 , 梁 营 . 基于AuNPs/PANI/TNTs纳米复合材料的电化学检测妥布霉素的适配体传感器[J]. 电化学, 2019 , 25(6) : 720 -730 . DOI: 10.13208/j.electrochem.180612

Key words: aptasensor; tobramycin; electrochemical analysis; Au nanoparticles
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |