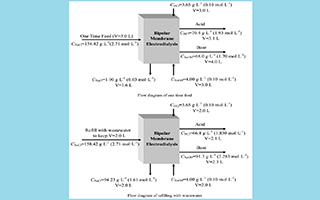
采用双极膜电渗析法处理某企业的工业高盐香料废水,旨在将无机盐氯化钠从香料废水中脱除并转化为附加值更高、较高浓度的盐酸和氢氧化钠. 当一次性处理3 L废水时,保证了足够的处理时间,生成盐酸和氢氧化钠的浓度分别能达到1.93 mol·L-1和1.70 mol·L-1,脱盐率为99.4%,生成盐酸和氢氧化钠的电流效率分别为30.7%和36.0%,电耗为2.58 kW·h·kg-1. 分别通过向盐室中补加废水原料和氯化钠固体的方式,均可抑制盐室中氯化钠浓度的减小,将生成的氢氧化钠浓度显著地提高,且后者提高的程度更为明显. 为提高酸、碱产品的纯度,分别考察了阳离子交换膜和阴离子交换膜对Cl-和Na+的阻隔效果,阳离子交换膜对Cl-的阻隔效果有着JAM-II>N2030>TRJCM的顺序,阴离子交换膜JAM-II对Na+的阻隔效果高于TRJAM. JCM-II相比于N2030膜有着更低的膜电阻. 综合考虑使用JAM-II/BPM-I/JCM-II组合时效果最好,电耗最低.
Large amount of organic saline wastewater is generated from various chemical industries. The contents of organic saline wastewater are more and more complicated as they are created from different types of industries. Directly discharging the organic saline wastewater without pre-treatment can generate severe environmental problem and waste useful resources. It is necessary to use an economical method to treat the organic saline wastewater and recover the salt into useful materials to achieve resource reuse. Bipolar-membrane electrodialysis (BMED) is one of the methods that can remove salt from the wastewater and convert it into certain acid and base with higher value than salt. After BMED process, the organicsleft in the treated wastewater can be further removed by normal methods. This research focuses on treating an industrial saline perfume wastewater, which contains high contents of NaCl and organic compounds, with BMED method. The purpose is to reduce the NaCl concentration and convert it into high valued acid and base with high concentrations. When 3 liters of wastewater were treated, the processing time is guaranteed. The concentrations of recovered acid and base were 1.93 mol·L-1 and 1.70 mol·L-1, respectively. The desalination rate reached 99.4%, and current efficient and electricity consumption were 30.7% and 2.58 kW·h·kg-1, respectively. By adding waste water raw material and NaCl solid in the salt compartment, the reduction of NaCl concentration in salt compartment could be inhibited, and the concentration of NaOH was increased significantly, and the degree of the latter became more obvious. For cathodic exchange membranes, their ability to prevent Cl- penetration decreased as following order: JCM-II>N2030>TRJCM. For anodic exchange membranes, JAM-II had better Na+ penetration preventing ability than TRJAM. JCM-II had lower membrane resistance, so that it consumed less electrical energy than N2030. Overall, a combination of JAM-II/BPM-I/JAM-II membranes showed the best performance and least electricity consumption.