

脉冲电沉积抑制锂枝晶生成的研究
收稿日期: 2017-05-03
修回日期: 2017-05-12
网络出版日期: 2018-04-20
基金资助
安徽省石油化工新材料协同创新中心资助
A Study of Pulse Electrodeposition on Suppressing the Formation of Lithium Dendrite
Received date: 2017-05-03
Revised date: 2017-05-12
Online published: 2018-04-20
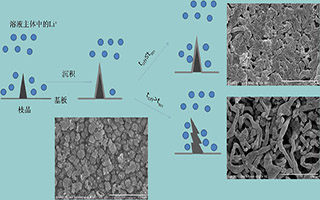
采用脉冲充电方法替代传统充电方法,研究了在有机电解液 0.5 mol·L-1 LiBr/PC (碳酸丙烯酯)中,在铜电极上沉积锂的表面变化. 扫描电镜观测结果显示,在传统直流充电时电极表面明显地出现了枝晶,而使用脉冲充电时能够抑制枝晶的生长. 交流阻抗测试结果显示,在占空比为 0.5 时,沉积锂表面固体电解质界面(solid electrolyte interphase,SEI)膜电阻最大,沉积锂表面枝晶较少;单次脉冲电沉积时间过长,会使沉积锂表面 SEI 膜电阻减小,沉积锂表面枝晶增加;电流密度大于等于 2 mA·cm-2时,脉冲电沉积可有效抑制枝晶生长.
郭文君 , 李紫琼 , 柯若昊 , 钮东方 , 徐衡 , 张新胜 . 脉冲电沉积抑制锂枝晶生成的研究[J]. 电化学, 2018 , 24(3) : 246 -252 . DOI: 10.13208/j.electrochem.170503
A pulse charge method was used to suppress the formation of lithium dendrite on the copper electrode in 0.5 mol·L-1 LiBr/propylene carbonate (PC) electrolyte. The surface variation of lithium deposition was investigated by scanning electron microscope and impedance measurement. The SEM test showed that the lithium dendrites were formed on the copper electrode during the traditional process of electrodeposition. However, the formed dendrite was suppressed by pulse charge method. The results of the impedance measurement confirmed that the pulse electrodeposition could suppress the dendrite under the optimized duty ratio (0.5). The long single pulse deposition time decreased the resistance of SEI film and led to the lithium dendrite growth. The current density had an effect on dendrite and the dendrite could be effectively suppressed with no less than 2 mA·cm-2 of current density.

Key words: pulse electrodeposition; SEI film; lithium dendrites; duty ratio
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |