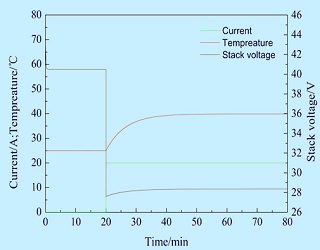
本文以等效电路模型为基础模型,结合动态气体压力模型和动态热传输模型建立了集总参数模型,在SIMULINK环境下,利用建立的模型模拟了电池启动过程,发现了电压的下冲现象,且电压的响应时间与电池温度的响应时间基本一致,说明启停过程中电池温度对电池的动态性能影响很大. 进一步从温度角度对模型中决定电池输出电压大小的热力学电动势、活化过电势、欧姆过电势和浓差过电势的动态响应情况进行了分析,发现启动过程电压的下冲现象主要由电池活化过电势和欧姆过电势的过冲引起;当以阶跃信号形式输入温度时,启动过程电池输出电压响应很快且未发生下冲现象,说明提高电池温度的响应速度能够改善电池的动态性能.
Based on the equivalent circuit model, by considering both the dynamic gas pressure model and the dynamic heat transfer model, a lumped parameter model is developed. The start process of the fuel cell is simulated by using SIMULINK software. The undershoot of the voltage is observed from the simulation results, and the response time of the voltage is basically the same as that of the fuel cell temperature, which indicates that the temperature has great influence on the dynamic performance of the fuel cell. From the perspective of the temperature, the dynamic responses of the thermodynamic potential, the activation overvoltage, the ohmic overvoltage and the concentration overvoltage of the fuel cell iare analyzed. It is found that the overshoot of the activation overvoltage and the ohmic overvoltage cause the voltage undershoot. When the temperature is input in the form of a step signal, the output voltage response of the fuel cell is fast, and thus, undershoot and overshoot do not occur. Therefore, it can improve the dynamic performance of the fuel cell with the increasing of temperature response speed.