

分级过程对LiFePO4/C电池性能的影响
收稿日期: 2016-09-30
修回日期: 2017-01-14
网络出版日期: 2017-06-08
基金资助
安徽省科技攻关项目(No. 1501021011)资助
Effects of jet milling and classifying process on the performance of LiFePO4/C in full batteries
Received date: 2016-09-30
Revised date: 2017-01-14
Online published: 2017-06-08
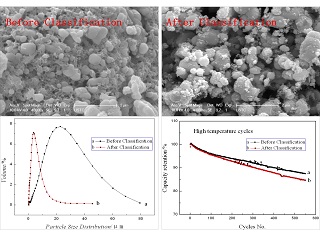
刘兴亮 , 杨茂萍 , 汪伟伟 , 曹勇 . 分级过程对LiFePO4/C电池性能的影响[J]. 电化学, 2017 , 23(6) : 661 -666 . DOI: 10.13208/j.electrochem.160930

/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |