

外部电场下水分子间静电相互作用的分子动力学研究
收稿日期: 2017-01-16
修回日期: 2017-03-06
网络出版日期: 2017-03-24
基金资助
Supported by the national Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 21673111)
Electrostatic Interactions of Water in External Electric Field: Molecular Dynamics Simulations
Received date: 2017-01-16
Revised date: 2017-03-06
Online published: 2017-03-24
Supported by
Supported by the national Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 21673111)
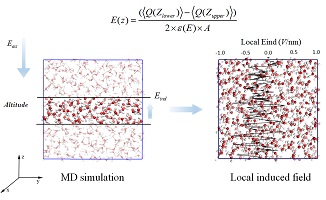
本文利用分子动力学模拟探讨了不同外电场下,液态水的分子间作用及分子排布的变化. 在不同外电场下,O…O原子间的径向分布函数差别很小,但是单个水分子的偶极矩的取向变化却很大. 当外电场为0时,单个水分子偶极取向的范围很宽(30-150度). 与此同时,本文给出了局域诱导电场随着位置的变化关系图. 当外加电场增强时,局域的诱导电场强度也随之增加. 由于电场下偶极矩有序性的增加,局域诱导的静电相互作用能显著增加. 计算结果表明,相对介电常数随着电场强度的增加而呈现指数衰减的变化形式. 这一变化趋势可以用来理解不同电化学环境下,静电相互作用和局域诱导电场的变化.
朱强 , 阚子规 , 马晶 . 外部电场下水分子间静电相互作用的分子动力学研究[J]. 电化学, 2017 , 23(4) : 391 -399 . DOI: 10.13208/j.electrochem.170143
A series of molecular dynamics simulations with or without external electric field have been carried out for a bulk water with periodic boundary condition. The difference in radial distribution function of interatomic O…O distance is subtle, with and without external electric field, except for the orientation of dipole moments of water molecules. Without the applied external electric field, distribution of the orientation angle of dipole moments is rather broad. The induced local electric field is analyzed as a function of altitude in direction of electric field. The variation of the local induced electric field is increased as the increase of the external electric field. The local induced electrostatic energy is mainly originated from the increase in the ordering of dipole orientation under the external electric field. Dielectric constant is evaluated according to the fluctuation of total dipole moment of the whole system. The change of relative dielectric constant under the different external electric fields can be described in an exponential decay equation as the increase of the strength of electric field. This simple rule can be applied to understand the electrostatic interaction and local induced electric field under various electrochemical environments.

/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |